热点文献带您关注模式识别——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(21)
2020-09-28

在上一期AI文献推荐中,我们为您推荐了关于图神经网络的热点论文。在本期推荐中,我们将为您推荐模式识别的前沿论文。
近年来,以深度神经网络为代表的模式识别技术取得了重大突破,在文字识别、指纹识别、人脸识别、语音识别、遥感、医学诊断、数字水印技术等领域都有了长足发展。模式识别研究主要集中在两方面,一是研究生物体是如何感知对象的,二是如何用计算机实现模式识别的理论和方法。
本期选取了4篇文献,介绍模式识别的最新动态,包括具有线性和对称电导更新特性的Van Der Waals混合突触在声学模式识别中的应用、在掺杂冷原子反铁磁体的Hubbard模型中利用模式识别算法进行图像分析、基于模式识别揭示高次谐波物质波射流的高阶相关性、用于细粒度视觉识别的基于深度注意力的空间递归网络等文献,推送给相关领域的科研人员。

Artificial van der Waals hybrid synapse and its application to acoustic pattern recognition
Seo, Seunghwan, etc.
NATURE COMMUNICATIONS, 2020, 11(1): 3936
Brain-inspired parallel computing, which is typically performed using a hardware neural-network platform consisting of numerous artificial synapses, is a promising technology for effectively handling large amounts of informational data. However, the reported nonlinear and asymmetric conductance-update characteristics of artificial synapses prevent a hardware neural-network from delivering the same high-level training and inference accuracies as those delivered by a software neural-network. Here, we developed an artificial van-der-Waals hybrid synapse that features linear and symmetric conductance-update characteristics. Tungsten diselenide and molybdenum disulfide channels were used selectively to potentiate and depress conductance. Subsequently, via training and inference simulation, we demonstrated the feasibility of our hybrid synapse toward a hardware neural-network and also delivered high recognition rates that were comparable to those delivered using a software neural-network. This simulation involving the use of acoustic patterns was performed with a neural network that was theoretically formed with the characteristics of the hybrid synapses. Designing high-performance and energy efficient neural network hardware remains a challenge. Here, the authors develop a van der Waals hybrid synaptic device that features linear and symmetric conductance-update characteristics and demonstrate the feasibility for hardware neural network performing acoustic pattern recognition.
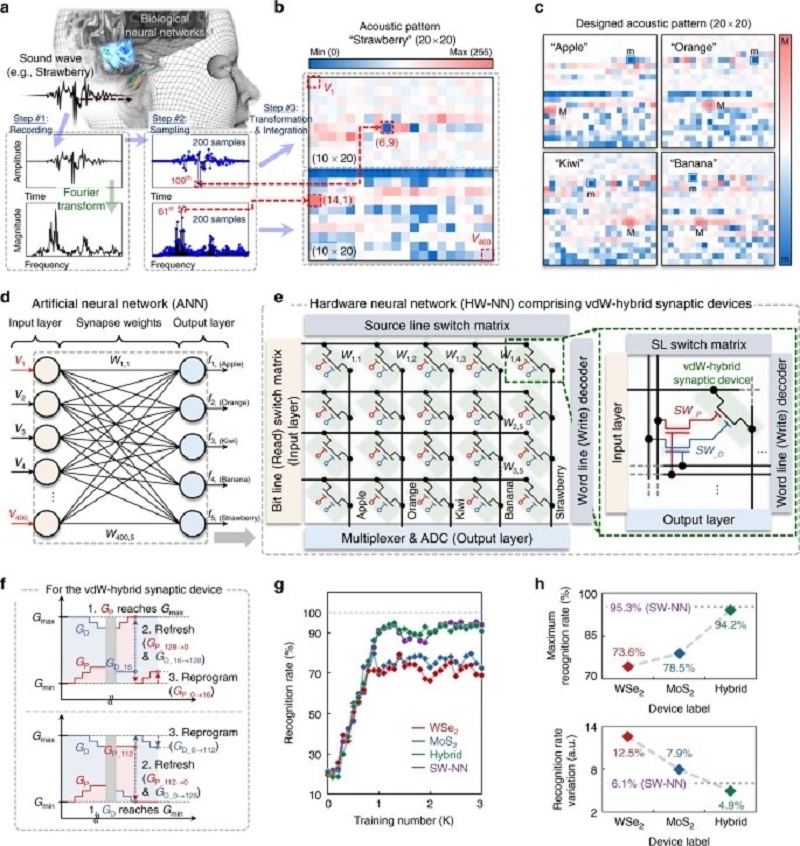
Acoustic pattern recognition task

