热点论文带您探索智能化以及超表面在未来通信中的应用——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(62)
2022-04-11

在上一期前沿文献中推荐中,介绍了未来通信的研究热点,包括:智简无线网络理论与技术,低轨卫星通信遥感融合:架构、技术与试验,用于5G通信的紧凑型二元MIMO天线,以及适用于72.5-81GHz频率范围片上应用的一种基于超材料的新型天线。
在本期的文献推荐中,关注点着眼于智能化以及超表面在未来通信中的应用,选取了:基于数字编码超表面阵列的可编程衍射深度神经网络、用于 5G 应用的基于VO2的超可重构智能反射面、面向未来超 5G、6G 和超级物联网应用的效应曲面法优化 RF-MEMS 可重构器件的开发、基于无线信号的人工智能四篇文献,供相关领域的科研人员参考。
领域一 基于数字编码超表面阵列的可编程衍射深度神经网络
A programmable diffractive deep neural network based on a digital-coding metasurface array
Che Liu, etc.
Nature Electronics, 2022, 5:113-122
The development of artificial intelligence is typically focused on computer algorithms and integrated circuits. Recently, all-optical diffractive deep neural networks have been created that are based on passive structures and can perform complicated functions designed by computer-based neural networks. However, once a passive diffractive deep neural network architecture is fabricated, its function is fixed. Here we report a programmable diffractive deep neural network that is based on a multi-layer digital-coding metasurface array. Each meta-atom on the metasurfaces is integrated with two amplifier chips and acts an active artificial neuron, providing a dynamic modulation range of 35 dB (from −22 dB to 13 dB). We show that the system, which we term a programmable artificial intelligence machine, can handle various deep learning tasks for wave sensing, including image classification, mobile communication coding–decoding and real-time multi-beam focusing. We also develop a reinforcement learning algorithm for on-site learning and a discrete optimization algorithm for digital coding.
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41928-022-00719-9
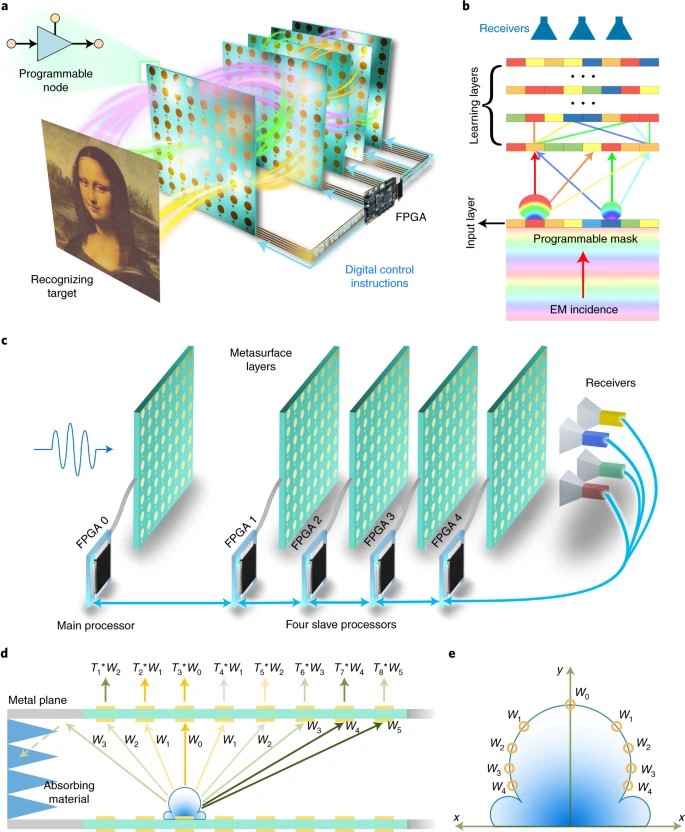
Fig. A reprogrammable D2NN platform
领域二 用于 5G 应用的基于VO2的超可重构智能反射面
VO2-based ultra-reconfigurable intelligent reflective surface for 5G applications
Randy Matos, etc.
