热点论文带您探索新型网络架构以及超表面在未来通信中的应用——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(66)
2022-05-25

在第62期前沿文献中推荐中,介绍了智能化以及超表面在未来通信中的应用,包括:基于数字编码超表面阵列的可编程衍射深度神经网络,用于 5G 应用的基于VO2的超可重构智能反射面,面向未来超 5G、6G 和超级物联网应用的效应曲面法优化 RF-MEMS 可重构器件的开发,基于无线信号的人工智能。
在本期的文献推荐中,关注点着眼于新型网络架构以及超表面在未来通信中的应用,选取了:极高可靠和低延迟通信,基于瓷片可拓宽MIMO以及相控阵的5G/B5G智能相控阵和智能可重配表面,借助超材料单元实现的BiCMOS片上亚太赫兹天线增益增强,用于毫米波领域的高性价比宽带介质平面透镜天线四篇文献,供相关领域的科研人员参考。
领域一 极高可靠和低延迟通信
Extreme ultra-reliable and low-latency communication
Jihong Park, etc.
Nature Electronics, 2022, 5:133-141
Ultra-reliable and low-latency communication (URLLC) is central to fifth-generation (5G) communication systems, but the fundamentals of URLLC remain elusive. New immersive and high-stake control applications with stricter reliability, latency and scalability requirements are now also creating unprecedented challenges for URLLC. Here we examine the limitations of 5G URLLC and propose key research directions for the next generation of URLLC, which we term extreme ultra-reliable and low-latency communication (xURLLC). xURLLC is underpinned by three concepts: the leveraging of recent advances in machine learning for faster and more reliable data-driven predictions; complementing radiofrequency signal transmission with non-radiofrequency data and passive signal reflection to combat rare events at scale; emphasizing joint communication and control co-design, as opposed to the communication-centric approach of 5G URLLC. For each of these concepts, we consider the challenges and opportunities, and illustrate the effectiveness of the proposed solutions through selected use cases.
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41928-022-00728-8
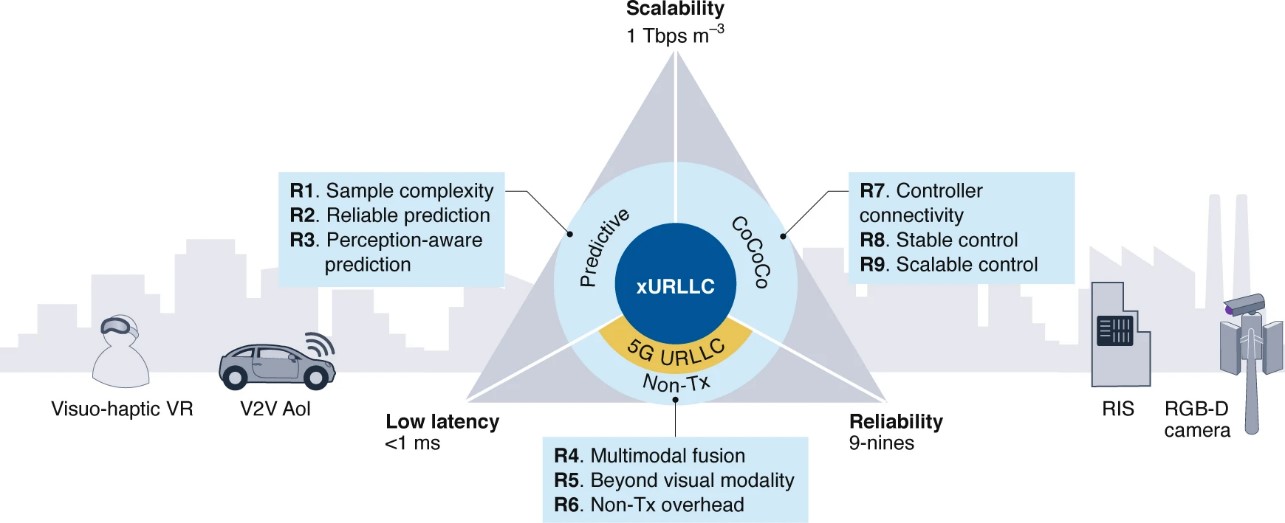
Fig. Anatomy of xURLLC with key research challenges and opportunities, R1–R9.
领域二 基于瓷片可拓宽MIMO以及相控阵的5G/B5G智能相控阵和智能可重配表面
Tile-based massively scalable MIMO and phased arrays for 5G/B5G-enabled smart skins and reconfigurable intelligent surfaces
Xuanke He, etc.
