热点文献带您关注AI深度学习的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(59)
2022-03-07

在上一期AI文献推荐中,我们为您推荐了视频动作识别的热点文献,包括野生灵长类动物行为的自动化视听动作识别,基于多任务深度学习的实时三维人体姿态估计和动作识别,在缺乏上下文的情况下基于单个时间卷积浅神经网络的动作识别,基于骨骼的人类动作识别等方面的文献。
在中科院与科睿唯安发布的《2021研究前沿》报告中,与深度学习相关的主题占据了信息科学领域Top 10热点前沿的大部分主题。本期我们为您选取了4篇文献,介绍深度学习的热点文献。包括通过深度学习预测未知原发性癌症的起源,基于贝叶斯深度学习的晶体结构识别方法,基于深度学习的步态识别,面向手绘素描数据的深度学习技术及其应用,推送给相关领域的科研人员。
文献一 通过深度学习预测未知原发性癌症的起源
AI-based pathology predicts origins for cancers of unknown primary
Lu, Ming Y., etc.
NATURE, 2021, 594(7861): 106-110
Cancer of unknown primary (CUP) origin is an enigmatic group of diagnoses in which the primary anatomical site of tumour origin cannot be determined(1,2). This poses a considerable challenge, as modern therapeutics are predominantly specific to the primary tumour(3). Recent research has focused on using genomics and transcriptomics to identify the origin of a tumour(4-9). However, genomic testing is not always performed and lacks clinical penetration in low-resource settings. Here, to overcome these challenges, we present a deep-learning-based algorithm-Tumour Origin Assessment via Deep Learning (TOAD)-that can provide a differential diagnosis for the origin of the primary tumour using routinely acquired histology slides. We used whole-slide images of tumours with known primary origins to train a model that simultaneously identifies the tumour as primary or metastatic and predicts its site of origin. On our held-out test set of tumours with known primary origins, the model achieved a top-1 accuracy of 0.83 and a top-3 accuracy of 0.96, whereas on our external test set it achieved top-1 and top-3 accuracies of 0.80 and 0.93, respectively. We further curated a dataset of 317 cases of CUP for which a differential diagnosis was assigned. Our model predictions resulted in concordance for 61% of cases and a top-3 agreement of 82%. TOAD can be used as an assistive tool to assign a differential diagnosis to complicated cases of metastatic tumours and CUPs and could be used in conjunction with or in lieu of ancillary tests and extensive diagnostic work-ups to reduce the occurrence of CUP.
阅读原文:https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-021-03512-4
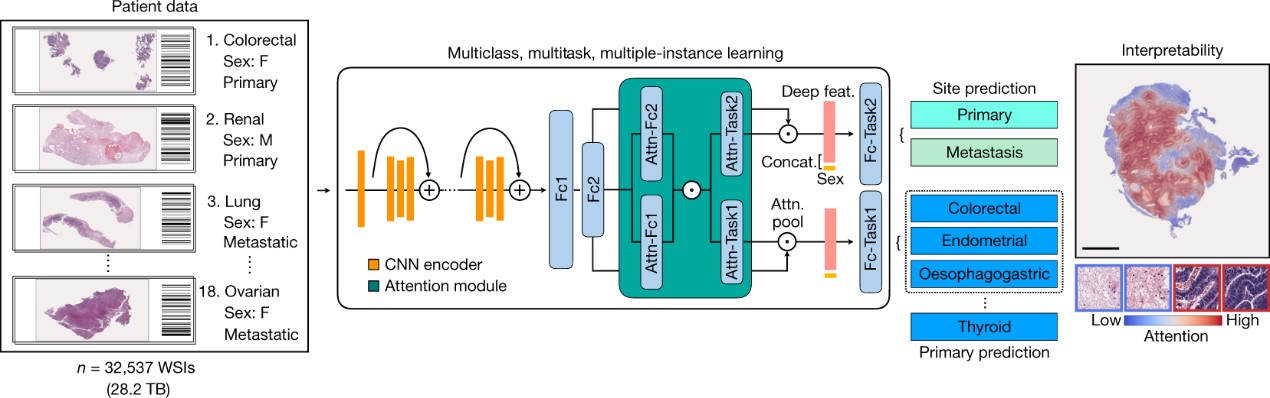
Tumour Origin Assessment via Deep Learning (TOAD) workflow
文献二 基于贝叶斯深度学习的晶体结构识别方法
Robust recognition and exploratory analysis of crystal structures via Bayesian deep learning
Leitherer, Andreas, etc.