Scientific Reports, 2022, 12
As demand for higher capacity wireless communications increases, new approaches are needed to improve capacity. The lack of configurable radio platforms and power consumed to create new signals are some of the limitations preventing further advancements. To address these limitations, we propose an Ultra-Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface (URIS) platform based on the metal-to-insulator transition property of VO2. A VO2 layer is placed on a high-density micro-heater matrix consisting of pixels that can be electronically switched on. With this manner of control, heat can be transferred to selected areas of the VO2 layer and convert it to highly conductive metallic phase. This technique allows dynamically changing the shape of the reflection surface with high speed. We numerically investigated the heat activated switching and RF reflection characteristics of a reflectarray designed for potential 5G applications operating at 32 GHz. It consists of heating pixels with the size of 40 × 40 μm which can generate metallic VO2 patches or arbitrary shapes with ~ 100 × 100 μm spatial resolution. Our analyses resulted in large phase range of ~ 300° and approximate losses of −2 dB. The proposed device can serve as a novel platform for ultra-reconfigurable reflectarrays, other IRSs, and various wide spectral range RF applications.
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-022-08458-9
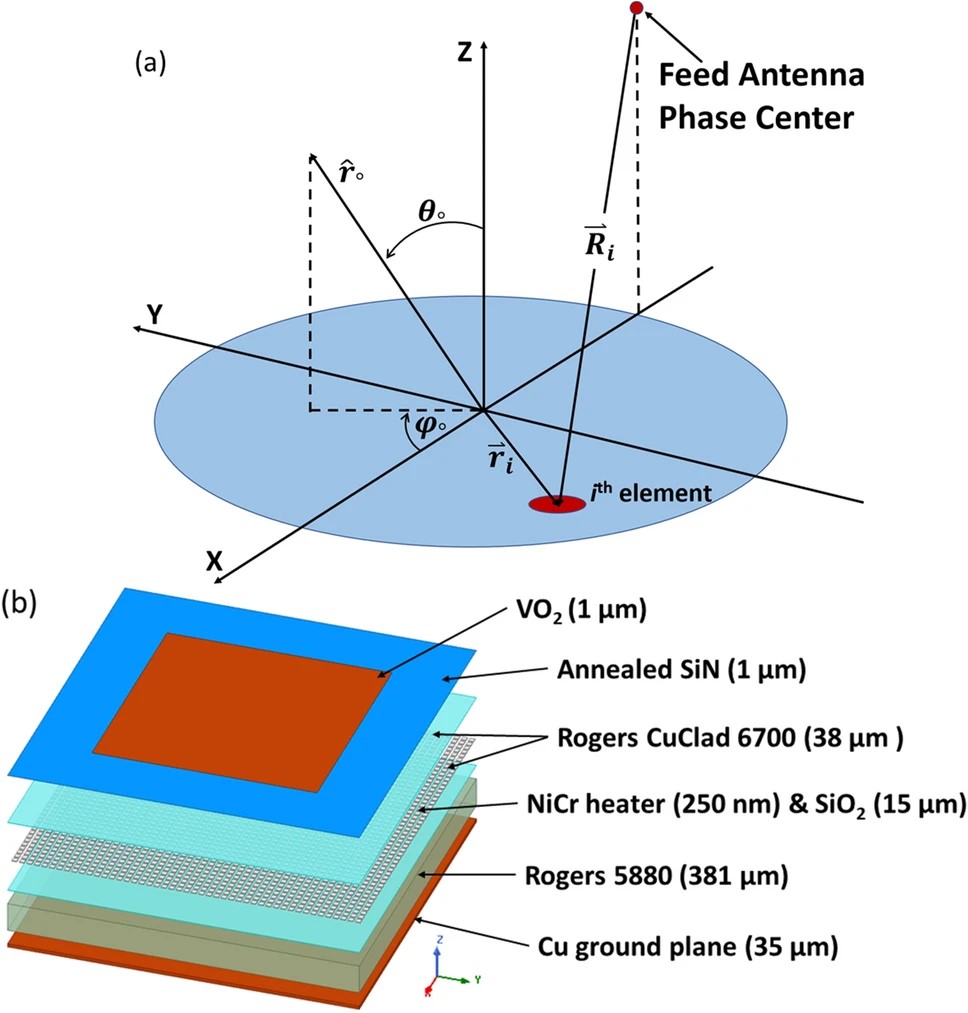
Fig. (a) Diagram describing differential spatial phase delay of a reflectarray.
