热点论文带您领略未来通信在新材料技术领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(54)
2021-12-06

在上一期前沿文献中推荐中,介绍了通信新材料及相关技术领域的最新进展,包括:用于5G和6G的氧化物电子器件,一种基于大面积电子器件的工作频率位千兆赫的相控阵,5G基础设施的治理:介于路径依赖和基于风险的方法之间,以及基于可编程元曲面的5G移动通信波束控制。
可重构智能表面(RIS),以及智能反射面(IRS)被认为可以应用于优化未来的无线网络。在本期的文献推荐中,关注点着眼于相关技术的研究进展,选取了:具有集成传感能力的可重构智能表面、智能反射面辅助无线通信的教程、多用户MISO无线通信中的信道估计,以及可抵御分布式窃听攻击的安全时空调制毫米波无线链路四篇文献,供相关领域的科研人员参考。
领域一 具有集成传感能力的可重构智能表面
A reconfigurable intelligent surface with integrated sensing capability
Idban Alamzadeh, etc.
Scientific Reports, 2021
Reconfigurable reflective surfaces can alter the propagation environment to improve wireless communication and power transfer. Paramount to this operation—which has attracted much attention recently—is the assumption that the reflective surface has prior knowledge of the propagation environment, for example, the direction/location of the transmitter and the intended receiver(s). To address this need, we propose a reconfigurable reflective metasurface with integrated sensing capabilities. By modifying the tunable meta-atoms constituting the metasurface, we couple small portions of the incident wave to an array of sensing waveguides. As an illustrative example, we demonstrate the ability to use the sampled incident wave to detect its angle of arrival. In addition, we propose and numerically demonstrate the possibility to reduce the required sensors, i.e., the number of radio frequency (RF) chains needed to acquire the sensed signals, by leveraging the inherent metasurface’s tunable multiplexing capability. A reconfigurable reflective metasurface with integrated sensing capabilities can benefit wireless communications, wireless power transfer, RF sensing, and smart sensors.
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-021-99722-x
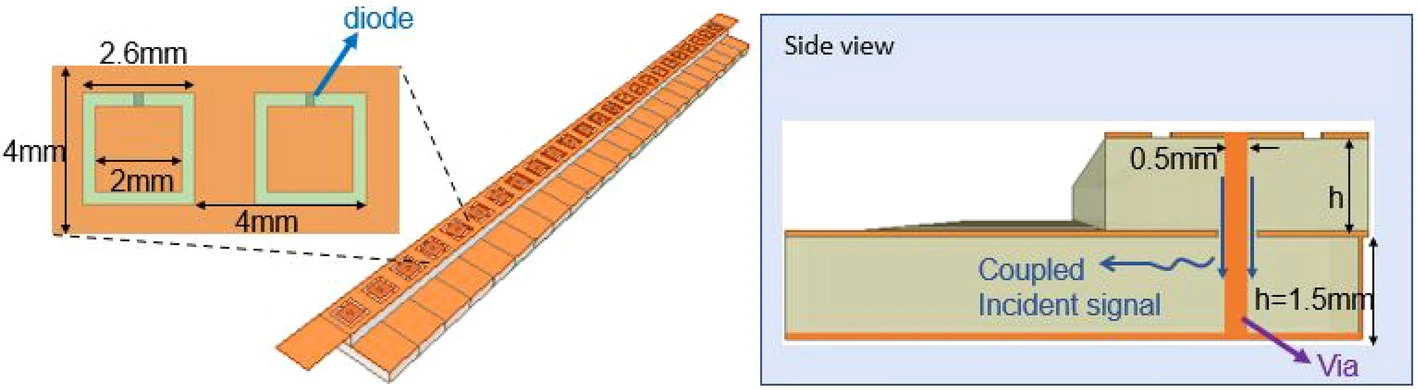
Fig. Proposed hybrid RIS hardw are design with integrated sensing capability.
领域二 智能反射面辅助无线通信的教程
Intelligent Reflecting Surface-Aided Wireless Communications: A Tutorial
Qingqing Wu, etc.
IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2021, 69(5): 3313-3351
Intelligent reflecting surface (IRS) is an enabling technology to engineer the radio signal propagation in wireless networks. By smartly tuning the signal reflection via a large number of low-cost passive reflecting elements, IRS is capable of dynamically altering wireless channels to enhance the communication performance. It is thus expected that the new IRS-aided hybrid wireless network comprising both active and passive components will be highly promising to achieve a sustainable capacity growth cost-effectively in the future. Despite its great potential, IRS faces new challenges to be efficiently integrated into wireless networks, such as reflection optimization, channel estimation, and deployment from communication design perspectives. In this paper, we provide a tutorial overview of IRS-aided wireless communications to address the above issues, and elaborate its reflection and channel models, hardware architecture and practical constraints, as well as various appealing applications in wireless networks. Moreover, we highlight important directions worthy of further investigation in future work.
https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9326394
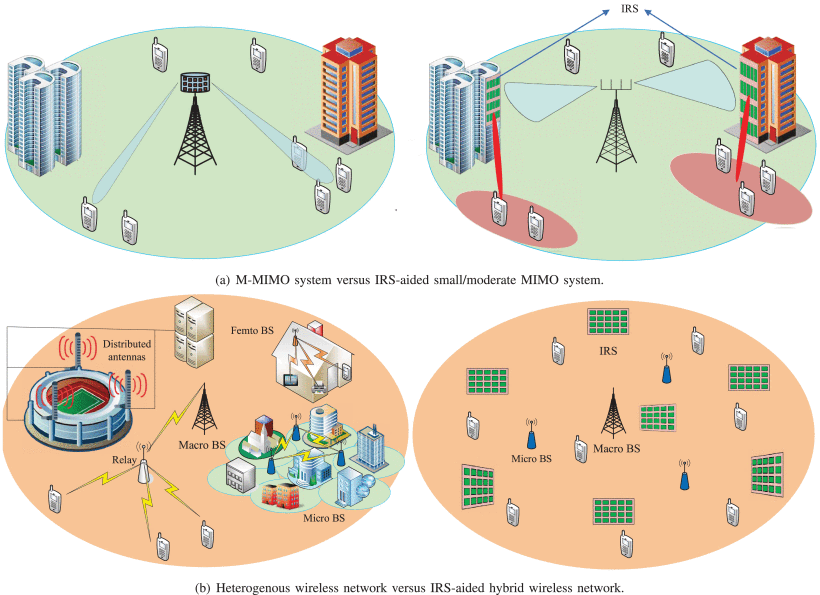
Fig. Potential paradigm shifts of wireless system/network designs with IRS.
领域三 多用户MISO无线通信中的信道估计
Channel Estimation for RIS-Empowered Multi-User MISO Wireless Communications
Li Wei, etc.
IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2021, 69(6): 4144-4157
Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces (RISs) have been recently considered as an energy-efficient solution for future wireless networks due to their fast and low-power configuration, which has increased potential in enabling massive connectivity and low-latency communications. Accurate and low-overhead channel estimation in RIS-based systems is one of the most critical challenges due to the usually large number of RIS unit elements and their distinctive hardware constraints. In this paper, we focus on the uplink of a RIS-empowered multi-user Multiple Input Single Output (MISO) uplink communication systems and propose a channel estimation framework based on the parallel factor decomposition to unfold the resulting cascaded channel model. We present two iterative estimation algorithms for the channels between the base station and RIS, as well as the channels between RIS and users. One is based on alternating least squares (ALS), while the other uses vector approximate message passing to iteratively reconstruct two unknown channels from the estimated vectors. To theoretically assess the performance of the ALS-based algorithm, we derived its estimation Cramér-Rao Bound (CRB). We also discuss the downlink achievable sum rate computation with estimated channels and different precoding schemes for the base station. Our extensive simulation results show that our algorithms outperform benchmark schemes and that the ALS technique achieves the CRB. It is also demonstrated that the sum rate using the estimated channels always reach that of perfect channels under various settings, thus, verifying the effectiveness and robustness of the proposed estimation algorithms.
