热点论文带您探索未来网络中使用的新材料以及相关技术 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(70)
2022-09-29

在第68期前沿文献中推荐中,介绍了新型网络架构以及超材料在未来通信中的应用,包括:用于5G无线系统的芯片级Floquet拓扑绝缘体;一种适用于5G-MIMO通信系统的新型高隔离度天线阵;用于改善单极子天线增益的基于间隙耦合对称分裂环谐振器的近零折射率负介电常数超材料;内生智能和端到端服务化的6G无线网络架构设计。
在本期的文献推荐中,关注点着眼于未来网络中使用的新材料以及相关技术,选取了:100GHz以上有源和无源用户之间的动态频谱共享;用于6G通信系统的单层二硫化钼开关;使用轨道角动量复用的太赫兹无线链路中接收器孔径和多径对功率损耗和模式串扰的影响;用于5G应用的具有任意输出的紧凑型功率分配器的反向设计四篇文献,供相关领域的科研人员参考。
领域一 100GHz以上有源和无源用户之间的动态频谱共享
Dynamic spectrum sharing between active and passive users above 100 GHz
Michele Polese, etc.
Communications Engineering, 2022
Sixth-generation wireless networks will aggregate higher-than-ever mobile traffic into ultra-high capacity backhaul links, which could be deployed on the largely untapped spectrum above 100 GHz. Current regulations however prevent the allocation of large contiguous bands for communications at these frequencies, since several narrow bands are reserved to protect passive sensing services. These include radio astronomy and Earth exploration satellites using sensors that suffer from harmful interference from active transmitters. Here we show that active and passive spectrum sharing above 100 GHz is feasible by introducing and experimentally evaluating a real-time, dual-band backhaul prototype that tracks the presence of passive users (in this case the NASA satellite Aura) and avoids interference by automatically switching bands (123.5–140 GHz and 210–225 GHz). Our system enables wide-band transmissions in the above-100-GHz spectrum, while avoiding harmful interference to satellite systems, paving the way for innovative spectrum policy and technologies in these crucial bands.