(b) Exploded device structure with materials.
领域三 面向未来超 5G、6G 和超级物联网应用的效应曲面法优化 RF-MEMS 可重构器件的开发
Exploitation of response surface method for the optimization of RF-MEMS reconfigurable devices in view of future beyond-5G, 6G and super-IoT applications
Jacopo Iannacci, etc.
Scientific Reports, 2022, 12
The emerging paradigms of the Beyond-5G, 6G and Super-IoT will demand for high-performance Radio Frequency (RF) passive components, and RF-MEMS technology, i.e. Microsystems-based RF passives, is a good candidate to meet such a challenge. As known, RF-MEMS have a complex behavior, that crosses different physical domains (mechanical; electrical; electromagnetic), making the whole design optimization and trimming phases particularly articulated and time consuming. In this work, we propose a novel design optimization approach based on the Response Surface Method (RSM) statistical methodology, focusing on a class of RF-MEMS-based programmable step power attenuators. The proposed method is validated both against physical simulations, performed with Finite Element Method (FEM) commercial software tools, as well as experimental measurements of physical devices. The case study here discussed features 3 DoFs (Degrees of Freedom), comprising both geometrical and material parameters, and aims to optimize the RF performances of the MEMS attenuator in terms of attenuation (S21 Scattering parameter) and reflection (VSWR—Voltage Standing Wave Ratio). When validated, the proposed RSM-based method allows avoiding physical FEM simulations, thus making the design optimization considerably faster and less complex, both in terms of time and computational load.
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-022-07643-0
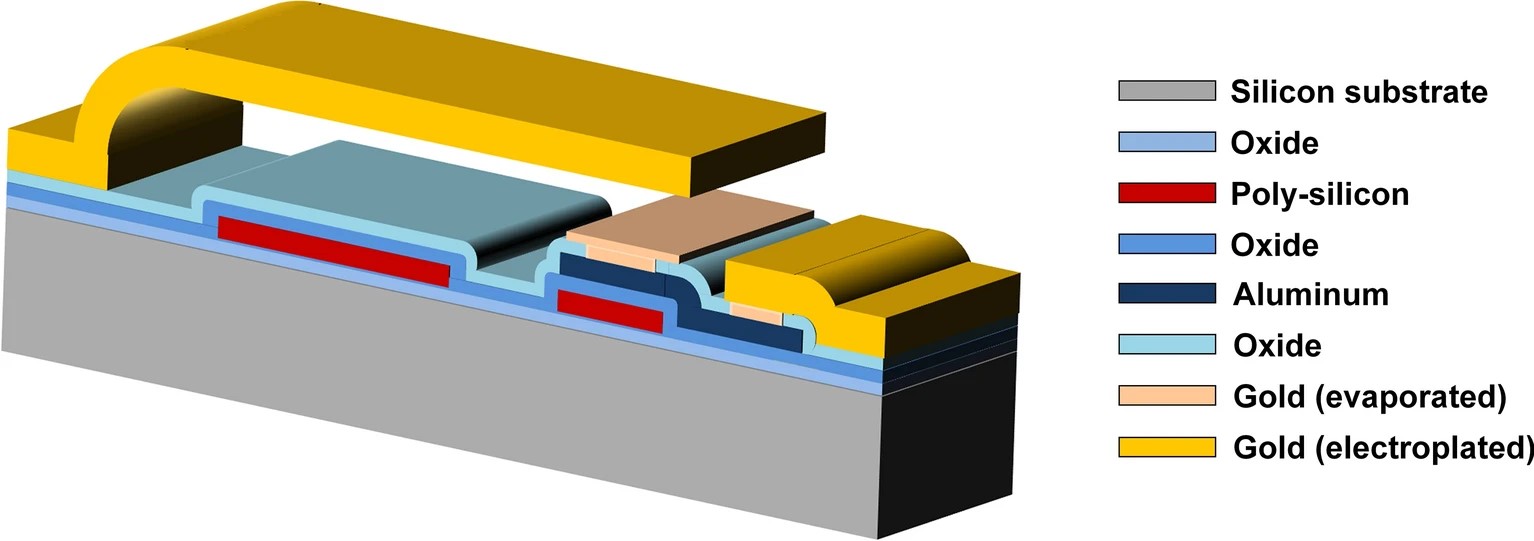
Fig. Cross-section of the RF-MEMS technology employed in this study. Image created with Microsoft Office 365 PowerPoint
领域四 基于无线信号的人工智能
Artificial intelligence built on wireless signals
Xing Lin, etc.
