热点文献带您关注半导体集成电路的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(86)
2024-01-08
本期我们为您选取了4篇文献,介绍半导体与集成电路的最新应用,包括清华大学发表的首颗基于忆阻器的片上学习存算一体芯片“面向边缘学习的全集成忆阻器存算一体芯片”、用于高速视觉任务的全模拟光电芯片、可编程梯度掺杂用于可重构碲化钼器件、北京邮电大学屈贺如歌老师与复旦大学合作发表的“层状铁电半导体中的极化-电导耦合机制”。

Edge learning using a fully integrated neuro-inspired memristor chip
Zhang, Wenbin, etc.
SCIENCE, 2023, 381(6663): 1205–1211
Learning is highly important for edge intelligence devices to adapt to different application scenes and owners. Current technologies for training neural networks require moving massive amounts of data between computing and memory units, which hinders the implementation of learning on edge devices. We developed a fully integrated memristor chip with the improvement learning ability and low energy cost. The schemes in the STELLAR architecture, including its learning algorithm, hardware realization, and parallel conductance tuning scheme, are general approaches that facilitate on-chip learning by using a memristor crossbar array, regardless of the type of memristor device. Tasks executed in this study included motion control, image classification, and speech recognition.
阅读原文:https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.ade3483
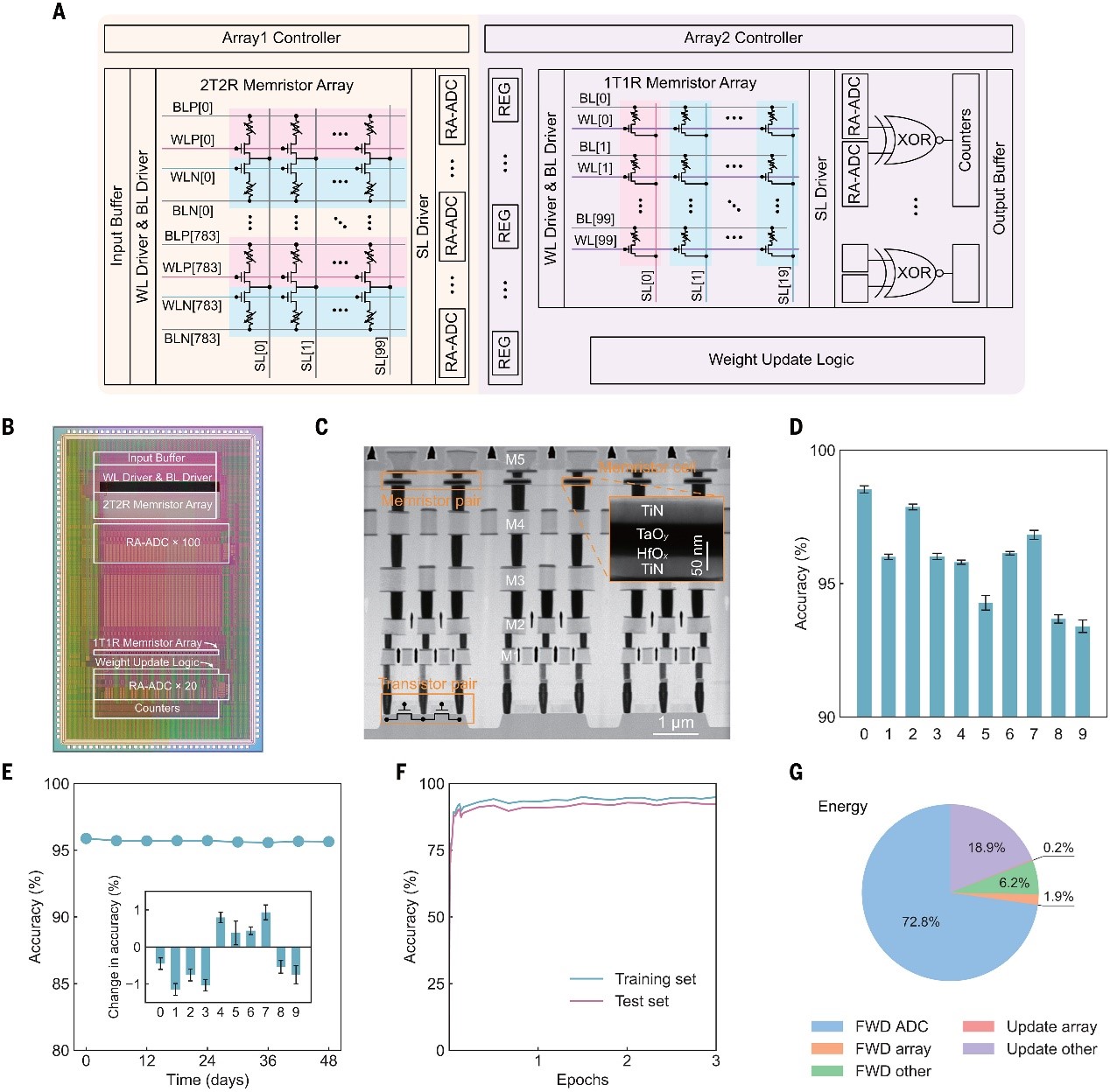
The memristor chip for on-chip learning

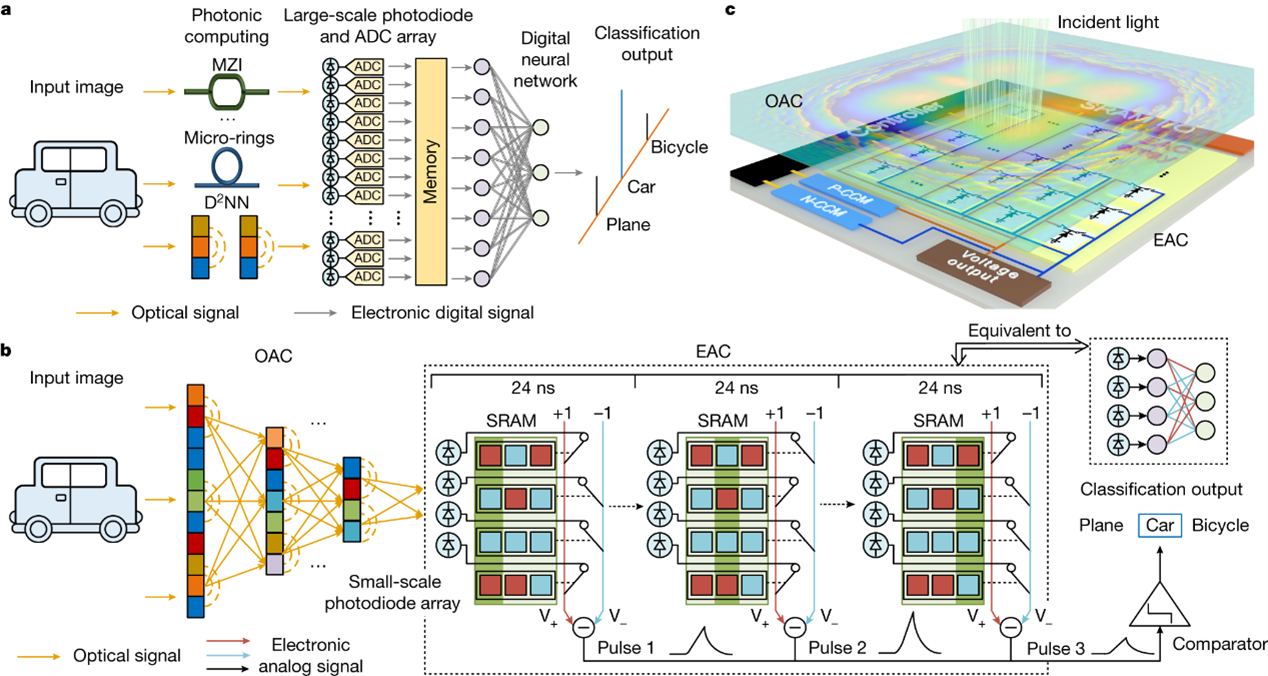
All-analog photoelectronic chip for high-speed vision tasks
Chen, Yitong, etc.
NATURE, 2023, 623: 48–57
Photonic computing enables faster and more energy-efficient processing of vision data. However, experimental superiority of deployable systems remains a challenge because of complicated optical nonlinearities, considerable power consumption of analog-to-digital converters (ADCs) for downstream digital processing and vulnerability to noises and system errors. Here we propose an all-analog chip combining electronic and light computing (ACCEL). It has a systemic energy efficiency of 74.8 peta-operations per second per watt and a computing speed of 4.6 peta-operations per second (more than 99% implemented by optics), corresponding to more than three and one order of magnitude higher than state-of-the-art computing processors, respectively. After applying diffractive optical computing as an optical encoder for feature extraction, the light-induced photocurrents are directly used for further calculation in an integrated analog computing chip without the requirement of analog-to-digital converters, leading to a low computing latency of 72 ns for each frame. With joint optimizations of optoelectronic computing and adaptive training, ACCEL achieves competitive classification accuracies of 85.5%, 82.0% and 92.6%, respectively, for Fashion-MNIST, 3-class ImageNet classification and time-lapse video recognition task experimentally, while showing superior system robustness in low-light conditions (0.14 fJ μm−2 each frame). ACCEL can be used across a broad range of applications such as wearable devices, autonomous driving and industrial inspections.
