热点论文带您探索新型网络架构以及超材料在未来通信中的应用——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(68)
2022-06-22
在第66期前沿文献中推荐中,介绍了新型网络架构以及超表面在未来通信中的应用,包括:极高可靠和低延迟通信,基于瓷片可拓宽MIMO以及相控阵的5G/B5G智能相控阵和智能可重配表面,借助超材料单元实现的BiCMOS片上亚太赫兹天线增益增强,用于毫米波领域的高性价比宽带介质平面透镜天线。
在本期的文献推荐中,关注点着眼于新型网络架构以及超材料在未来通信中的应用,选取了:用于5G无线系统的芯片级Floquet拓扑绝缘体;一种适用于5G-MIMO通信系统的新型高隔离度天线阵;用于改善单极子天线增益的基于间隙耦合对称分裂环谐振器的近零折射率负介电常数超材料;内生智能和端到端服务化的6G无线网络架构设计四篇文献,供相关领域的科研人员参考。
领域一 用于5G无线系统的芯片级Floquet拓扑绝缘体
Chip-scale Floquet topological insulators for 5G wireless systems
Aravind Nagulu, etc.
Nature Electronics, 2022
Floquet topological insulators, which have an exotic topological order sustained by time-varying Hamiltonians, could be of use in a range of technologies, including wireless communications, radar and quantum information processing. However, demonstrations of photonic Floquet topological insulators have been limited to systems that emulate time with a spatial dimension, which preserves time-reversal symmetry and thus removes valuable features including non-reciprocal topological protection. Here we report photonic Floquet topological insulators based on quasi-electrostatic wave propagation in switched-capacitor networks. The approach provides non-reciprocal Floquet topological insulators for electromagnetic waves and opens a large topological bandgap that spans up to gigahertz frequencies. Our devices exploit time modulation to operate beyond the delay–bandwidth limit of conventional linear time-invariant electromagnetic structures and therefore offer large delays, despite the broad bandwidth. The Floquet topological insulator is integrated into a complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS) chip, and we illustrate its potential for 5G wireless systems by showing that it can be used for multi-antenna full-duplex wireless operation and true-time-delay-based broadband beamforming.https://www.nature.com/articles/s41928-022-00751-9
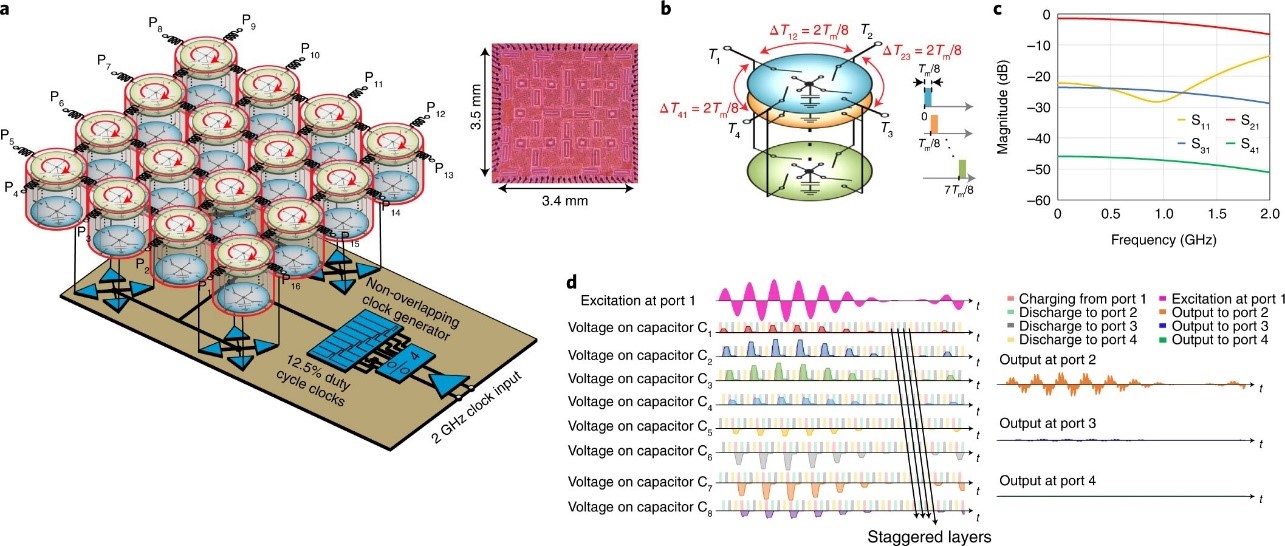
Fig. Anatomy of xURLLC with key research challenges and opportunities, R1–R9.
