热点文献带您关注AI的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(71)
2022-10-17
在第69期AI文献推荐中,我们为您推荐了图神经网络的热点文献,包括利用GNN量化城市道路网的空间同质性,基于图神经网络对分子表征进行分子对比学习,基于GNN的深度学习框架快速预测共晶体的形成,以及图神经网络的自监督学习综述。
本期我们为您选取了4篇文献,介绍人工智能的最新发展前沿,包括用于图像分类的片上光子深度神经网络,基于多层数字编码超表面阵列的可编程衍射深度神经网络,一种基于尖峰神经形态硬件的长短时记忆,适用于多智能任务机器人的时空弹性神经形态计算芯片TianjicX,推送给相关领域的科研人员。
文献一 用于图像分类的片上光子深度神经网络
An on-chip photonic deep neural network for image classificationAshtiani, Farshid, etc.
NATURE, 2022, 606(7914): 501–506
Deep neural networks with applications from computer vision to medical diagnosis are commonly implemented using clock-based processors, in which computation speed is mainly limited by the clock frequency and the memory access time. In the optical domain, despite advances in photonic computation, the lack of scalable on-chip optical non-linearity and the loss of photonic devices limit the scalability of optical deep networks. Here we report an integrated end-to-end photonic deep neural network (PDNN) that performs sub-nanosecond image classification through direct processing of the optical waves impinging on the on-chip pixel array as they propagate through layers of neurons. In each neuron, linear computation is performed optically and the non-linear activation function is realized opto-electronically, allowing a classification time of under 570 ps, which is comparable with a single clock cycle of state-of-the-art digital platforms. A uniformly distributed supply light provides the same per-neuron optical output range, allowing scalability to large-scale PDNNs. Two-class and four-class classification of handwritten letters with accuracies higher than 93.8% and 89.8%, respectively, is demonstrated. Direct, clock-less processing of optical data eliminates analogue-to-digital conversion and the requirement for a large memory module, allowing faster and more energy efficient neural networks for the next generations of deep learning systems.
阅读原文:https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-022-04714-0
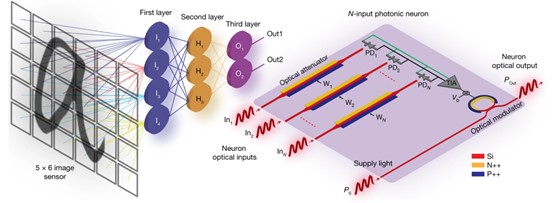
The architecture of the implemented PDNN chip and the structure of an N-input photonic neuron within the PDNN chip
文献二 基于多层数字编码超表面阵列的可编程衍射深度神经网络
A programmable diffractive deep neural network based on a digital-coding metasurface arrayLiu, Che, etc.
NATURE ELECTRONICS, 2022, 5(2): 113-122
The development of artificial intelligence is typically focused on computer algorithms and integrated circuits. Recently, all-optical diffractive deep neural networks have been created that are based on passive structures and can perform complicated functions designed by computer-based neural networks. However, once a passive diffractive deep neural network architecture is fabricated, its function is fixed. Here we report a programmable diffractive deep neural network that is based on a multi-layer digital-coding metasurface array. Each meta-atom on the metasurfaces is integrated with two amplifier chips and acts an active artificial neuron, providing a dynamic modulation range of 35 dB (from −22 dB to 13 dB). We show that the system, which we term a programmable artificial intelligence machine, can handle various deep learning tasks for wave sensing, including image classification, mobile communication coding–decoding and real-time multi-beam focusing. We also develop a reinforcement learning algorithm for on-site learning and a discrete optimization algorithm for digital coding.