Scientific Reports, 2022, 12
This work presents a novel tile based approach to constructing, in a modular fashion, massively scalable MIMO and phased arrays for 5G/B5G millimeter-wave smart skins and large-area reconfigurable intelligent surfaces for Smart Cities and IoT applications. A proof-of-concept 29 GHz 32 elements phased array utilizing 2×2 “8-element subarray” tiles was fabricated and measured and demonstrates +/− 30beamsteering capability. The unique benefits of the proposed tile approach utilizes the fact that tiles of identical sizes can be manufactured in large quantities rather than have arrays of multiple sizes serve various user capacity coverage areas. It has to be stressed that the proof-of-concept flexible 2×2 tile array features no performance degradation when it is wrapped around a 3.5 cm radius curvature. This topology can be easily scaled up to massively large arrays by simply adding more tiles and extending the feeding network on the mounting tiling layer. The tiles are assembled onto a single flexible substrate which interconnects the RF, DC and digital traces, allowing for the easy realization of on-demand very large antenna arrays on virtually any practical conformal platform for frequencies up to sub-THz frequency range.
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-022-06096-9
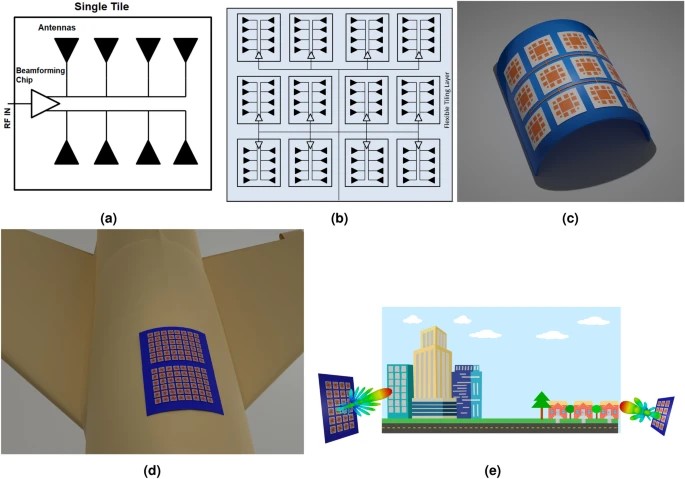
Fig. Design architecture and applications
领域三 借助超材料单元实现的BiCMOS片上亚太赫兹天线增益增强
Gain enhancement of BiCMOS on-chip sub-THz antennas by mean of meta-cells
Matteo Stocchi, etc.
Scientific Reports, 2022, 12
A MM-loaded sub-THz on-chip antenna with a narrow beamwidth, 9 dB gain and a simulated peak efficiency of 76% at the center frequency of 300 GHz is presented. By surrounding the antenna with a single MM-cell ring defined solely on the top metal of the back-end of line, an efficient suppression of the surface waves is obtained. The on-chip antenna has been designed using IHPs 130 nm SiGe BiCMOS technology with a 7-layer metallization stack, combined with the local backside etching process aimed to creating an air cavity which is then terminated by a reflective plane. By comparing the measured MM-loaded antenna performances to its non-MM-loaded counterpart, an enhanced integrity of the main lobe due to the MM-cells shielding effect can be observed. An excellent agreement between the simulated and measured performances has been found, which makes the MM-loaded antennas a valid alternative for the upcoming next-generation sub-THz transceivers.
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-022-07902-0

Fig. The fabricated MM-loaded and non-MM-loaded antennas.
领域四 用于毫米波领域的高性价比宽带介质平面透镜天线
Cost-effective wideband dielectric planar lens antenna for millimeter wave applications
José-Manuel Poyanco, etc.
Scientific Reports, 2022, 12
This article presents a fully 3D-printed dielectric planar lens operating in the entire Ka-band manufactured using additive manufacturing and a relatively low-cost 3D-printer. The lens consists of ten concentric rings implemented using low-loss ABS filaments with high permittivity values. By varying the infill percentages of them the required refractive indexes of each section are achieved. An additional 3D-printed matching layer, using the same manufacturing and design method was included in the lens, to reduce reflections. Simulation and measurement results show a very good agreement, which confirms the possibility of manufacturing a cost-effective broadband and planar lens solution operating in millimeter wave bands, where Low Earth Orbit Satellites (LEO) networks, future mobile communication systems (5G, 6G) and radar systems operate.