领域二 一种适用于5G-MIMO通信系统的新型高隔离度天线阵
An innovative antenna array with high inter element isolation for sub-6 GHz 5G MIMO communication systems
Mohammad Alibakhshikenari, etc.
Scientific Reports, 2022
A novel technique is shown to improve the isolation between radiators in antenna arrays. The proposed technique suppresses the surface-wave propagation and reduces substrate loss thereby enhancing the overall performance of the array. This is achieved without affecting the antenna’s footprint. The proposed approach is demonstrated on a four-element array for 5G MIMO applications. Each radiating element in the array is constituted from a 3 × 3 matrix of interconnected resonant elements. The technique involves (1) incorporating matching stubs within the resonant elements, (2) framing each of the four-radiating elements inside a dot-wall, and (3) defecting the ground plane with dielectric slots that are aligned under the dot-walls. Results show that with the proposed approach the impedance bandwidth of the array is increased by 58.82% and the improvement in the average isolation between antennas #1&2, #1&3, #1&4 are 8 dB, 14 dB, 16 dB, and 13 dB, respectively. Moreover, improvement in the antenna gain is 4.2% and the total radiation efficiency is 23.53%. These results confirm the efficacy of the technique. The agreement between the simulated and measured results is excellent. Furthermore, the manufacture of the antenna array using the proposed approach is relatively straightforward and cost effective.https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-022-12119-2
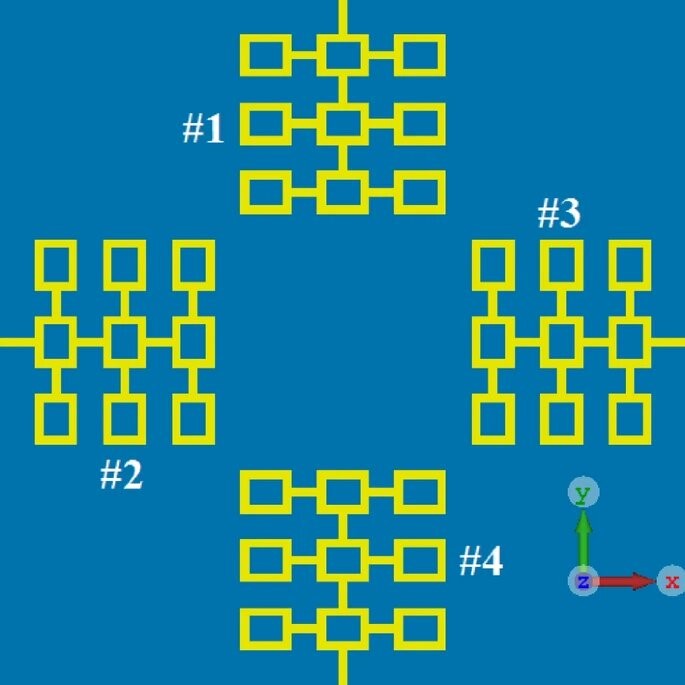
Fig. Top view showing the layout of the proposed antenna array consisting of four radiating elements with a standard ground plane.
领域三 用于改善单极子天线增益的基于间隙耦合对称分裂环谐振器的近零折射率负介电常数超材料
Gap coupled symmetric split ring resonator based near zero index ENG metamaterial for gain improvement of monopole antenna
Md. Moniruzzaman, etc.
Scientific Reports, 2022
In this article, a symmetric split ring resonator (SRR) based metamaterial (MTM) is presented that exhibits three resonances of transmission coefficient (S21) covering S, C, and X-bands with epsilon negative (ENG) and near zero index properties. The proposed MTM is designed on an FR4 substrate with the copper resonator at one side formed with two square rings and one circular split ring. The two square rings are coupled together around the split gap of the outer ring, whereas two split semicircles are also coupled together near the split gaps. Thus, gap coupled symmetric SRR is formed, which helps to obtain resonances at 2.78 GHz, 7.7 GHz and 10.16 GHz with desired properties of the MTM unit cell. The MTM unit cell's symmetric nature helps reduce the mutual coupling effect among the array elements. Thus, different array of unit cells provides a similar response to the unit cell compared with numerical simulation performed in CST microwave studio and validated by measurement. The equivalent circuit is modelled for the proposed MTM unit cell in Advanced Design System (ADS) software, and circuit validation is accomplished by comparing S21 obtained in ADS with the same of CST. The effective medium ratio (EMR) of 10.7 indicates the compactness of the proposed MTM. A test antenna is designed to observe the effect of the MTM over it. Numerical analysis shows that the proposed MTM have an impact on the antenna when it is used as the superstrate and helps to increase the gain of the antenna by 95% with increased directivity. Thus, compact size, high EMR, negative permittivity, near zero permeability and refractive index makes this MTM suitable for S, C and X band applications, especially for antenna gain with directivity enhancement.https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-022-11029-7
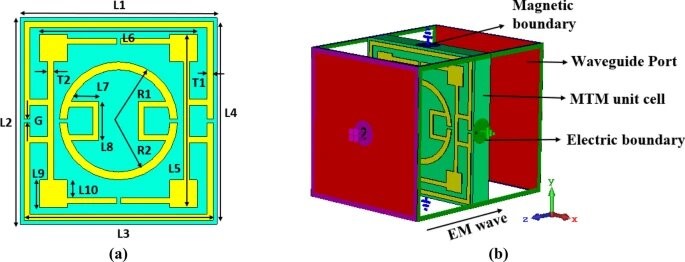
Fig. (a) Schematic layout of the unit cell and (b) simulation arrangement
领域四 内生智能和端到端服务化的6G无线网络架构设计
Native AI and Service Based Architecture for 6G Wireless Network
刘光毅, etc.
