热点论文与带您领略5G/6G的硬科技与新思路 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(14)
2020-06-05
随着5G部署的展开,无线研究的重点越来越转向6G,科研人员试图描绘一幅6G框架内的通信需求和技术全景图,通过可能出现在未来的主题来塑造6G系统的需求和技术。众所周知,5G、6G通信系统带来了更快的数据传输能力,而物理器件的性能往往成为了最终的系统瓶颈。为了带来更高的时频转换效率,科研人员使用了氮化硼单分子膜作为模拟开关,证明了其在5G和太赫兹通信系统中的应用潜力。此外,为了应对日益增长的数据速率的挑战,下一代光通信网络需要电子和光子的协同集成,科研人员报告了一种单片集成的光电发射器,它可以达到超过100GBd的符号速率,并给出了两种基于该技术的调制器的实现方案。最后,结合未来网络在健康行业中的应用场景,研究人员介绍了一种跨学科的方法,将电子医疗、优先权、大数据分析(BDA)和无线资源优化等概念应该用到多优先级调度的5G网络中,根据患者医疗状态的严重性展开调度算法的优化。
本期选取了4篇文献,讨论的内容包括6G时代需要的通信技术支撑,使用氮化硼单分子膜的模拟开关在5G和太赫兹通信系统中的应用,一种单片双极CMOS电子等离子体高速发射机,以及以患者为中心的异构网络与未来通信系统的融合,推送给相关领域的科研人员,共同探讨。

Communications in the 6G Era
Harish Viswanathan, etc.
IEEE Access,2020,8: 57063 - 57074
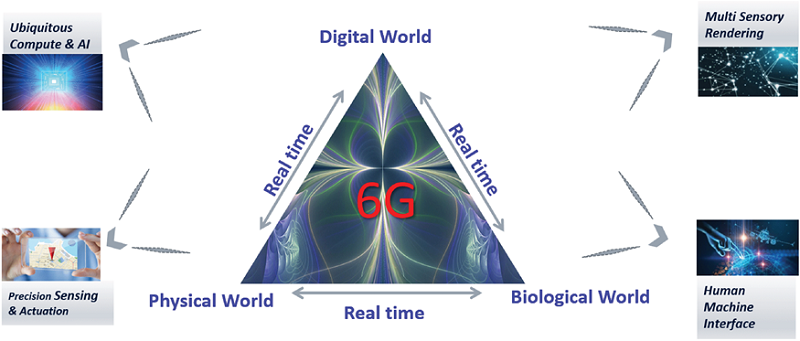
The focus of wireless research is increasingly shifting toward 6G as 5G deployments get underway. At this juncture, it is essential to establish a vision of future communications to provide guidance for that research. In this paper, we attempt to paint a broad picture of communication needs and technologies in the timeframe of 6G. The future of connectivity is in the creation of digital twin worlds that are a true representation of the physical and biological worlds at every spatial and time instant, unifying our experience across these physical, biological and digital worlds. New themes are likely to emerge that will shape 6G system requirements and technologies, such as: (i) new man-machine interfaces created by a collection of multiple local devices acting in unison; (ii) ubiquitous universal computing distributed among multiple local devices and the cloud; (iii) multi-sensory data fusion to create multi-verse maps and new mixed-reality experiences; and (iv) precision sensing and actuation to control the physical world. With rapid advances in artificial intelligence, it has the potential to become the foundation for the 6G air interface and network, making data, compute and energy the new resources to be exploited for achieving superior performance. In addition, in this paper we discuss the other major technology transformations that are likely to define 6G: (i) cognitive spectrum sharing methods and new spectrum bands; (ii) the integration of localization and sensing capabilities into the system definition, (iii) the achievement of extreme performance requirements on latency and reliability; (iv) new network architecture paradigms involving sub-networks and RAN-Core convergence; and (v) new security and privacy schemes.
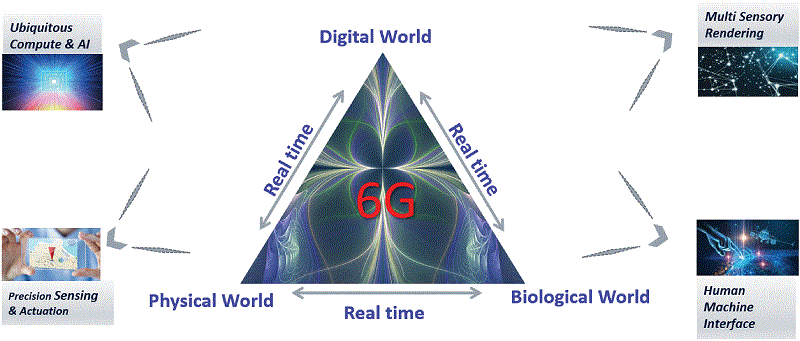
6G for the inter-connection of physical, biological, and digital worlds