https://www.nature.com/articles/s44172-022-00002-x
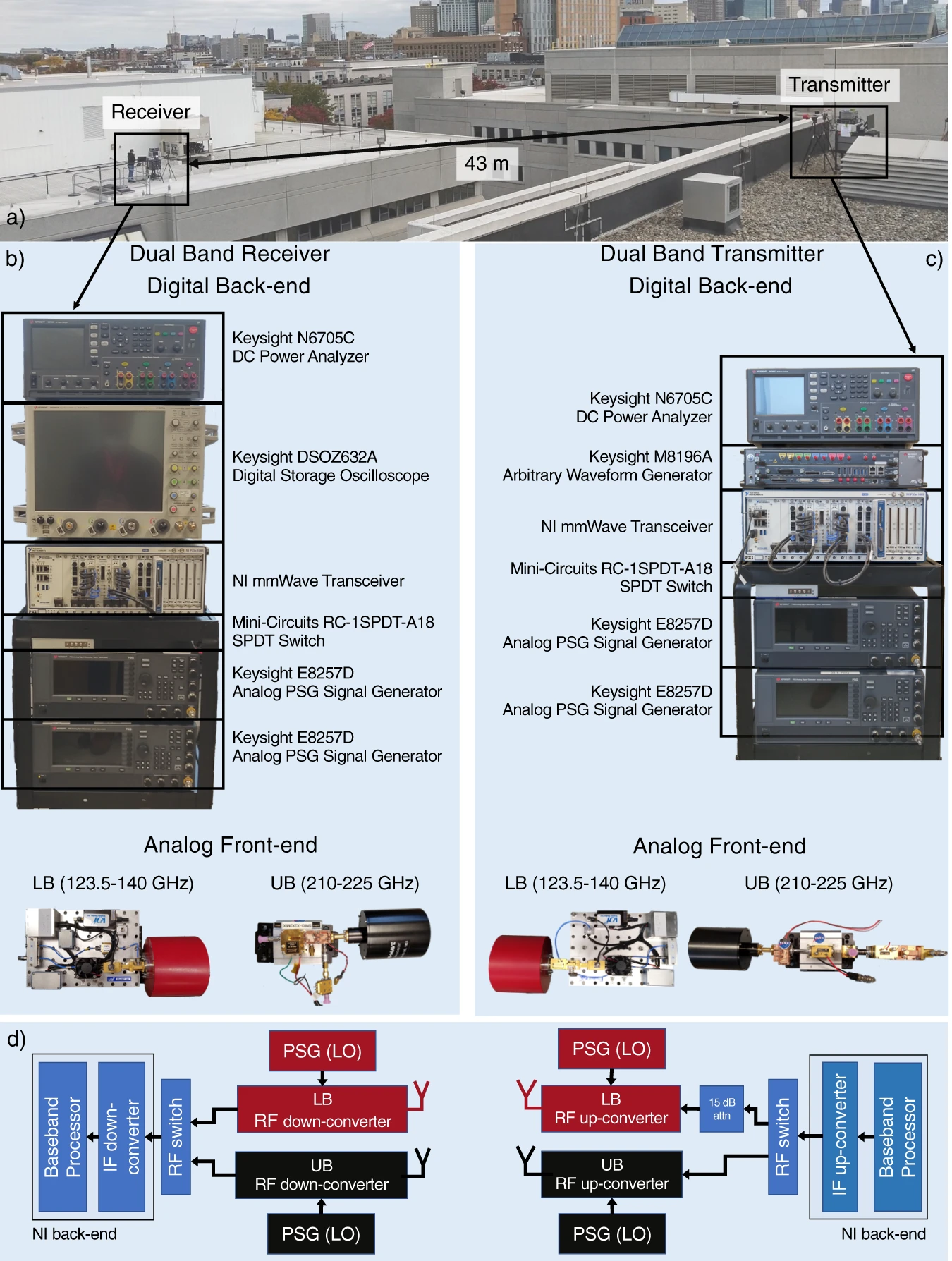
Fig. Prototype schematics and dual-band backhaul link deployment.
领域二 用于6G通信系统的单层二硫化钼开关
Monolayer molybdenum disulfide switches for 6G communication systems
Myungsoo Kim, etc.
Nature Electronics, 2022
Atomically thin two-dimensional materials—including transitional metal dichalcogenides and hexagonal boron nitride—can exhibit non-volatile resistive switching. This switching behaviour could be used to create analogue switches for use in high-frequency communication, but has so far been limited to frequencies relevant to the fifth generation of wireless communication technology. Here we show that non-volatile switches made from monolayer molybdenum disulfide in a metal–insulator–metal structure can operate at frequencies corresponding to the sixth-generation communication band (around 100–500 GHz). The switches exhibit low insertion loss in the ON state and high isolation in the OFF state up to 480 GHz with sub-nanosecond pulse switching. We obtain the eye diagrams and constellation diagrams at various data transmission rates and modulations to evaluate the device performance, including real-time data communication up to 100 Gbit s−1 at a carrier frequency of 320 GHz, with a low bit error rate and high signal-to-noise ratio.