无线电通信技术, 2022
为了解决5G网络能耗高、结构复杂和运维管理难度大等问题,同时使得网络具备更极致的全场景适应能力,从网络功能、网络结构、网络运行三个方面对未来6G网络进行设计,实现6G网络的智慧内生和极简。在网络功能层面,提出端到端微服务化的架构,通过按需功能组合与编排提升行业用户乃至个人用户定制化需求的满足能力;在网络结构层面,提出一种低、中、高多频段协同的信令广域覆盖机制及相关方案设计,实现多制式、多频段小区的统一管理,进一步降低整网信令开销、小区管理复杂度和网络能耗;在网络运营层面,不同于5G外挂式AI,提出网络内生智能设计和AI服务质量(Quality of AI Service,QoAIS)指标体系及保障机制,将AI打造成6G网络的一种基础能力和服务。最后,对内生AI网络架构中基于QoAIS的AI工作流编排方案进行了仿真分析。仿真结果表明,在性能和开销方面,三种典型方案(集中式、分布式和协同式)各有优缺点,需要针对QoAIS的具体要求,决定AI工作流中相关任务的分布,并调度所需资源,以保证QoAIS的达成。https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CAPJ&dbname=CAPJLAST&filename=WXDT20220511000&uniplatform=NZKPT&v=iAz5YBXLPwXUEx2TEIHy2CyrP8-33zzcb7HDc2kDAgBrf6SDTahV5vaPEm2ZzKI
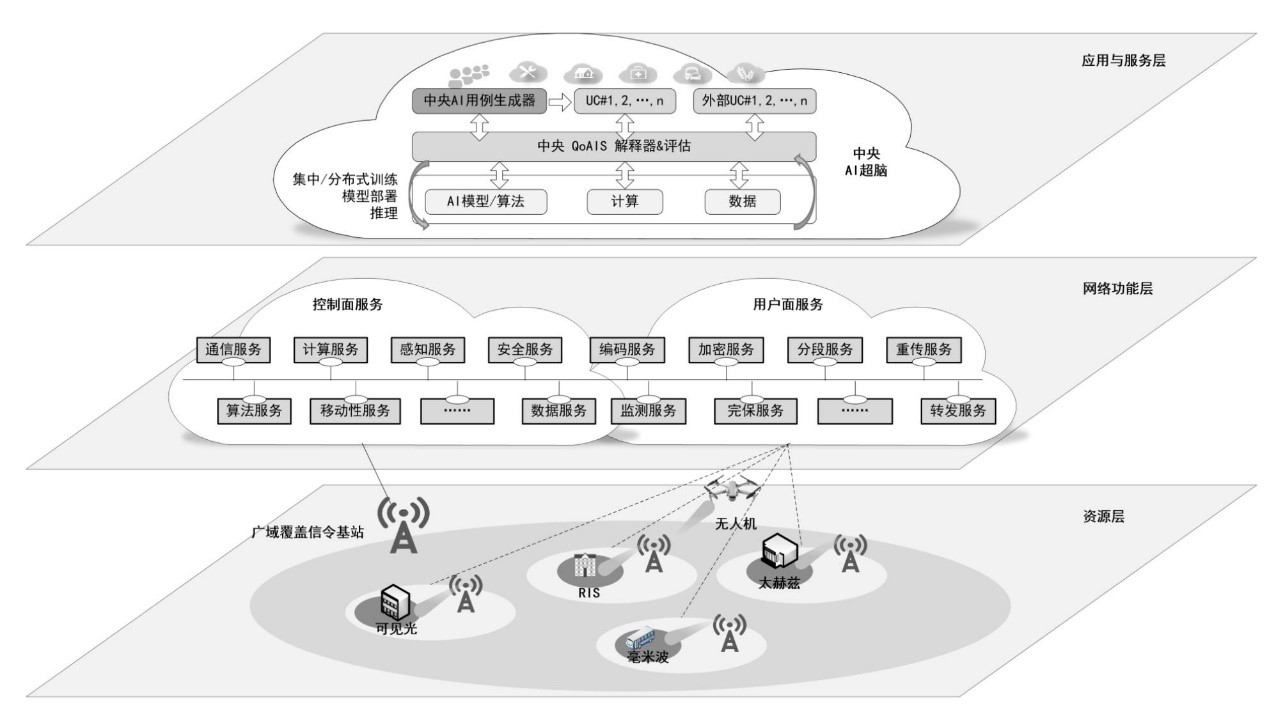
Fig. Intelligent and lite network prospect
往期精彩推荐
前沿论文带您解读5G应用领域 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(2)
热点论文解读AI应用领域 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(3)
热点论文带您探究5G和未来通信——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务 (4)
前沿文献带您解读自然语言处理技术 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(5)
热点论文带您探究5G和未来通信材料技术领域 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(6)
热点论文解读AI应用领域 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(3)
热点论文带您探究5G和未来通信——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务 (4)
前沿文献带您解读自然语言处理技术 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(5)
热点论文带您探究5G和未来通信材料技术领域 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(6)
热点文献带您关注AI情感分类技术 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(7)
热点论文带您探究6G的无限可能——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(8)
热点文献带您关注AI文本摘要自动生成 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(9)
热点论文:5G/6G引领社会新进步——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(10)
热点文献带您关注AI机器翻译 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(11)
热点论文与您探讨5G/6G网络技术新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(12)
热点文献带您关注AI计算机视觉 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(13)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G的硬科技与新思路 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(14)
热点文献带您关注AI计算机视觉 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(15)
热点论文带您领略5G/6G的最新技术动向 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(18)
热点文献带您关注图神经网络——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(19)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G材料技术的最新发展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(20)
热点文献带您关注模式识别——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(21)
热点论文与带您领略6G网络技术的最新发展趋势 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(22)
热点文献带您关注机器学习与量子物理 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(23)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G通信器件材料的最新进展 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(24)
热点文献带您关注AI自动驾驶——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(25)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G网络安全和技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(26)
热点文献带您关注AI神经网络与忆阻器——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(27)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G电子器件和太赫兹方面的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(28)