阅读原文:https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-023-06558-8

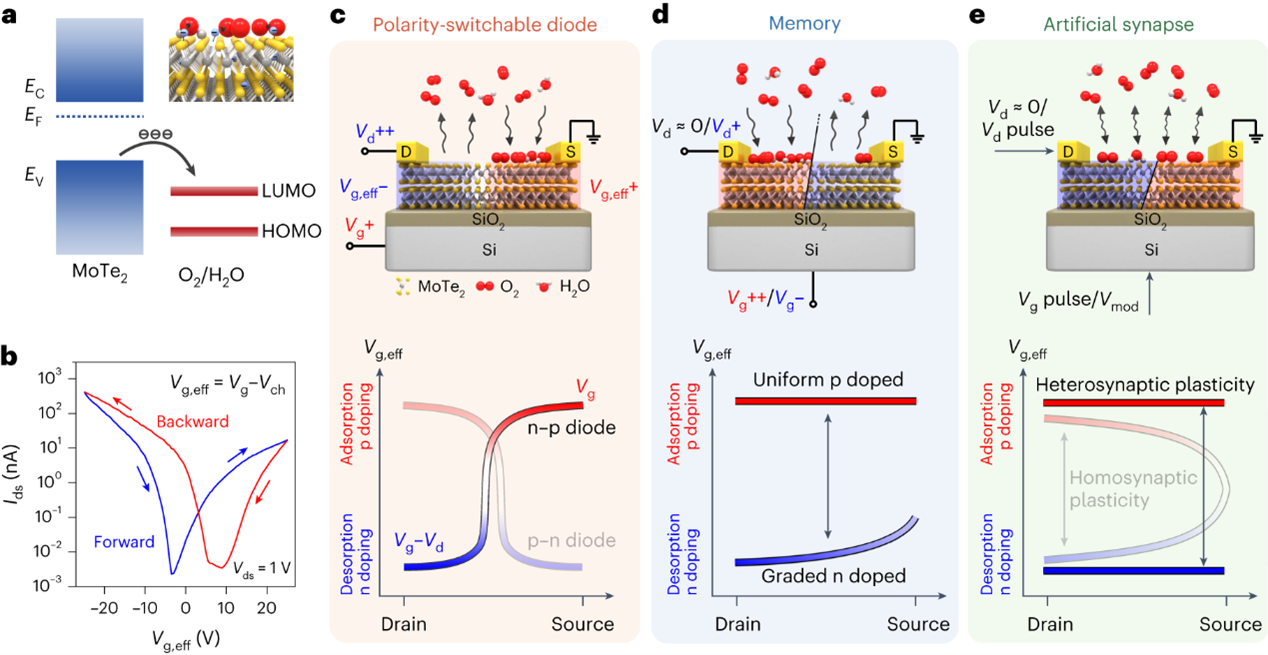
Programmable graded doping for reconfigurable molybdenum ditelluride devices
Peng, Ruixuan, etc.
NATURE ELECTRONICS, 2023, 6: 852–861
Non-volatile reconfigurable devices have the potential to improve integration levels and lower power consumption in next-generation electronics. Two-dimensional semiconductors are promising materials for making non-volatile reconfigurable devices due to their atomic thinness and strong gate control, but it is challenging to create varied reconfigurable functions with a simple device configuration. Here we show that an effective-gate-voltage-programmed graded-doping strategy can be used to create a single-gate two-dimensional molybdenum ditelluride device with multiple reconfigurable functions. The device can be programmed to function as a polarity-switchable diode, memory, in-memory Boolean logic gates and artificial synapses with homosynaptic plasticity and heterosynaptic plasticity. As a diode, the device exhibits a rectification ratio of up to 104; as an artificial heterosynapse, it shows heterosynaptic metaplasticity with a modulatory power consumption that can be reduced to 7.3 fW.
阅读原文:https://www.nature.com/articles/s41928-023-01056-1

Asymmetric conducting route and potential redistribution determine the polarization-dependent conductivity in layered ferroelectrics
Quhe, Ruge, etc.
NATURE NANOTECHNOLOGY, 2023
Precise control of the conductivity of layered ferroelectric semiconductors is required to make these materials suitable for advanced transistor, memory and logic circuits. Although proof-of-principle devices based on layered ferroelectrics have been demonstrated, it remains unclear how the polarization inversion induces conductivity changes. Therefore, function design and performance optimization remain cumbersome. Here we combine ab initio calculations with transport experiments to unveil the mechanism underlying the polarization-dependent conductivity in ferroelectric channel field-effect transistors. We find that the built-in electric field gives rise to an asymmetric conducting route formed by the hidden Stark effect and competes with the potential redistribution caused by the external field of the gate. Furthermore, leveraging our mechanistic findings, we control the conductivity threshold in α-In2Se3 ferroelectric channel field-effect transistors. We demonstrate logic-in-memory functionality through the implementation of electrically self-switchable primary (AND, OR) and composite (XOR, NOR, NAND) logic gates. Our work provides mechanistic insights into conductivity modulation in a broad class of layered ferroelectrics, providing foundations for their application in logic and memory electronics.