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41928-022-00766-2
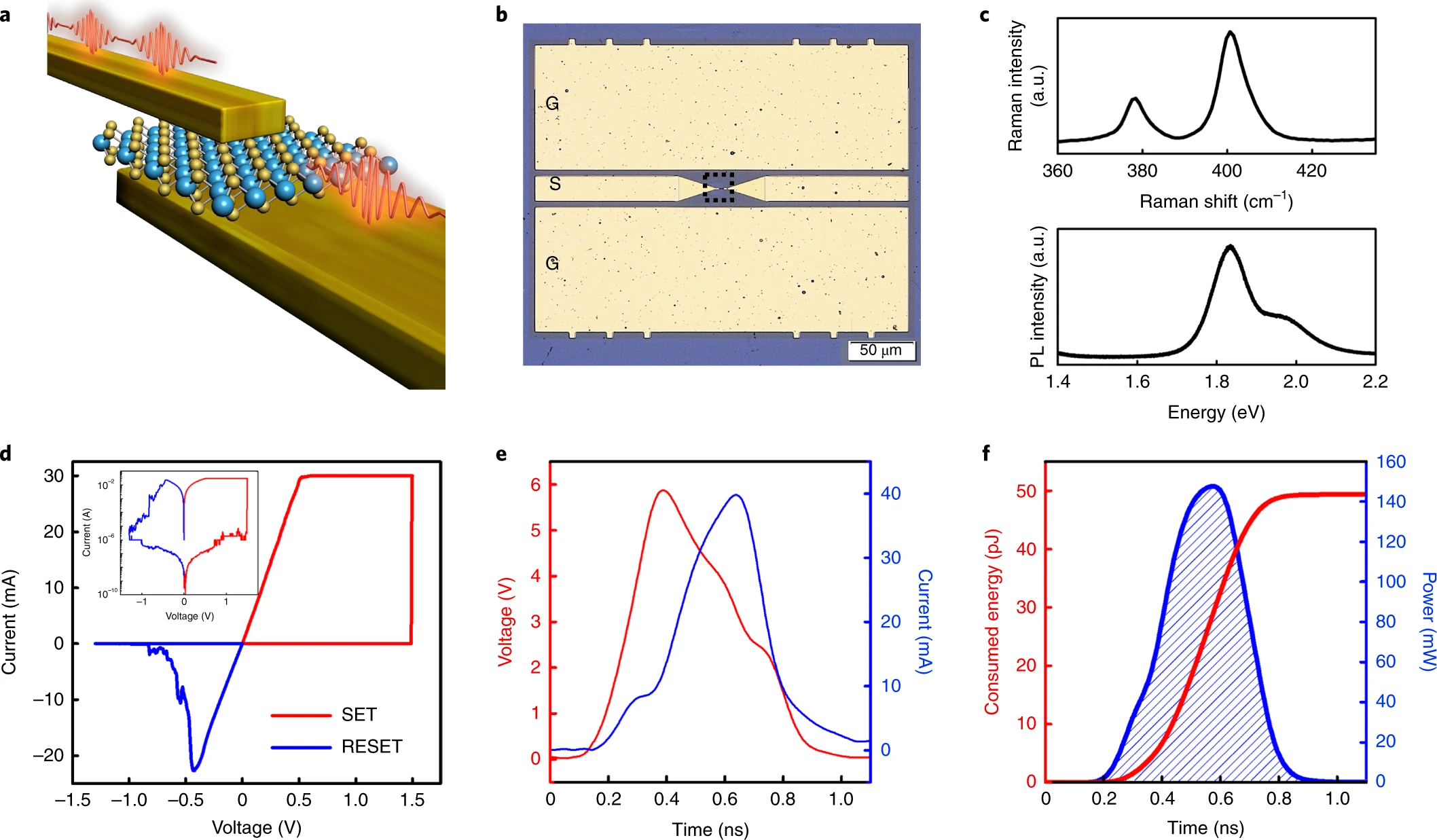
Fig. Material, device structure, and d.c. and pulse switching.
领域三 使用轨道角动量复用的太赫兹无线链路中接收器孔径和多径对功率损耗和模式串扰的影响
Receiver aperture and multipath effects on power loss and modal crosstalk in a THz wireless link using orbital-angular-momentum multiplexing
Xinzhou Su, etc.