https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9366805
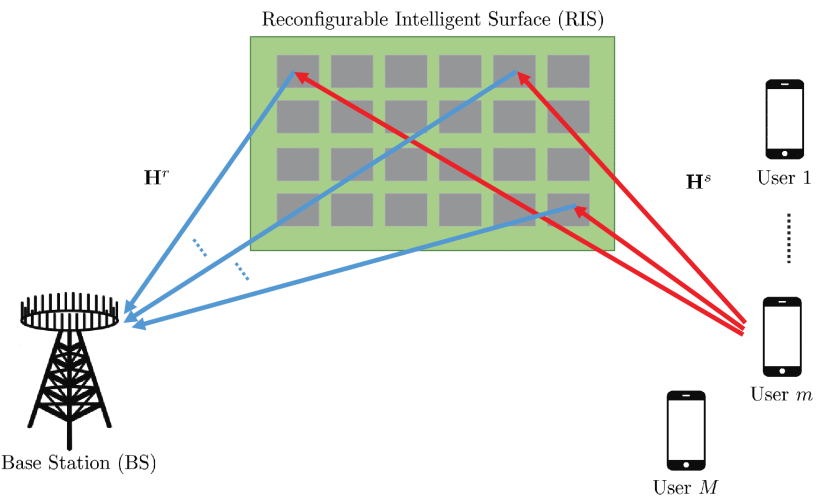
Fig. The considered RIS-empowered multi-user MISO communication system consisting of an K -antenna BS and M single-antenna mobile users.
领域四 可抵御分布式窃听攻击的安全时空调制毫米波无线链路
Secure space–time-modulated millimetre-wave wireless links that are resilient to distributed eavesdropper attacks
Suresh Venkatesh, etc.
Nature Electronics, 2021
As wireless networks move to millimetre-wave (mm-wave) and terahertz (THz) frequencies for 5G communications and beyond, ensuring security and resilience to eavesdropper attacks has become increasingly important. Traditional encryption methods are challenging to scale for high-bandwidth, ultralow-latency applications. An alternative approach is to use physical-layer techniques that rely on the physics of signal propagation to incorporate security features without the need for an explicit key exchange. Ensuring security through the use of directional, narrow-beam-like features of mm-wave/THz signals has proven to be vulnerable to passive eavesdroppers. Here we report a space-time modulation approach that ensures security by enforcing loss of information through selective spectral aliasing towards the direction of eavesdroppers, even though the channel can be physically static. This is achieved by using custom-designed spatio-temporal transmitter arrays realized in silicon chips with packaged antennas operating in the 71–76 GHz range. We also analytically and experimentally demonstrate the resilience of our links against distributed and synchronized eavesdropper attacks in the mm-wave band.
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41928-021-00664-z
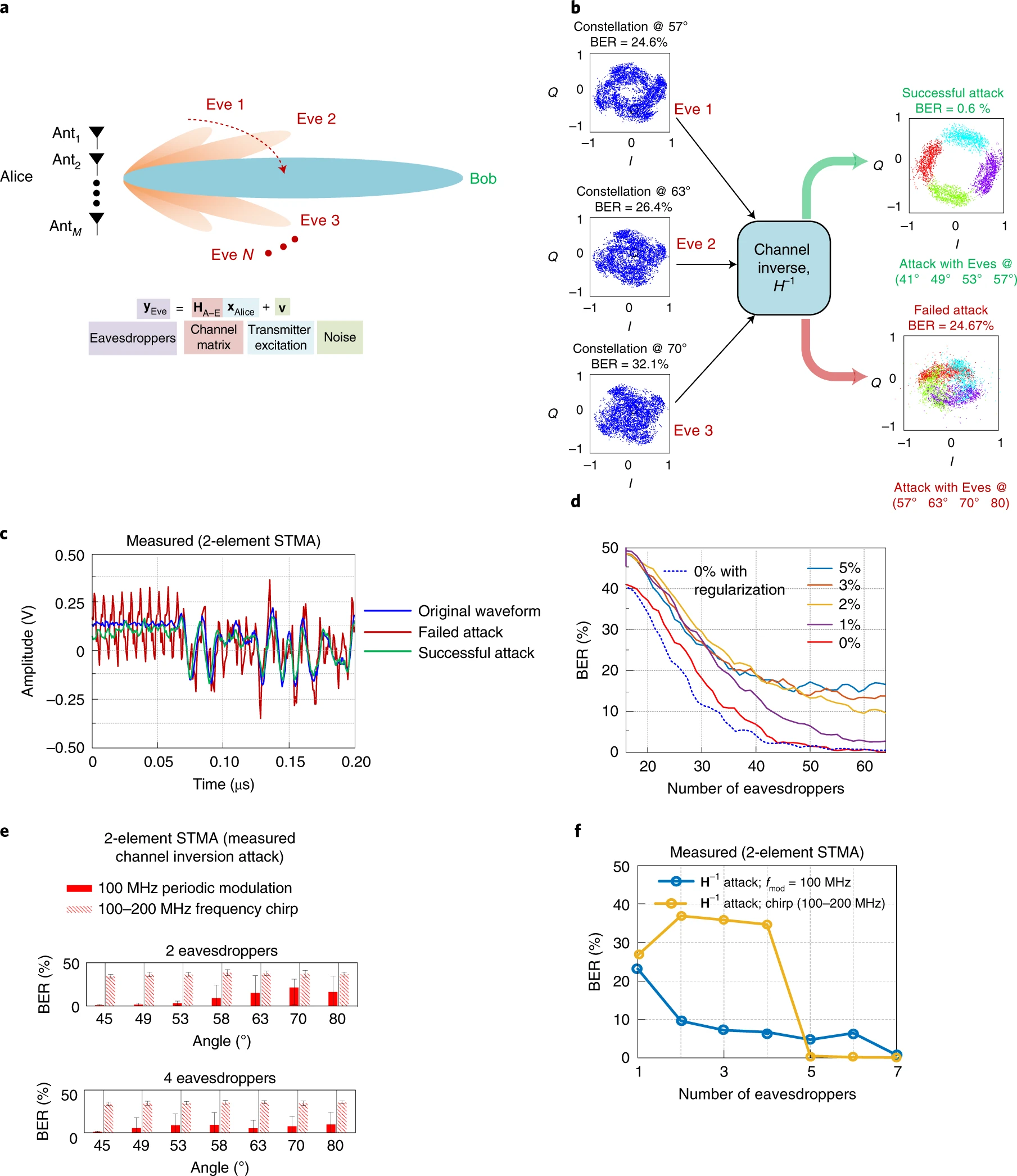
Fig. Measured resilience against a distributed and colluding eavesdropper attack with known channel (channel inversion attack) on the presented STMA in the 71–76 GHz range.
往期精彩推荐
前沿论文带您解读5G应用领域 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(2)
热点论文解读AI应用领域 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(3)
热点论文带您探究5G和未来通信——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务 (4)
前沿文献带您解读自然语言处理技术 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(5)
热点论文带您探究5G和未来通信材料技术领域 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(6)
热点论文解读AI应用领域 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(3)
热点论文带您探究5G和未来通信——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务 (4)
前沿文献带您解读自然语言处理技术 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(5)
热点论文带您探究5G和未来通信材料技术领域 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(6)
热点文献带您关注AI情感分类技术 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(7)
热点论文带您探究6G的无限可能——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(8)
热点文献带您关注AI文本摘要自动生成 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(9)
热点论文:5G/6G引领社会新进步——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(10)
热点文献带您关注AI机器翻译 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(11)
热点论文与您探讨5G/6G网络技术新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(12)
热点文献带您关注AI计算机视觉 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(13)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G的硬科技与新思路 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(14)
