热点文献带您关注AI与医学研究——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(43)
2021-06-16

在上一期AI文献推荐中,我们为您推荐了人工智能视觉跟踪领域的热点论文,包括视觉跟踪中基于深度强化学习的动态超参数优化、基于动态记忆网络的视觉跟踪、基于深度学习的视频显著性预测、基于神经网络的石墨烯透明焦堆成像系统三维跟踪等方面的文献。
本期我们为您选取了4篇文献,介绍基于人工智能的病理学预测原发部位不明癌症的起源、人工智能乳腺癌筛查系统、结合深度学习CT扫描模型预测COVID-19患者的严重程度、利用图像标题或医学图像报告中的语义信息指导CNN训练等文献,推送给相关领域的科研人员。
文献一 基于人工智能的病理学预测原发部位不明癌症的起源
AI-based pathology predicts origins for cancers of unknown primary
Lu, Ming Y., etc.
NATURE, 2021, 594: 106-110
Cancer of unknown primary (CUP) origin is an enigmatic group of diagnoses in which the primary anatomical site of tumour origin cannot be determined1,2. This poses a considerable challenge, as modern therapeutics are predominantly specific to the primary tumour3. Recent research has focused on using genomics and transcriptomics to identify the origin of a tumour4,5,6,7,8,9. However, genomic testing is not always performed and lacks clinical penetration in low-resource settings. Here, to overcome these challenges, we present a deep-learning-based algorithm—Tumour Origin Assessment via Deep Learning (TOAD)—that can provide a differential diagnosis for the origin of the primary tumour using routinely acquired histology slides. We used whole-slide images of tumours with known primary origins to train a model that simultaneously identifies the tumour as primary or metastatic and predicts its site of origin. On our held-out test set of tumours with known primary origins, the model achieved a top-1 accuracy of 0.83 and a top-3 accuracy of 0.96, whereas on our external test set it achieved top-1 and top-3 accuracies of 0.80 and 0.93, respectively. We further curated a dataset of 317 cases of CUP for which a differential diagnosis was assigned. Our model predictions resulted in concordance for 61% of cases and a top-3 agreement of 82%. TOAD can be used as an assistive tool to assign a differential diagnosis to complicated cases of metastatic tumours and CUPs and could be used in conjunction with or in lieu of ancillary tests and extensive diagnostic work-ups to reduce the occurrence of CUP.
阅读原文 https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-021-03512-4
文献二 人工智能乳腺癌筛查系统
International evaluation of an AI system for breast cancer screening
McKinney, Scott Mayer, etc.
NATURE, 2020, 577(7788): 89-94
Screening mammography aims to identify breast cancer at earlier stages of the disease, when treatment can be more successful(1). Despite the existence of screening programmes worldwide, the interpretation of mammograms is affected by high rates of false positives and false negatives(2). Here we present an artificial intelligence (AI) system that is capable of surpassing human experts in breast cancer prediction. To assess its performance in the clinical setting, we curated a large representative dataset from the UK and a large enriched dataset from the USA. We show an absolute reduction of 5.7% and 1.2% (USA and UK) in false positives and 9.4% and 2.7% in false negatives. We provide evidence of the ability of the system to generalize from the UK to the USA. In an independent study of six radiologists, the AI system outperformed all of the human readers: the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC-ROC) for the AI system was greater than the AUC-ROC for the average radiologist by an absolute margin of 11.5%. We ran a simulation in which the AI system participated in the double-reading process that is used in the UK, and found that the AI system maintained non-inferior performance and reduced the workload of the second reader by 88%. This robust assessment of the AI system paves the way for clinical trials to improve the accuracy and efficiency of breast cancer screening.
阅读原文 https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-019-1799-6
文献三 结合深度学习CT扫描模型预测COVID-19患者的严重程度
Integrating deep learning CT-scan model, biological and clinical variables to predict severity of COVID-19 patients
Lassau, Nathalie, etc.
NATURE COMMUNICATIONS, 2021, 12(1)
The SARS-COV-2 pandemic has put pressure on intensive care units, so that identifying predictors of disease severity is a priority. We collect 58 clinical and biological variables, and chest CT scan data, from 1003 coronavirus-infected patients from two French hospitals. We train a deep learning model based on CT scans to predict severity. We then construct the multimodal AI-severity score that includes 5 clinical and biological variables (age, sex, oxygenation, urea, platelet) in addition to the deep learning model. We show that neural network analysis of CT-scans brings unique prognosis information, although it is correlated with other markers of severity (oxygenation, LDH, and CRP) explaining the measurable but limited 0.03 increase of AUC obtained when adding CT-scan information to clinical variables. Here, we show that when comparing AI-severity with 11 existing severity scores, we find significantly improved prognosis performance; AI-severity can therefore rapidly become a reference scoring approach. The SARS-COV-2 pandemic has put pressure on intensive care units, so that predicting severe deterioration early is a priority. Here, the authors develop a multimodal severity score including clinical and imaging features that has significantly improved prognostic performance in two validation datasets compared to previous scores.