阅读原文:https://www.nature.com/articles/s41928-022-00719-9
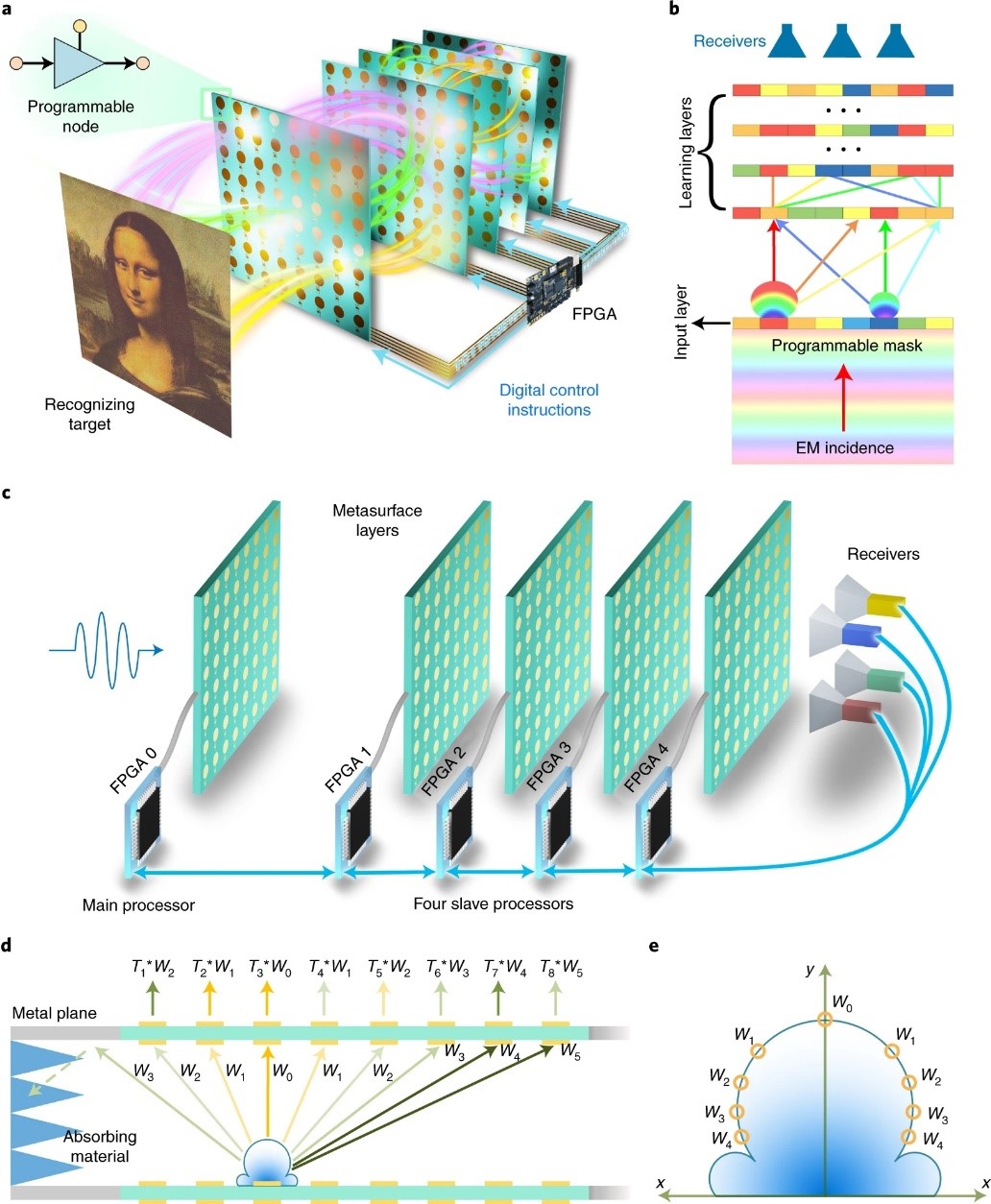
The reprogrammable D2NN platform
文献三 一种基于尖峰神经形态硬件的长短时记忆
A Long Short-Term Memory for AI Applications in Spike-based Neuromorphic HardwareRao, Arjun, etc.
NATURE MACHINE INTELLIGENCE, 2022, 4(5): 467-479
Spike-based neuromorphic hardware holds promise for more energy-efficient implementations of deep neural networks (DNNs) than standard hardware such as GPUs. But this requires us to understand how DNNs can be emulated in an event-based sparse firing regime, as otherwise the energy advantage is lost. In particular, DNNs that solve sequence processing tasks typically employ long short-term memory units that are hard to emulate with few spikes. We show that a facet of many biological neurons, slow after-hyperpolarizing currents after each spike, provides an efficient solution. After-hyperpolarizing currents can easily be implemented in neuromorphic hardware that supports multi-compartment neuron models, such as Intel’s Loihi chip. Filter approximation theory explains why after-hyperpolarizing neurons can emulate the function of long short-term memory units. This yields a highly energy-efficient approach to time-series classification. Furthermore, it provides the basis for an energy-efficient implementation of an important class of large DNNs that extract relations between words and sentences in order to answer questions about the text.
阅读原文:https://www.nature.com/articles/s42256-022-00480-w
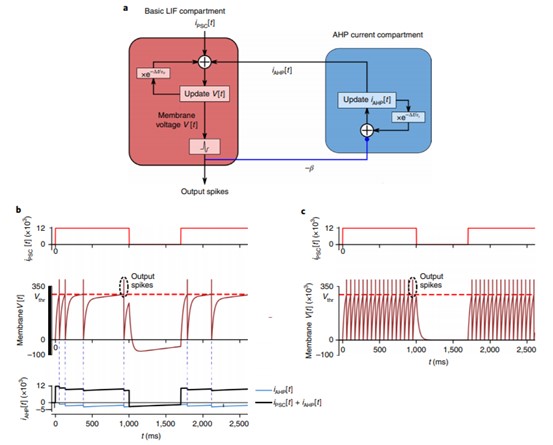
Schematics and dynamics of a two-compartment LIF neuron model with AHP currents
文献四 适用于多智能任务机器人的时空弹性神经形态计算芯片TianjicX
Neuromorphic computing chip with spatiotemporal elasticity for multi-intelligent-tasking robotsMa, Songchen, etc.