String patterns in the doped Hubbard model
Chiu, Christie S., etc.
SCIENCE, 2019, 365(6450) SI: 251-+
Understanding strongly correlated quantum many-body states is one of the most difficult challenges in modern physics. For example, there remain fundamental open questions on the phase diagram of the Hubbard model, which describes strongly correlated electrons in solids. In this work, we realize the Hubbard Hamiltonian and search for specific patterns within the individual images of many realizations of strongly correlated ultracold fermions in an optical lattice. Upon doping a cold-atom antiferromagnet, we find consistency with geometric strings, entities that may explain the relationship between hole motion and spin order, in both pattern-based and conventional observables. Our results demonstrate the potential for pattern recognition to provide key insights into cold-atom quantum many-body systems.
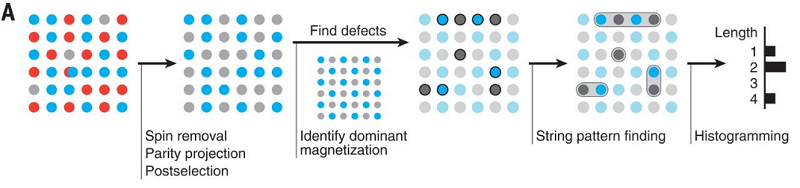
Schematic explanation of the string-pattern identification algorithm

Correlations in high-harmonic generation of matter-wave jets revealed by pattern recognition
Feng, Lei, etc.
SCIENCE, 2019, 363(6426): 521-+
Correlations in interacting many-body systems are key to the study of quantum matter. The complexity of the correlations typically grows quickly as the system evolves and thus presents a challenge for experimental characterization and intuitive understanding. In a strongly driven Bose-Einstein condensate, we observe the high-harmonic generation of matter-wave jets with complex correlations as a result of bosonic stimulation. Based on a pattern recognition scheme, we identify a pattern of correlations that reveals the underlying secondary scattering processes and higher-order correlations. We show that pattern recognition offers a versatile strategy to visualize and analyze the quantum dynamics of a many-body system.
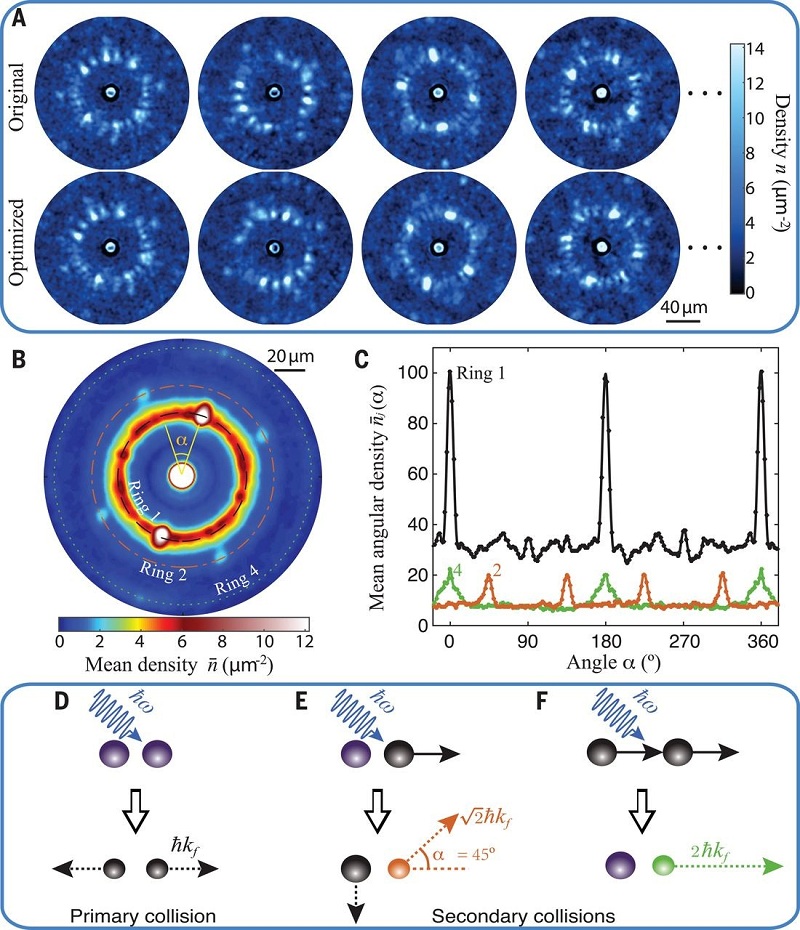
Pattern recognition and microscopic interpretation