NATURE COMMUNICATIONS, 2021, 12(1)
The present manuscript reports a Bayesian deep-learning approach for the automatic, robust classification of polycrystalline systems of both synthetic and experimental origin. The unsupervised analysis of the internal neural-network representations reveals physically understandable patterns.
Due to their ability to recognize complex patterns, neural networks can drive a paradigm shift in the analysis of materials science data. Here, we introduce ARISE, a crystal-structure identification method based on Bayesian deep learning. As a major step forward, ARISE is robust to structural noise and can treat more than 100 crystal structures, a number that can be extended on demand. While being trained on ideal structures only, ARISE correctly characterizes strongly perturbed single- and polycrystalline systems, from both synthetic and experimental resources. The probabilistic nature of the Bayesian-deep-learning model allows to obtain principled uncertainty estimates, which are found to be correlated with crystalline order of metallic nanoparticles in electron tomography experiments. Applying unsupervised learning to the internal neural-network representations reveals grain boundaries and (unapparent) structural regions sharing easily interpretable geometrical properties. This work enables the hitherto hindered analysis of noisy atomic structural data from computations or experiments.
阅读原文:https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-021-26511-5
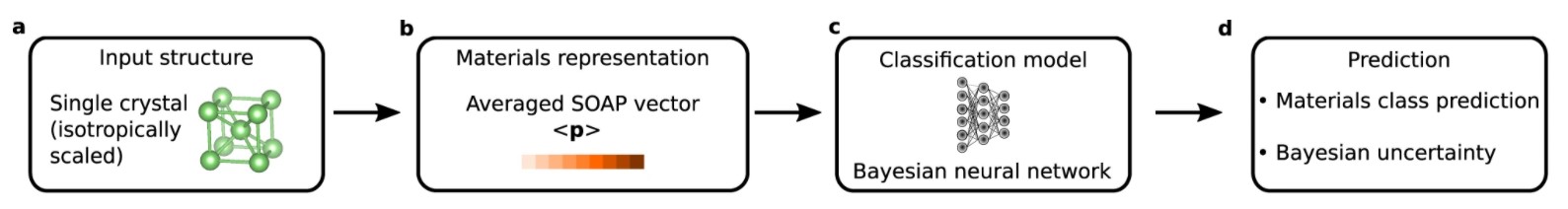
Prediction pipeline of the single-crystal classification model ARISE
文献三 基于深度学习的步态识别综述
Deep Gait Recognition: A Survey
Alireza Sepas-Moghaddam, etc.
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON PATTERN ANALYSIS AND MACHINE INTELLIGENCE, 2022, Early Access
Gait recognition is an appealing biometric modality which aims to identify individuals based on the way they walk. Deep learning has reshaped the research landscape in this area since 2015 through the ability to automatically learn discriminative representations. Gait recognition methods based on deep learning now dominate the state-of-the-art in the field and have fostered real-world applications. In this paper, we present a comprehensive overview of breakthroughs and recent developments in gait recognition with deep learning, and cover broad topics including datasets, test protocols, state-of-the-art solutions, challenges, and future research directions. We first review the commonly used gait datasets along with the principles designed for evaluating them. We then propose a novel taxonomy made up of four separate dimensions namely body representation, temporal representation, feature representation, and neural architecture, to help characterize and organize the research landscape and literature in this area. Following our proposed taxonomy, a comprehensive survey of gait recognition methods using deep learning is presented with discussions on their performances, characteristics, advantages, and limitations. We conclude this survey with a discussion on current challenges and mention a number of promising directions for future research in gait recognition.