Analogue switches made from boron nitride monolayers for application in 5G and terahertz communication systems
Myungsoo Kim, etc.
Nature Electronics ,2020
Hexagonal boron nitride (hBN) has a large bandgap, high phonon energies and an atomically smooth surface absent of dangling bonds. As a result, it has been widely used as a dielectric to investigate electron physics in two-dimensional heterostructures and as a dielectric in the fabrication of two-dimensional transistors and optoelectronic devices. Here we show that hBN can be used to create analogue switches for applications in communication systems across radio, 5G and terahertz frequencies. Our approach relies on the non-volatile resistive switching capabilities of atomically thin hBN. The switches are composed of monolayer hBN sandwiched between two gold electrodes and exhibit a cutoff-frequency figure of merit of around 129 THz with a low insertion loss (≤0.5 dB) and high isolation (≥10 dB) from 0.1 to 200 GHz, as well as a high power handling (around 20 dBm) and nanosecond switching speeds, metrics that are superior to those of existing solid-state switches. Furthermore, the switches are 50 times more efficient than other non-volatile switches in terms of a d.c. energy-consumption metric, which is an important consideration for ubiquitous mobile systems. We also illustrate the potential of the hBN switches in a communication system with an 8.5 Gbit s–1 data transmission rate at 100 GHz with a low bit error rate under 10−10.

A monolithic bipolar CMOS electronic–plasmonic high-speed transmitter
Ueli Koch, etc
Nature Electronics,2020
To address the challenge of increasing data rates, next-generation optical communication networks will require the co-integration of electronics and photonics. Heterogeneous integration of these technologies has shown promise, but will eventually become bandwidth-limited. Faster monolithic approaches will therefore be needed, but monolithic approaches using complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS) electronics and silicon photonics are typically limited by their underlying electronic or photonic technologies. Here, we report a monolithically integrated electro-optical transmitter that can achieve symbol rates beyond 100 GBd. Our approach combines advanced bipolar CMOS with silicon plasmonics, and addresses key challenges in monolithic integration through co-design of the electronic and plasmonic layers, including thermal design, packaging and a nonlinear organic electro-optic material. To illustrate the potential of our technology, we develop two modulator concepts—an ultra-compact plasmonic modulator and a silicon-plasmonic modulator with photonic routing—both directly processed onto the bipolar CMOS electronics.

Patient-Centric HetNets Powered by Machine Learning and Big Data Analytics for 6G Networks
Mohammed S. Hadi, etc.
IEEE Access,2020,8: 85639 - 85655
Having a cognitive and self-optimizing network that proactively adapts not only to channel conditions, but also according to its users’ needs can be one of the highest forthcoming priorities of future 6G Heterogeneous Networks (HetNets). In this paper, we introduce an interdisciplinary approach linking the concepts of e-healthcare, priority, big data analytics (BDA) and radio resource optimization in a multi-tier 5G network. We employ three machine learning (ML) algorithms, namely, naïve Bayesian (NB) classifier, logistic regression (LR), and decision tree (DT), working as an ensemble system to analyze historical medical records of stroke out-patients (OPs) and readings from body-attached internet-of-things (IoT) sensors to predict the likelihood of an imminent stroke. We convert the stroke likelihood into a risk factor functioning as a priority in a mixed integer linear programming (MILP) optimization model. Hence, the task is to optimally allocate physical resource blocks (PRBs) to HetNet users while prioritizing OPs by granting them high gain PRBs according to the severity of their medical state. Thus, empowering the OPs to send their critical data to their healthcare provider with minimized delay. To that end, two optimization approaches are proposed, a weighted sum rate maximization (WSRMax) approach and a proportional fairness (PF) approach. The proposed approaches increased the OPs’ average signal to interference plus noise (SINR) by 57% and 95%, respectively. The WSRMax approach increased the system’s total SINR to a level higher than that of the PF approach, nevertheless, the PF approach yielded higher SINRs for the OPs, better fairness and a lower margin of error.
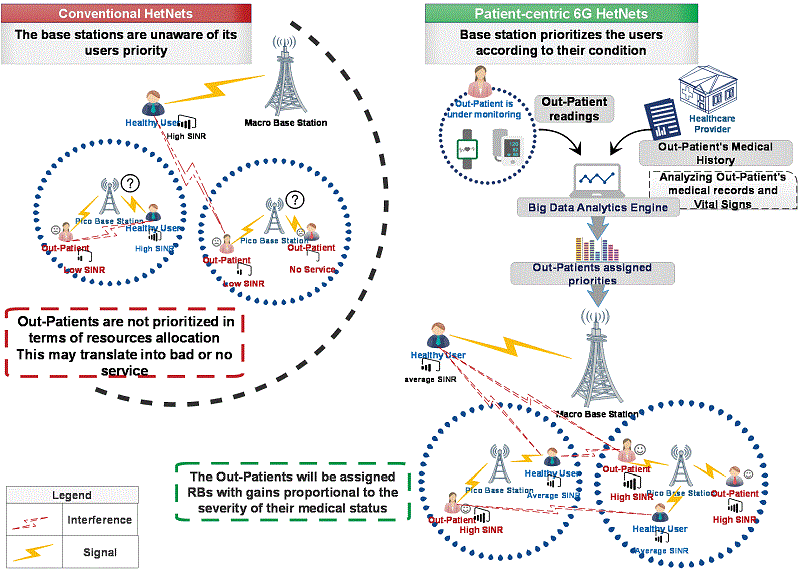
Patient-Aware 6G HetNet