热点文献带您关注AI在集成电路领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(51)
2021-11-12
在上一期AI文献推荐中,我们为您推荐了人工智能在人脸识别研究方面的热点文献,包括基于深度神经网络的人脸识别高效逆向图形模型,用于高性能人脸检测的细化神经网络,一种对抗性学习策略的隐私保护神经网络特征表示方法,用于近红外可见光人脸识别的大规模多姿态高质量数据库等方面的文献。
本期我们为您选取了4篇文献,介绍AI在集成电路领域的热点文献,包括通过使用纳米级CMOS工艺在同一晶片上协同集成单晶体管神经元和突触来制造高度可扩展的类脑神经拟态硬件,一种用于高性能神经形态计算和神经网络剪枝的基于拓扑相变的模拟记忆突触,一种由包含片上内存的计算芯片网络组成的DNN推理系统,基于二维半导体光电二极管阵列神经网络图像传感器的超快机器视觉等文献,推送给相关领域的科研人员。
文献一 一种高度可扩展的类脑神经拟态硬件
Cointegration of single-transistor neurons and synapses by nanoscale CMOS fabrication for highly scalable neuromorphic hardware
Han, Joon-Kyu, etc.
SCIENCE ADVANCES, 2021, 7(32)
Cointegration of multistate single-transistor neurons and synapses was demonstrated for highly scalable neuromorphic hardware, using nanoscale complementary metal-oxide semiconductor (CMOS) fabrication. The neurons and synapses were integrated on the same plane with the same process because they have the same structure of a metal-oxide semiconductor field-effect transistor with different functions such as homotype. By virtue of 100% CMOS compatibility, it was also realized to cointegrate the neurons and synapses with additional CMOS circuits. Such cointegration can enhance packing density, reduce chip cost, and simplify fabrication procedures. The multistate single-transistor neuron that can control neuronal inhibition and the firing threshold voltage was achieved for an energy-efficient and reliable neural network. Spatiotemporal neuronal functionalities are demonstrated with fabricated single-transistor neurons and synapses. Image processing for letter pattern recognition and face image recognition is performed using experimental-based neuromorphic simulation.
阅读原文 https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/sciadv.abg8836
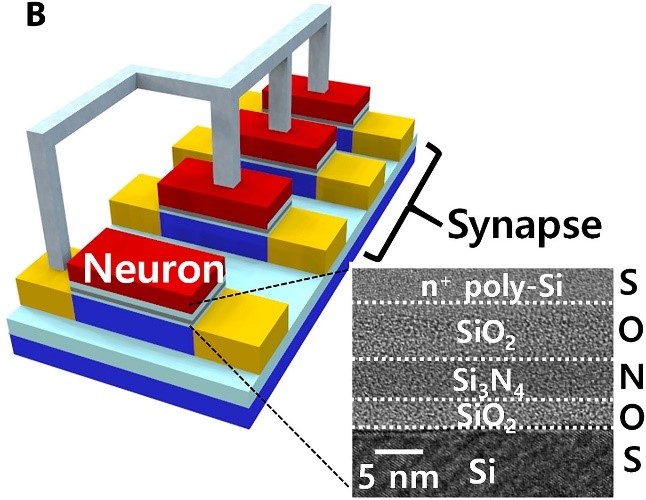
Schematic of cointegrated single-transistor neurons and synapses
文献二 用于神经形态计算和神经网络剪枝的基于拓扑相变的模拟记忆突触
Analog memristive synapse based on topotactic phase transition for high-performance neuromorphic computing and neural network pruning
Mou, Xing, etc.
SCIENCE ADVANCES, 2021, 7(29)
Inspired by the human brain, nonvolatile memories (NVMs)-based neuromorphic computing emerges as a promising paradigm to build power-efficient computing hardware for artificial intelligence. However, existing NVMs still suffer from physically imperfect device characteristics. In this work, a topotactic phase transition random-access memory (TPT-RAM) with a unique diffusive nonvolatile dual mode based on SrCoOx is demonstrated. The reversible phase transition of SrCoOx is well controlled by oxygen ion migrations along the highly ordered oxygen vacancy channels, enabling reproducible analog switching characteristics with reduced variability. Combining density functional theory and kinetic Monte Carlo simulations, the orientation-dependent switching mechanism of TPT-RAM is investigated synergistically. Furthermore, the dual-mode TPT-RAM is used to mimic the selective stabilization of developing synapses and implement neural network pruning, reducing similar to 84.2% of redundant synapses while improving the image classification accuracy to 99%. Our work points out a new direction to design bioplausible memristive synapses for neuromorphic computing.