Deep Attention-Based Spatially Recursive Networks for Fine-Grained Visual Recognition
Wu, Lin, etc.
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CYBERNETICS, 2019, 49(5): 1791-1802
Fine-grained visual recognition is an important problem in pattern recognition applications. However, it is a challenging task due to the subtle interclass difference and large intraclass variation. Recent visual attention models are able to automatically locate critical object parts and represent them against appearance variations. However, without consideration of spatial dependencies in discriminative feature learning, these methods are underperformed in classifying fine-grained objects. In this paper, we present a deep attention-based spatially recursive model that can learn to attend to critical object parts and encode them into spatially expressive representations. Our network is technically premised on bilinear pooling, enabling local pairwise feature interactions between outputs from two different convolutional neural networks (CNNs) that correspond to distinct region detection and relevant feature extraction. Then, spatial long-short term memory (LSTMs) units are introduced to generate spatially meaningful hidden representations via the long-range dependency on all features in two dimensions. The attention model is leveraged between bilinear outcomes and spatial LSTMs for dynamic selection on varied inputs. Our model, which is composed of two-stream CNN layers, bilinear pooling, and spatial recursive encoding with attention, is end-to-end trainable to serve as the part detector and feature extractor whereby relevant features are localized, extracted, and encoded spatially for recognition purpose. We demonstrate the superiority of our method over two typical fine-grained recognition tasks: fine-grained image classification and person re-identification.
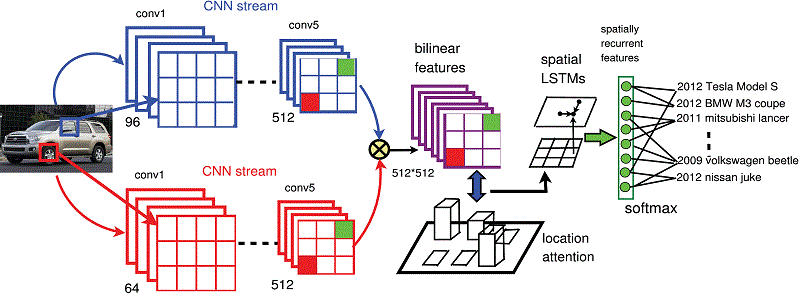
Proposed deep attention-based spatially recursive network
热点论文解读AI应用领域 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(3)
热点论文带您探究5G和未来通信——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务 (4)
前沿文献带您解读自然语言处理技术 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(5)
热点论文带您探究5G和未来通信材料技术领域 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(6)
热点文献带您关注AI情感分类技术 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(7)
热点论文带您探究6G的无限可能——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(8)
热点文献带您关注AI文本摘要自动生成 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(9)
热点论文:5G/6G引领社会新进步——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(10)
热点文献带您关注AI机器翻译 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(11)
热点论文与您探讨5G/6G网络技术新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(12)
热点文献带您关注AI计算机视觉 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(13)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G的硬科技与新思路 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(14)
热点文献带您关注AI计算机视觉 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(15)