热点文献带您关注AI与机器人——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(29)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G热点技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(30)
热点文献带您关注AI与触觉传感技术——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(31)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G热点技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(32)
热点文献带您关注AI深度学习与计算机视觉——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(33)
热点论文与带您领略未来通信的热点技术及最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(34)
热点文献带您关注AI强化学习——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(35)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G基础研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(36)
热点文献带您关注AI与边缘计算——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(37)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G领域热点研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(38)
热点文献带您关注AI技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(39)
热点论文与带您领略5G相关领域研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(40)
热点文献带您关注AI视觉跟踪——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(41)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在海空领域研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(42)
热点文献带您关注AI与医学研究——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(43)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在材料领域研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(44)
热点文献带您关注AI与医学图像——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(45)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在光电材料及信息编码领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(46)
热点文献带您关注AI与生物学——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(47)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在新材料技术领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(48)
热点文献带您关注AI与人脸识别——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(49)
热点论文带您领略光电半导体领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(50)
热点文献带您关注AI在集成电路领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(51)
热点论文带您领略半导体领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(52)
热点文献带您关注AI在光神经网络领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(53)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在新材料技术领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(54)
热点文献带您关注AI深度神经网络的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(55)
热点论文带您领略新材料半导体领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(56)
热点文献带您关注AI视频动作识别的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(57)
热点论文带您领略未来通信热点技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(58)
热点文献带您关注AI深度学习的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(59)
热点论文带您领略未来通信研究热点的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(60)
热点文献带您关注AI领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(61)
热点论文带您探索智能化以及超表面在未来通信中的应用——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(62)
热点文献带您关注AI领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(63)
热点论文带您领略半导体领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(64)
热点文献带您关注AI领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(65)
热点论文带您探索新型网络架构以及超表面在未来通信中的应用——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(66)
热点文献带您关注AI深度强化学习的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(67)