阅读原文 https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/sciadv.abh0648
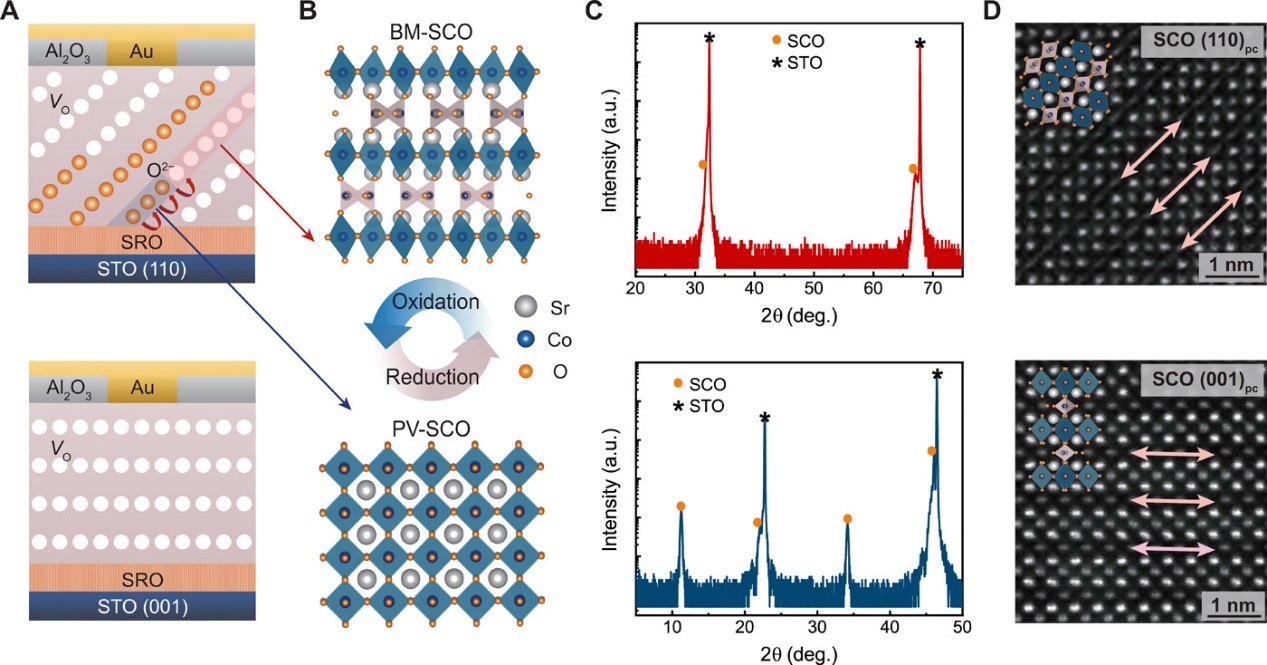
Design of the SCO-based TPT-RAM synaptic devices
文献三 一种由计算芯片网络组成的DNN推理系统
Illusion of large on-chip memory by networked computing chips for neural network inference
Radway, Robert M., etc.
NATURE ELECTRONICS, 2021, 4(1): 71-80
Hardware for deep neural network (DNN) inference often suffers from insufficient on-chip memory, thus requiring accesses to separate memory-only chips. Such off-chip memory accesses incur considerable costs in terms of energy and execution time. Fitting entire DNNs in on-chip memory is challenging due, in particular, to the physical size of the technology. Here, we report a DNN inference system-termed Illusion-that consists of networked computing chips, each of which contains a certain minimal amount of local on-chip memory and mechanisms for quick wakeup and shutdown. An eight-chip Illusion system hardware achieves energy and execution times within 3.5% and 2.5%, respectively, of an ideal single chip with no off-chip memory. Illusion is flexible and configurable, achieving near-ideal energy and execution times for a wide variety of DNN types and sizes. Our approach is tailored for on-chip non-volatile memory with resilience to permanent write failures, but is applicable to several memory technologies. Detailed simulations also show that our hardware results could be scaled to 64-chip Illusion systems.
