热点文献带您关注AI领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(65)
2022-05-16

我校人工智能学院邓伟洪教授课题组在蒙面人脸识别中的研究成果“基于SFace深度学习的人脸识别”,基于未经训练深度神经网络的人脸检测,基于复数神经网络的虹膜识别,以及可处理缺失输入模式的多模式步态识别。
本期我们为您选取了4篇文献,介绍利用表面温度的变化调节手指摩擦的方法,利用taxel等值线理论指导超分辨率触觉皮肤的设计,一种拇指大小基于视觉的三维触觉传感器,以及基于主动学习和数据增强的软机器自动应变传感器设计的热点文献。
文献一 利用表面温度的变化调节手指摩擦的方法
Surface haptic rendering of virtual shapes through change in surface temperature
Choi, Changhyun, etc.
SCIENCE ROBOTICS, 2022, 7(63)
Compared to relatively mature audio and video human-machine interfaces, providing accurate and immersive touch sensation remains a challenge owing to the substantial mechanical and neurophysical complexity of touch. Touch sensations during relative lateral motion between a skin-screen interface are largely dictated by interfacial friction, so controlling interfacial friction has the potential for realistic mimicry of surface texture, shape, and material composition. In this work, we show a large modulation of finger friction by locally changing surface temperature. Experiments showed that finger friction can be increased by similar to 50% with a surface temperature increase from 23 degrees to 42 degrees C, which was attributed to the temperature dependence of the viscoelasticity and the moisture level of human skin. Rendering virtual features, including zoning and bump(s), without thermal perception was further demonstrated with surface temperature modulation. This method of modulating finger friction has potential applications in gaming, virtual and augmented reality, and touchscreen human-machine interaction.
阅读原文:https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/scirobotics.abl4543
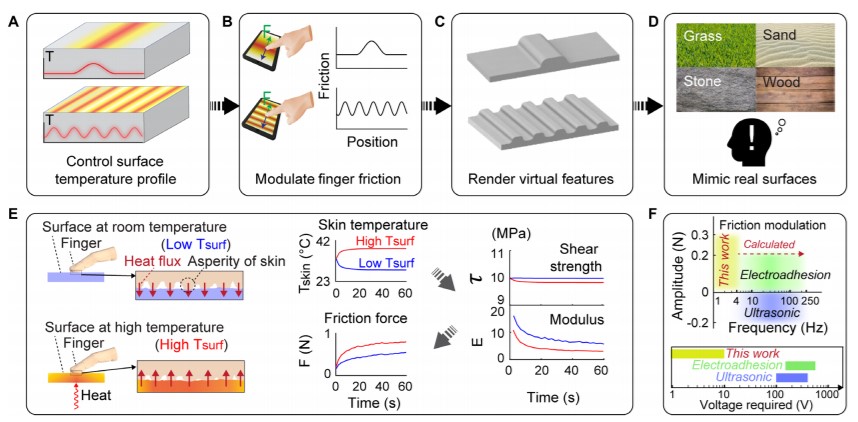
The schematic of the desired flow map in this work
文献二 利用taxel等值线理论指导超分辨率触觉皮肤的设计
Guiding the design of superresolution tactile skins with taxel value isolines theory
Sun, Huanbo, etc.
SCIENCE ROBOTICS, 2022, 7(63)
Tactile feedback is essential to make robots more agile and effective in unstructured environments. However, high-resolution tactile skins are not widely available; this is due to the large size of robust sensing units and because many units typically lead to fragility in wiring and to high costs. One route toward high-resolution and robust tactile skins involves the embedding of a few sensor units (taxels) into a flexible surface material and the use of signal processing to achieve sensing with superresolution accuracy. Here, we propose a theory for geometric superresolution to guide the development of tactile sensors of this kind and link it to machine learning techniques for signal processing. This theory is based on sensor isolines and allows us to compute the possible force sensitivity and accuracy in contact position and force magnitude as a spatial quantity before building a sensor. We evaluate the influence of different factors, such as elastic properties of the material, structure design, and transduction methods, using finite element simulations and by implementing real sensors. We empirically determine sensor isolines and validate the theory in two custom-built sensors with 1D and 2D measurement surfaces that use barometric units. Using machine learning methods to infer contact information, our sensors obtain an average superresolution factor of over 100 and 1200, respectively. Our theory can guide future tactile sensor designs and inform various design choices.