Nature Electronics, 2022, 5
Multi-layer programmable metasurfaces can be used to construct diffractive neural networks in which radio waves are directly processed.
Wireless sensing and communication technology is a dominant feature of modern life — from mobile phones to broadcast television to wireless networks — and is based on the manipulation of radio waves1, electromagnetic waves with frequencies ranging from 30 Hz to 300 GHz. Processing the information carried by radio waves typically requires converting them into electronic signals and computing with electronic processors. However, the increasing demand for high-speed sensing and high-throughput transmission creates challenges for such an approach, and alternative techniques will be required to effectively process radio-wave signals in the next generation of wireless sensing and communication systems.
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41928-022-00724-y
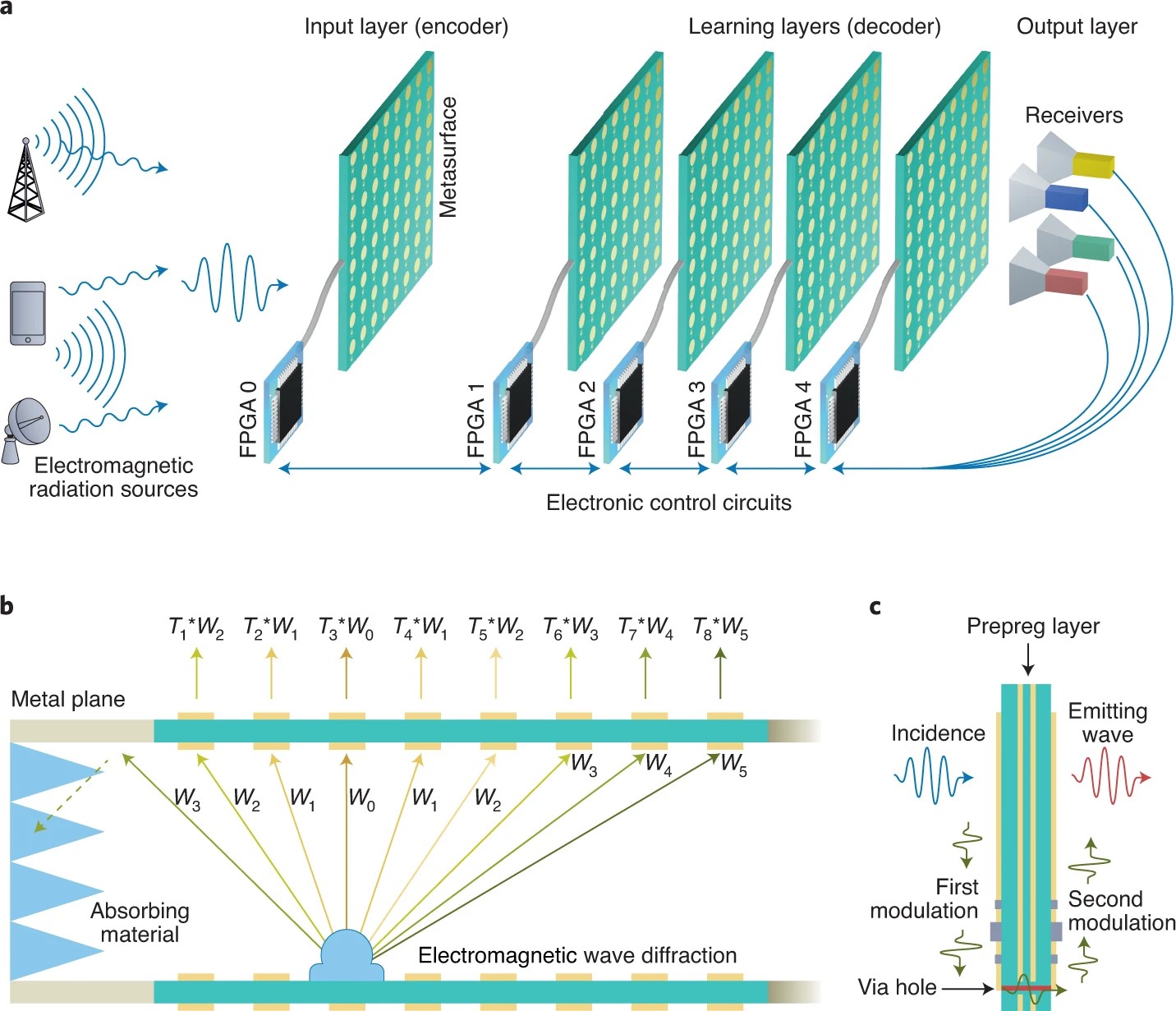
Fig. The PAIM architecture
往期精彩推荐
前沿论文带您解读5G应用领域 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(2)
热点论文解读AI应用领域 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(3)
热点论文带您探究5G和未来通信——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务 (4)
前沿文献带您解读自然语言处理技术 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(5)
热点论文带您探究5G和未来通信材料技术领域 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(6)
热点论文解读AI应用领域 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(3)
热点论文带您探究5G和未来通信——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务 (4)
前沿文献带您解读自然语言处理技术 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(5)
热点论文带您探究5G和未来通信材料技术领域 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(6)
热点文献带您关注AI情感分类技术 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(7)
热点论文带您探究6G的无限可能——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(8)
热点文献带您关注AI文本摘要自动生成 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(9)
热点论文:5G/6G引领社会新进步——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(10)
热点文献带您关注AI机器翻译 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(11)
热点论文与您探讨5G/6G网络技术新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(12)
热点文献带您关注AI计算机视觉 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(13)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G的硬科技与新思路 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(14)
热点文献带您关注AI计算机视觉 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(15)
热点论文带您领略5G/6G的最新技术动向 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(18)
热点文献带您关注图神经网络——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(19)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G材料技术的最新发展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(20)
热点文献带您关注模式识别——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(21)
热点论文与带您领略6G网络技术的最新发展趋势 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(22)
热点文献带您关注机器学习与量子物理 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(23)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G通信器件材料的最新进展 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(24)