阅读原文 https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-020-20657-4
文献四 利用图像标题或医学图像报告中的语义信息指导CNN训练
Text-Guided Neural Network Training for Image Recognition in Natural Scenes and Medicine
Zhang, Zizhao, etc.
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON PATTERN ANALYSIS AND MACHINE INTELLIGENCE, 2021, 43(5): 1733-1745
Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) are widely recognized as the foundation for machine vision systems. The conventional rule of teaching CNNs to understand images requires training images with human annotated labels, without any additional instructions. In this article, we look into a new scope and explore the guidance from text for neural network training. We present two versions of attention mechanisms to facilitate interactions between visual and semantic information and encourage CNNs to effectively distill visual features by leveraging semantic features. In contrast to dedicated text-image joint embedding methods, our method realizes asynchronous training and inference behavior: a trained model can classify images, irrespective of the text availability. This characteristic substantially improves the model scalability to multiple (multimodal) vision tasks. We also apply the proposed method onto medical imaging, which learns from richer clinical knowledge and achieves attention-based interpretable decision-making. With comprehensive validation on two natural and two medical datasets, we demonstrate that our method can effectively make use of semantic knowledge to improve CNN performance. Our method performs substantial improvement on medical image datasets. Meanwhile, it achieves promising performance for multi-label image classification and caption-image retrieval as well as excellent performance for phrase-based and multi-object localization on public benchmarks.
阅读原文 https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8911262
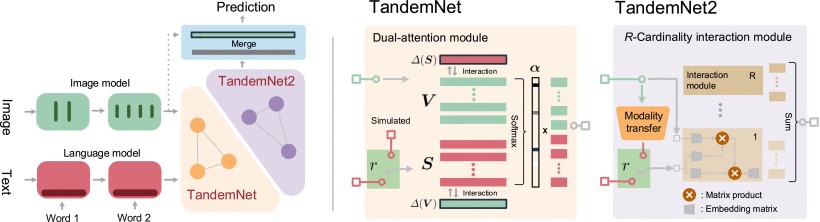
Overview of the proposed method
往期精彩推荐
前沿论文带您解读5G应用领域 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(2)
热点论文解读AI应用领域 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(3)
热点论文带您探究5G和未来通信——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务 (4)
前沿文献带您解读自然语言处理技术 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(5)
热点论文带您探究5G和未来通信材料技术领域 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(6)
热点论文解读AI应用领域 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(3)
热点论文带您探究5G和未来通信——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务 (4)
前沿文献带您解读自然语言处理技术 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(5)
热点论文带您探究5G和未来通信材料技术领域 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(6)
热点文献带您关注AI情感分类技术 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(7)
热点论文带您探究6G的无限可能——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(8)
热点文献带您关注AI文本摘要自动生成 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(9)
热点论文:5G/6G引领社会新进步——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(10)
热点文献带您关注AI机器翻译 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(11)
热点论文与您探讨5G/6G网络技术新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(12)
热点文献带您关注AI计算机视觉 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(13)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G的硬科技与新思路 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(14)
热点文献带您关注AI计算机视觉 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(15)
热点论文带您领略5G/6G的最新技术动向 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(18)
热点文献带您关注图神经网络——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(19)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G材料技术的最新发展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(20)
热点文献带您关注模式识别——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(21)
热点论文与带您领略6G网络技术的最新发展趋势 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(22)
热点文献带您关注机器学习与量子物理 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(23)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G通信器件材料的最新进展 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(24)
热点文献带您关注AI自动驾驶——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(25)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G网络安全和技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(26)
热点文献带您关注AI神经网络与忆阻器——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(27)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G电子器件和太赫兹方面的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(28)
热点文献带您关注AI与机器人——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(29)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G热点技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(30)
热点文献带您关注AI与触觉传感技术——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(31)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G热点技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(32)
热点文献带您关注AI深度学习与计算机视觉——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(33)
热点论文与带您领略未来通信的热点技术及最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(34)
热点文献带您关注AI强化学习——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(35)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G基础研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(36)
热点文献带您关注AI与边缘计算——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(37)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G领域热点研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(38)
热点文献带您关注AI技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(39)
热点论文与带您领略5G相关领域研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(40)
热点文献带您关注AI视觉跟踪——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(41)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在海空领域研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(42)