阅读原文:https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/scirobotics.abm0608
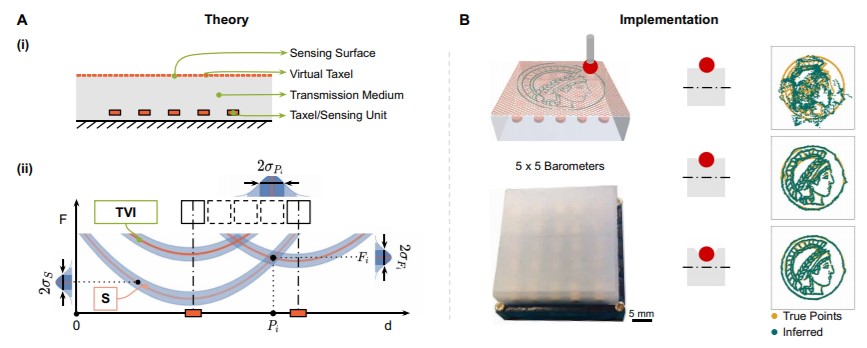
Overview of the sensor design approach
文献三 一种拇指大小基于视觉的三维触觉传感器
A soft thumb-sized vision-based sensor with accurate all-round force perception
Sun, Huanbo, etc.
NATURE MACHINE INTELLIGENCE, 2022, 4(2): 135-145
Vision-based haptic sensors have emerged as a promising approach to robotic touch due to affordable high-resolution cameras and successful computer vision techniques; however, their physical design and the information they provide do not yet meet the requirements of real applications. We present a robust, soft, low-cost, vision-based, thumb-sized three-dimensional haptic sensor named Insight, which continually provides a directional force-distribution map over its entire conical sensing surface. Constructed around an internal monocular camera, the sensor has only a single layer of elastomer over-moulded on a stiff frame to guarantee sensitivity, robustness and soft contact. Furthermore, Insight uniquely combines photometric stereo and structured light using a collimator to detect the three-dimensional deformation of its easily replaceable flexible outer shell. The force information is inferred by a deep neural network that maps images to the spatial distribution of three-dimensional contact force (normal and shear). Insight has an overall spatial resolution of 0.4 mm, a force magnitude accuracy of around 0.03 N and a force direction accuracy of around five degrees over a range of 0.03-2 N for numerous distinct contacts with varying contact area. The presented hardware and software design concepts can be transferred to a wide variety of robot parts.
阅读原文:https://www.nature.com/articles/s42256-021-00439-3
文献四 基于主动学习和数据增强的软机器自动应变传感器设计
Automatic strain sensor design via active learning and data augmentation for soft machines
Marin-Jimenez, Manuel J., etc.
NATURE MACHINE INTELLIGENCE, 2022, 4(1): 84-94
Emerging soft machines require high-performance strain sensors to achieve closed-loop feedback control. Machine learning is a versatile tool to uncover complex correlations between fabrication recipes and sensor performance at the device level. Here a three-stage machine learning framework was realized for a high-accuracy prediction model capable of automating the design of strain sensors. First, a support-vector machine classifier was trained by using 351 compositions of various nanomaterials. Second, through 12 active learning loops, 125 strain sensors were stagewise fabricated to enrich the multidimensional dataset. Third, to address the challenge of data scarcity, data augmentation was implemented to synthesize >10,000 virtual data points, followed by genetic algorithm-based selection to optimize the model's prediction accuracy. Several data-driven design rules for piezoresistive nanocomposites were generalized and validated by in situ microscopic studies. As final demonstrations, model-suggested strain sensors can be integrated into/onto various soft machines to endow them with real-time strain-sensing capabilities.