热点文献带您关注AI自动驾驶——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(25)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G网络安全和技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(26)
热点文献带您关注AI神经网络与忆阻器——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(27)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G电子器件和太赫兹方面的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(28)
热点文献带您关注AI与机器人——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(29)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G热点技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(30)
热点文献带您关注AI与触觉传感技术——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(31)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G热点技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(32)
热点文献带您关注AI深度学习与计算机视觉——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(33)
热点论文与带您领略未来通信的热点技术及最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(34)
热点文献带您关注AI强化学习——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(35)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G基础研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(36)
热点文献带您关注AI与边缘计算——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(37)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G领域热点研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(38)
热点文献带您关注AI技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(39)
热点论文与带您领略5G相关领域研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(40)
热点文献带您关注AI视觉跟踪——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(41)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在海空领域研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(42)
热点文献带您关注AI与医学研究——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(43)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在材料领域研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(44)
热点文献带您关注AI与医学图像——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(45)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在光电材料及信息编码领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(46)
热点文献带您关注AI与生物学——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(47)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在新材料技术领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(48)
热点文献带您关注AI与人脸识别——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(49)
热点论文带您领略光电半导体领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(50)
热点文献带您关注AI在集成电路领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(51)
热点论文带您领略半导体领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(52)
热点文献带您关注AI在光神经网络领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(53)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在新材料技术领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(54)
热点文献带您关注AI深度神经网络的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(55)
热点论文带您领略新材料半导体领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(56)
热点文献带您关注AI视频动作识别的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(57)
热点论文带您领略未来通信热点技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(58)
热点文献带您关注AI深度学习的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(59)
热点论文带您领略未来通信研究热点的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(60)
热点文献带您关注AI领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(61)