阅读原文:https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9714177
文献四 面向手绘素描数据的深度学习技术及其应用
Deep Learning for Free-Hand Sketch: A Survey
Xu, Peng, etc.
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON PATTERN ANALYSIS AND MACHINE INTELLIGENCE, 2022, Early Access
Free-hand sketches are highly illustrative, and have been widely used by humans to depict objects or stories from ancient times to the present. The recent prevalence of touchscreen devices has made sketch creation a much easier task than ever and consequently made sketch-oriented applications increasingly popular. The progress of deep learning has immensely benefited free-hand sketch research and applications. This paper presents a comprehensive survey of the deep learning techniques oriented at free-hand sketch data, and the applications that they enable. The main contents of this survey include: (i) A discussion of the intrinsic traits and unique challenges of free-hand sketch, to highlight the essential differences between sketch data and other data modalities, e.g., natural photos. (ii) A review of the developments of free-hand sketch research in the deep learning era, by surveying existing datasets, research topics, and the state-of-the-art methods through a detailed taxonomy and experimental evaluation. (iii) Promotion of future work via a discussion of bottlenecks, open problems, and potential research directions for the community.
阅读原文:https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9706366
往期精彩推荐
前沿论文带您解读5G应用领域 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(2)
热点论文解读AI应用领域 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(3)
热点论文带您探究5G和未来通信——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务 (4)
前沿文献带您解读自然语言处理技术 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(5)
热点论文带您探究5G和未来通信材料技术领域 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(6)
热点论文解读AI应用领域 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(3)
热点论文带您探究5G和未来通信——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务 (4)
前沿文献带您解读自然语言处理技术 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(5)
热点论文带您探究5G和未来通信材料技术领域 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(6)
热点文献带您关注AI情感分类技术 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(7)
热点论文带您探究6G的无限可能——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(8)
热点文献带您关注AI文本摘要自动生成 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(9)
热点论文:5G/6G引领社会新进步——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(10)
热点文献带您关注AI机器翻译 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(11)
热点论文与您探讨5G/6G网络技术新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(12)
热点文献带您关注AI计算机视觉 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(13)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G的硬科技与新思路 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(14)
热点文献带您关注AI计算机视觉 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(15)
热点论文带您领略5G/6G的最新技术动向 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(18)
热点文献带您关注图神经网络——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(19)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G材料技术的最新发展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(20)
热点文献带您关注模式识别——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(21)
热点论文与带您领略6G网络技术的最新发展趋势 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(22)
热点文献带您关注机器学习与量子物理 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(23)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G通信器件材料的最新进展 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(24)
热点文献带您关注AI自动驾驶——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(25)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G网络安全和技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(26)
热点文献带您关注AI神经网络与忆阻器——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(27)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G电子器件和太赫兹方面的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(28)
热点文献带您关注AI与机器人——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(29)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G热点技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(30)
热点文献带您关注AI与触觉传感技术——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(31)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G热点技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(32)
热点文献带您关注AI深度学习与计算机视觉——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(33)
热点论文与带您领略未来通信的热点技术及最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(34)
热点文献带您关注AI强化学习——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(35)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G基础研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(36)
热点文献带您关注AI与边缘计算——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(37)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G领域热点研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(38)
热点文献带您关注AI技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(39)
热点论文与带您领略5G相关领域研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(40)
热点文献带您关注AI视觉跟踪——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(41)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在海空领域研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(42)
热点文献带您关注AI与医学研究——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(43)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在材料领域研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(44)
热点文献带您关注AI与医学图像——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(45)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在光电材料及信息编码领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(46)
热点文献带您关注AI与生物学——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(47)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在新材料技术领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(48)
热点文献带您关注AI与人脸识别——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(49)
热点论文带您领略光电半导体领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(50)
热点文献带您关注AI在集成电路领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(51)
热点论文带您领略半导体领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(52)
热点文献带您关注AI在光神经网络领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(53)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在新材料技术领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(54)
热点文献带您关注AI深度神经网络的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(55)
热点论文带您领略新材料半导体领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(56)
热点文献带您关注AI视频动作识别的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(57)
热点论文带您领略未来通信热点技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(58)