SCIENCE ROBOTICS, 2022, 7(67)
Recent advances in artificial intelligence have enhanced the abilities of mobile robots in dealing with complex and dynamic scenarios. However, to enable computationally intensive algorithms to be executed locally in multitask robots with low latency and high efficiency, innovations in computing hardware are required. Here, we report TianjicX, a neuromorphic computing hardware that can support true concurrent execution of multiple cross-computing-paradigm neural network (NN) models with various coordination manners for robotics. With spatiotemporal elasticity, TianjicX can support adaptive allocation of computing resources and scheduling of execution time for each task. Key to this approach is a high-level model, “Rivulet,” which bridges the gap between robotic-level requirements and hardware implementations. It abstracts the execution of NN tasks through distribution of static data and streaming of dynamic data to form the basic activity context, adopts time and space slices to achieve elastic resource allocation for each activity, and performs configurable hybrid synchronous-asynchronous grouping. Thereby, Rivulet is capable of supporting independent and interactive execution. Building on Rivulet with hardware design for realizing spatiotemporal elasticity, a 28-nanometer TianjicX neuromorphic chip with event-driven, high parallelism, low latency, and low power was developed. Using a single TianjicX chip and a specially developed compiler stack, we built a multi-intelligent-tasking mobile robot, Tianjicat, to perform a cat-and-mouse game. Multiple tasks, including sound recognition and tracking, object recognition, obstacle avoidance, and decision-making, can be concurrently executed. Compared with NVIDIA Jetson TX2, latency is substantially reduced by 79.09 times, and dynamic power is reduced by 50.66%.
阅读原文:https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/scirobotics.abk2948
往期精彩推荐
热点论文解读AI应用领域 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(3)
热点论文带您探究5G和未来通信——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务 (4)
前沿文献带您解读自然语言处理技术 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(5)
热点论文带您探究5G和未来通信材料技术领域 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(6)
热点文献带您关注AI情感分类技术 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(7)
热点论文带您探究6G的无限可能——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(8)
热点文献带您关注AI文本摘要自动生成 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(9)
热点论文:5G/6G引领社会新进步——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(10)
热点文献带您关注AI机器翻译 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(11)
热点论文与您探讨5G/6G网络技术新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(12)
热点文献带您关注AI计算机视觉 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(13)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G的硬科技与新思路 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(14)
热点文献带您关注AI计算机视觉 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(15)
热点论文带您领略5G/6G的最新技术动向 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(18)
热点文献带您关注图神经网络——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(19)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G材料技术的最新发展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(20)
热点文献带您关注模式识别——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(21)
热点论文与带您领略6G网络技术的最新发展趋势 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(22)
热点文献带您关注机器学习与量子物理 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(23)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G通信器件材料的最新进展 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(24)
热点文献带您关注AI自动驾驶——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(25)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G网络安全和技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(26)
热点文献带您关注AI神经网络与忆阻器——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(27)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G电子器件和太赫兹方面的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(28)
热点文献带您关注AI与机器人——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(29)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G热点技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(30)
热点文献带您关注AI与触觉传感技术——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(31)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G热点技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(32)
热点文献带您关注AI深度学习与计算机视觉——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(33)
热点论文与带您领略未来通信的热点技术及最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(34)
热点文献带您关注AI强化学习——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(35)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G基础研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(36)
热点文献带您关注AI与边缘计算——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(37)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G领域热点研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(38)
热点文献带您关注AI技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(39)
热点论文与带您领略5G相关领域研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(40)
热点文献带您关注AI视觉跟踪——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(41)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在海空领域研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(42)
热点文献带您关注AI与医学研究——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(43)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在材料领域研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(44)
热点文献带您关注AI与医学图像——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(45)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在光电材料及信息编码领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(46)
热点文献带您关注AI与生物学——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(47)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在新材料技术领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(48)
热点文献带您关注AI与人脸识别——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(49)
热点论文带您领略光电半导体领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(50)
热点文献带您关注AI在集成电路领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(51)
热点论文带您领略半导体领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(52)
热点文献带您关注AI在光神经网络领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(53)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在新材料技术领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(54)
热点文献带您关注AI深度神经网络的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(55)
热点论文带您领略新材料半导体领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(56)
热点文献带您关注AI视频动作识别的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(57)
热点论文带您领略未来通信热点技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(58)
热点文献带您关注AI深度学习的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(59)
热点论文带您领略未来通信研究热点的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(60)
热点文献带您关注AI领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(61)
热点论文带您探索智能化以及超表面在未来通信中的应用——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(62)
热点文献带您关注AI领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(63)
热点论文带您领略半导体领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(64)
热点文献带您关注AI领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(65)
热点论文带您探索新型网络架构以及超表面在未来通信中的应用——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(66)
热点文献带您关注AI深度强化学习的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(67)
热点论文带您探索新型网络架构以及超材料在未来通信中的应用——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(68)
热点文献带您关注AI图神经网络的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(69)
热点论文带您探索未来网络中使用的新材料以及相关技术 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(70)