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-022-07911-z
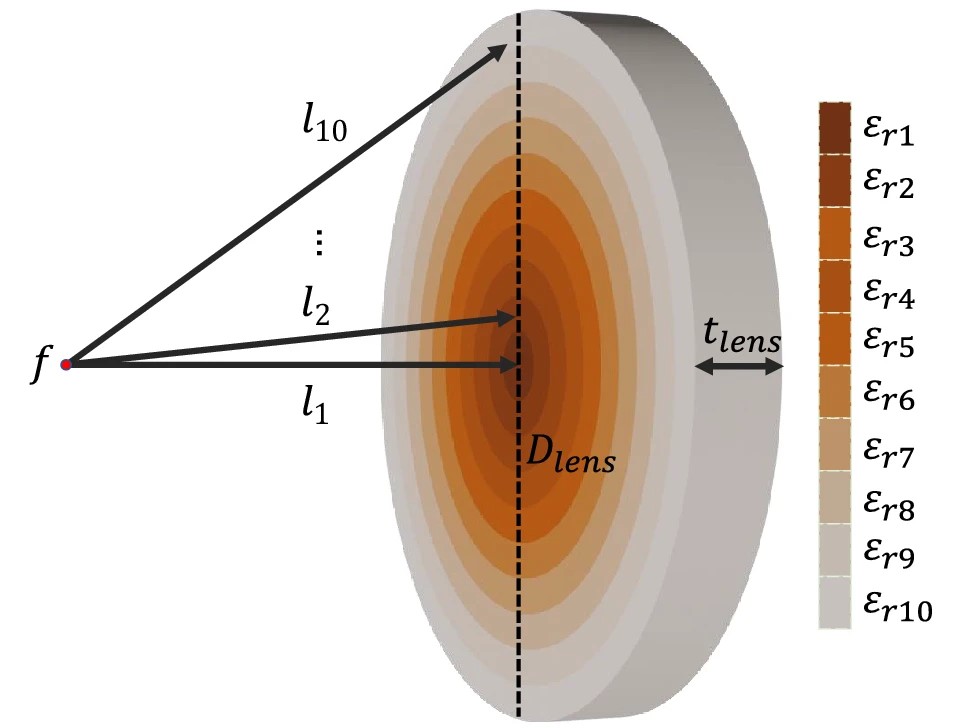
Fig. Proposed Graded Index (GRIN) planar lens antenna
往期精彩推荐
前沿论文带您解读5G应用领域 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(2)
热点论文解读AI应用领域 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(3)
热点论文带您探究5G和未来通信——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务 (4)
前沿文献带您解读自然语言处理技术 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(5)
热点论文带您探究5G和未来通信材料技术领域 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(6)
热点论文解读AI应用领域 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(3)
热点论文带您探究5G和未来通信——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务 (4)
前沿文献带您解读自然语言处理技术 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(5)
热点论文带您探究5G和未来通信材料技术领域 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(6)
热点文献带您关注AI情感分类技术 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(7)
热点论文带您探究6G的无限可能——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(8)
热点文献带您关注AI文本摘要自动生成 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(9)
热点论文:5G/6G引领社会新进步——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(10)
热点文献带您关注AI机器翻译 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(11)
热点论文与您探讨5G/6G网络技术新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(12)
热点文献带您关注AI计算机视觉 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(13)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G的硬科技与新思路 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(14)
热点文献带您关注AI计算机视觉 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(15)
热点论文带您领略5G/6G的最新技术动向 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(18)
热点文献带您关注图神经网络——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(19)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G材料技术的最新发展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(20)
热点文献带您关注模式识别——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(21)
热点论文与带您领略6G网络技术的最新发展趋势 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(22)
热点文献带您关注机器学习与量子物理 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(23)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G通信器件材料的最新进展 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(24)
热点文献带您关注AI自动驾驶——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(25)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G网络安全和技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(26)
热点文献带您关注AI神经网络与忆阻器——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(27)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G电子器件和太赫兹方面的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(28)
热点文献带您关注AI与机器人——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(29)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G热点技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(30)
热点文献带您关注AI与触觉传感技术——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(31)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G热点技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(32)
热点文献带您关注AI深度学习与计算机视觉——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(33)
热点论文与带您领略未来通信的热点技术及最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(34)
热点文献带您关注AI强化学习——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(35)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G基础研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(36)
热点文献带您关注AI与边缘计算——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(37)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G领域热点研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(38)
热点文献带您关注AI技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(39)
热点论文与带您领略5G相关领域研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(40)
热点文献带您关注AI视觉跟踪——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(41)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在海空领域研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(42)
热点文献带您关注AI与医学研究——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(43)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在材料领域研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(44)
热点文献带您关注AI与医学图像——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(45)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在光电材料及信息编码领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(46)
热点文献带您关注AI与生物学——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(47)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在新材料技术领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(48)
热点文献带您关注AI与人脸识别——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(49)
热点论文带您领略光电半导体领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(50)
热点文献带您关注AI在集成电路领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(51)
热点论文带您领略半导体领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(52)
热点文献带您关注AI在光神经网络领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(53)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在新材料技术领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(54)
热点文献带您关注AI深度神经网络的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(55)
热点论文带您领略新材料半导体领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(56)
热点文献带您关注AI视频动作识别的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(57)
热点论文带您领略未来通信热点技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(58)
热点文献带您关注AI深度学习的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(59)
热点论文带您领略未来通信研究热点的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(60)
热点文献带您关注AI领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(61)
热点论文带您探索智能化以及超表面在未来通信中的应用——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(62)
热点文献带您关注AI领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(63)
热点论文带您领略半导体领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(64)
热点文献带您关注AI领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(65)