阅读原文:https://www.nature.com/articles/s42256-021-00434-8
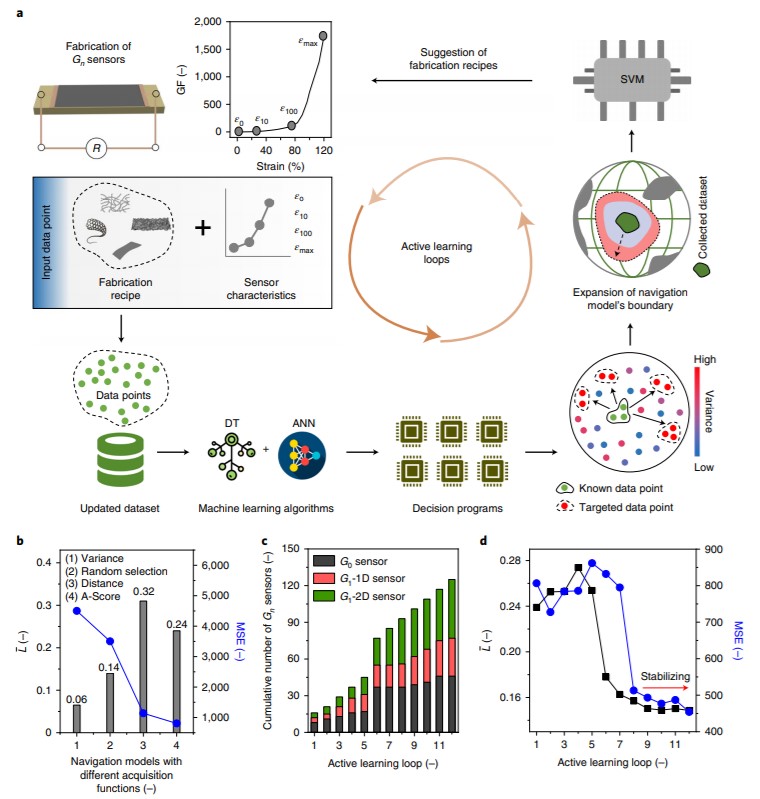
Progressive exploration of sensor design space through active learning
往期精彩推荐
前沿论文带您解读5G应用领域 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(2)
热点论文解读AI应用领域 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(3)
热点论文带您探究5G和未来通信——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务 (4)
前沿文献带您解读自然语言处理技术 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(5)
热点论文带您探究5G和未来通信材料技术领域 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(6)
热点论文解读AI应用领域 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(3)
热点论文带您探究5G和未来通信——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务 (4)
前沿文献带您解读自然语言处理技术 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(5)
热点论文带您探究5G和未来通信材料技术领域 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(6)
热点文献带您关注AI情感分类技术 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(7)
热点论文带您探究6G的无限可能——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(8)
热点文献带您关注AI文本摘要自动生成 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(9)
热点论文:5G/6G引领社会新进步——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(10)
热点文献带您关注AI机器翻译 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(11)
热点论文与您探讨5G/6G网络技术新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(12)
热点文献带您关注AI计算机视觉 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(13)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G的硬科技与新思路 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(14)
热点文献带您关注AI计算机视觉 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(15)
热点论文带您领略5G/6G的最新技术动向 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(18)
热点文献带您关注图神经网络——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(19)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G材料技术的最新发展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(20)
热点文献带您关注模式识别——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(21)
热点论文与带您领略6G网络技术的最新发展趋势 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(22)
热点文献带您关注机器学习与量子物理 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(23)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G通信器件材料的最新进展 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(24)
热点文献带您关注AI自动驾驶——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(25)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G网络安全和技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(26)
热点文献带您关注AI神经网络与忆阻器——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(27)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G电子器件和太赫兹方面的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(28)
热点文献带您关注AI与机器人——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(29)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G热点技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(30)
热点文献带您关注AI与触觉传感技术——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(31)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G热点技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(32)
热点文献带您关注AI深度学习与计算机视觉——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(33)
热点论文与带您领略未来通信的热点技术及最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(34)
热点文献带您关注AI强化学习——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(35)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G基础研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(36)
热点文献带您关注AI与边缘计算——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(37)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G领域热点研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(38)
热点文献带您关注AI技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(39)
热点论文与带您领略5G相关领域研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(40)
热点文献带您关注AI视觉跟踪——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(41)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在海空领域研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(42)
热点文献带您关注AI与医学研究——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(43)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在材料领域研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(44)
热点文献带您关注AI与医学图像——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(45)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在光电材料及信息编码领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(46)
热点文献带您关注AI与生物学——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(47)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在新材料技术领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(48)
热点文献带您关注AI与人脸识别——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(49)
热点论文带您领略光电半导体领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(50)
热点文献带您关注AI在集成电路领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(51)
热点论文带您领略半导体领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(52)
热点文献带您关注AI在光神经网络领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(53)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在新材料技术领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(54)
热点文献带您关注AI深度神经网络的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(55)
热点论文带您领略新材料半导体领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(56)
热点文献带您关注AI视频动作识别的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(57)
热点论文带您领略未来通信热点技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(58)
热点文献带您关注AI深度学习的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(59)
热点论文带您领略未来通信研究热点的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(60)
热点文献带您关注AI领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(61)
热点论文带您探索智能化以及超表面在未来通信中的应用——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(62)
热点文献带您关注AI领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(63)
热点论文带您领略半导体领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(64)