阅读原文 https://www.nature.com/articles/s41928-020-00515-3

Illusion system consists of a network of multiple DNN chips on an inter-chip network
文献四 基于二维材料神经网络图像传感器的超快机器视觉
Ultrafast machine vision with 2D material neural network image sensors
Mennel, Lukas, etc.
NATURE, 2020, 579(7797): 62-66
Machine vision technology has taken huge leaps in recent years, and is now becoming an integral part of various intelligent systems, including autonomous vehicles and robotics. Usually, visual information is captured by a frame-based camera, converted into a digital format and processed afterwards using a machine-learning algorithm such as an artificial neural network (ANN)(1). The large amount of (mostly redundant) data passed through the entire signal chain, however, results in low frame rates and high power consumption. Various visual data preprocessing techniques have thus been developed(2-7) to increase the efficiency of the subsequent signal processing in an ANN. Here we demonstrate that an image sensor can itself constitute an ANN that can simultaneously sense and process optical images without latency. Our device is based on a reconfigurable two-dimensional (2D) semiconductor(8,9) photodiode(10-12) array, and the synaptic weights of the network are stored in a continuously tunable photoresponsivity matrix. We demonstrate both supervised and unsupervised learning and train the sensor to classify and encode images that are optically projected onto the chip with a throughput of 20 million bins per second.
阅读原文 https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-020-2038-x

往期精彩推荐
前沿论文带您解读5G应用领域 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(2)
热点论文解读AI应用领域 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(3)
热点论文带您探究5G和未来通信——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务 (4)
前沿文献带您解读自然语言处理技术 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(5)
热点论文带您探究5G和未来通信材料技术领域 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(6)
热点论文解读AI应用领域 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(3)
热点论文带您探究5G和未来通信——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务 (4)
前沿文献带您解读自然语言处理技术 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(5)
热点论文带您探究5G和未来通信材料技术领域 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(6)
热点文献带您关注AI情感分类技术 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(7)
热点论文带您探究6G的无限可能——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(8)
热点文献带您关注AI文本摘要自动生成 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(9)
热点论文:5G/6G引领社会新进步——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(10)
热点文献带您关注AI机器翻译 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(11)
热点论文与您探讨5G/6G网络技术新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(12)
热点文献带您关注AI计算机视觉 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(13)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G的硬科技与新思路 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(14)
热点文献带您关注AI计算机视觉 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(15)
热点论文带您领略5G/6G的最新技术动向 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(18)
热点文献带您关注图神经网络——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(19)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G材料技术的最新发展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(20)
热点文献带您关注模式识别——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(21)
热点论文与带您领略6G网络技术的最新发展趋势 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(22)
热点文献带您关注机器学习与量子物理 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(23)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G通信器件材料的最新进展 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(24)
热点文献带您关注AI自动驾驶——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(25)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G网络安全和技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(26)
热点文献带您关注AI神经网络与忆阻器——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(27)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G电子器件和太赫兹方面的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(28)
热点文献带您关注AI与机器人——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(29)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G热点技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(30)
热点文献带您关注AI与触觉传感技术——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(31)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G热点技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(32)
热点文献带您关注AI深度学习与计算机视觉——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(33)
热点论文与带您领略未来通信的热点技术及最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(34)
热点文献带您关注AI强化学习——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(35)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G基础研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(36)
热点文献带您关注AI与边缘计算——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(37)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G领域热点研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(38)
热点文献带您关注AI技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(39)
热点论文与带您领略5G相关领域研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(40)
热点文献带您关注AI视觉跟踪——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(41)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在海空领域研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(42)
热点文献带您关注AI与医学研究——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(43)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在材料领域研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(44)
热点文献带您关注AI与医学图像——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(45)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在光电材料及信息编码领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(46)
热点文献带您关注AI与生物学——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(47)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在新材料技术领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(48)
热点文献带您关注AI与人脸识别——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(49)
热点论文带您领略光电半导体领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(50)