热点文献带您关注AI计算机视觉 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(15)
热点论文带您领略5G/6G的最新技术动向 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(18)
热点文献带您关注图神经网络——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(19)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G材料技术的最新发展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(20)
热点文献带您关注模式识别——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(21)
热点论文与带您领略6G网络技术的最新发展趋势 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(22)
热点文献带您关注机器学习与量子物理 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(23)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G通信器件材料的最新进展 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(24)
热点文献带您关注AI自动驾驶——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(25)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G网络安全和技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(26)
热点文献带您关注AI神经网络与忆阻器——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(27)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G电子器件和太赫兹方面的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(28)
热点文献带您关注AI与机器人——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(29)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G热点技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(30)
热点文献带您关注AI与触觉传感技术——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(31)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G热点技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(32)
热点文献带您关注AI深度学习与计算机视觉——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(33)
热点论文与带您领略未来通信的热点技术及最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(34)
热点文献带您关注AI强化学习——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(35)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G基础研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(36)
热点文献带您关注AI与边缘计算——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(37)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G领域热点研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(38)
热点文献带您关注AI技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(39)
热点论文与带您领略5G相关领域研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(40)
热点文献带您关注AI视觉跟踪——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(41)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在海空领域研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(42)
热点文献带您关注AI与医学研究——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(43)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在材料领域研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(44)
热点文献带您关注AI与医学图像——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(45)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在光电材料及信息编码领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(46)
热点文献带您关注AI与生物学——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(47)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在新材料技术领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(48)
热点文献带您关注AI与人脸识别——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(49)
热点论文带您领略光电半导体领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(50)
热点文献带您关注AI在集成电路领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(51)
热点论文带您领略半导体领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(52)
热点文献带您关注AI在光神经网络领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(53)