阅读原文:https://www.nature.com/articles/s41565-023-01539-4
联系人:杨老师 闫老师
邮箱:yandong80@bupt.edu.cn
电话:西土城校区图书馆125室 62281933 62283502
沙河校区图书馆东205室 66605330 66605331
往期精彩推荐
热点文献带您关注AI在气候领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(85)
热点文献带您关注通信领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(84)
热点文献带您关注AI与集成电路领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(83)
热点文献带您关注AI大型语言模型的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(82)
热点文献带您关注通信领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(81)
热点文献带您关注半导体领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(80)
热点文献带您关注AI领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(79)
热点文献带您关注通信领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(78)
热点文献带您关注半导体领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(77)
热点文献带您关注AI Transformer的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(76)
热点文献带您关注低轨卫星通信技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(75)
热点文献带您关注惯性测量单元的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(74)
热点文献带您关注存算一体技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(73)
热点文献带您关注电子皮肤的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(72)
热点文献带您关注AI的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(71)
热点论文带您探索未来网络中使用的新材料以及相关技术 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(70)
热点文献带您关注AI图神经网络的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(69)
热点论文带您探索新型网络架构以及超材料在未来通信中的应用——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(68)
热点文献带您关注AI深度强化学习的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(67)
热点论文带您探索新型网络架构以及超表面在未来通信中的应用——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(66)
热点文献带您关注AI领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(65)
热点论文带您领略半导体领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(64)
热点文献带您关注AI领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(63)
热点论文带您探索智能化以及超表面在未来通信中的应用——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(62)
热点文献带您关注AI领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(61)
热点论文带您领略未来通信研究热点的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(60)
热点文献带您关注AI深度学习的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(59)
热点论文带您领略未来通信热点技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(58)
热点文献带您关注AI视频动作识别的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(57)
热点论文带您领略新材料半导体领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(56)
热点文献带您关注AI深度神经网络的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(55)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在新材料技术领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(54)
热点文献带您关注AI在光神经网络领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(53)
热点论文带您领略半导体领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(52)
热点文献带您关注AI在集成电路领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(51)
热点论文带您领略光电半导体领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(50)
热点文献带您关注AI与人脸识别——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(49)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在新材料技术领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(48)
热点文献带您关注AI与生物学——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(47)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在光电材料及信息编码领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(46)
热点文献带您关注AI与医学图像——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(45)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在材料领域研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(44)
热点文献带您关注AI与医学研究——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(43)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在海空领域研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(42)
热点文献带您关注AI视觉跟踪——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(41)
热点论文与带您领略5G相关领域研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(40)
热点文献带您关注AI技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(39)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G领域热点研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(38)
热点文献带您关注AI与边缘计算——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(37)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G基础研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(36)
热点文献带您关注AI强化学习——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(35)
热点论文与带您领略未来通信的热点技术及最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(34)
热点文献带您关注AI深度学习与计算机视觉——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(33)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G热点技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(32)
热点文献带您关注AI与触觉传感技术——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(31)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G热点技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(30)
热点文献带您关注AI与机器人——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(29)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G电子器件和太赫兹方面的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(28)
热点文献带您关注AI自动驾驶——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(25)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G通信器件材料的最新进展 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(24)
热点文献带您关注机器学习与量子物理 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(23)
热点论文与带您领略6G网络技术的最新发展趋势 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(22)
热点文献带您关注模式识别——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(21)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G材料技术的最新发展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(20)
热点文献带您关注图神经网络——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(19)
热点论文带您领略5G/6G的最新技术动向 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(18)
热点文献带您关注AI主动视觉——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(17)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G的最新技术演进 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(16)
热点文献带您关注AI计算机视觉 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(15)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G的硬科技与新思路 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(14)
热点文献带您关注AI机器翻译 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(11)
热点论文:5G/6G引领社会新进步——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(10)
热点文献带您关注AI文本摘要自动生成 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(9)
热点论文带您探究6G的无限可能——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(8)
热点文献带您关注AI情感分类技术 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(7)
热点论文带您探究5G和未来通信材料技术领域 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(6)
前沿文献带您解读自然语言处理技术 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(5)
热点论文带您探究5G和未来通信——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务 (4)
热点论文解读AI应用领域 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(3)