Scientific Reports, 2022
The channel capacity of terahertz (THz) wireless communications can be increased by multiplexing multiple orthogonal data-carrying orbital-angular-momentum (OAM) beams. In THz links using OAM multiplexing (e.g., Laguerre-Gaussian LGℓ,p beams with p = 0), the system performance might degrade due to limited receiver aperture size and multipath effects. A limited-size aperture can truncate the received beam profile along the radial direction. In addition, due to beam divergence, part of the beam might interact with reflectors in the environment, causing the signal to reflect and interfere at the receiver with the directly propagating part of the beam; this is known as the multipath effect. In this paper, we simulate and analyze the impact of both effects on the equality of the THz OAM link by considering a full two-dimensional (2-D) LG modal set. The simulation results show (i) a limited-size receiver aperture can induce power loss and modal power coupling mainly to LG modes with the same ℓ but p > 0 for directly propagated OAM beams; (ii) the multipath effect can induce modal power coupling across multiple 2-D LG modes, which leads to inter-channel coupling among the different channels in an OAM multiplexed link; (iii) the interference between the reflected and direct beams can induce intra-channel coupling between the received signals from the reflected and direct beams; and (iv) beams with a higher OAM order (e.g., from ± 1 to ± 5) or a lower carrier frequency (e.g., from 0.1 to 1 THz) experience larger intra- and inter-channel coupling. The intra- and inter-channel coupling in an OAM-multiplexed THz link can degrade the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and induce SNR penalty when compared to a single-channel system.
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-022-18444-w

Fig. Schematic of limited-size receiver aperture and multipath effects in a THz OAM link.
Inverse design of compact power divider with arbitrary outputs for 5G applications
Maryam Shadi, etc.
Scientific Reports, 2022
Since the recent on-demand applications need more sophisticated circuits and subsystems, components with configurable capabilities attract attention more than before in commercial systems, specifically the fifth generation (5G). Power dividers play a crucial role in 5G phased array systems, and their role becomes more significant if the output powers ratio is adjustable. Here, we suggest a design methodology by which planar power splitters with arbitrary output power levels can be designed in light of very simple perturbations, i.e., vias. Through our design procedure, we find an optimized pattern for hybrid vias-some of them are made of PEC, and others are dielectric, e.g., air, high-permittivity materials. Thanks to deep neural networks, we demonstrate that this technique can be employed to design power splitters whose output ports have different amplitudes. In light of the proposed method, we fabricated and measured a 4-way power divider realizing Chebyshev coefficients for sidelobe reduction of a 4-element array at 28 GHz as a proof-of-concept. We believe that this methodology in which hybrid perturbation is the key spot paves a way to implement complex functions in various platforms and other structures, e.g., SIWs, ridge waveguides, rather than the one we investigated (planar/microstrip).
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-022-17212-0

Fig. (a) Traditional feeding network in sub-array antenna (b) new compact and affordable structure to control amplitude level of primary array’s elements.
往期精彩推荐
热点论文解读AI应用领域 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(3)
热点论文带您探究5G和未来通信——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务 (4)
前沿文献带您解读自然语言处理技术 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(5)
热点论文带您探究5G和未来通信材料技术领域 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(6)
热点文献带您关注AI情感分类技术 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(7)
热点论文带您探究6G的无限可能——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(8)
热点文献带您关注AI文本摘要自动生成 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(9)
热点论文:5G/6G引领社会新进步——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(10)
热点文献带您关注AI机器翻译 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(11)
热点论文与您探讨5G/6G网络技术新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(12)
热点文献带您关注AI计算机视觉 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(13)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G的硬科技与新思路 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(14)
热点文献带您关注AI计算机视觉 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(15)
热点论文带您领略5G/6G的最新技术动向 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(18)
热点文献带您关注图神经网络——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(19)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G材料技术的最新发展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(20)
热点文献带您关注模式识别——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(21)
热点论文与带您领略6G网络技术的最新发展趋势 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(22)
热点文献带您关注机器学习与量子物理 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(23)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G通信器件材料的最新进展 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(24)
热点文献带您关注AI自动驾驶——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(25)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G网络安全和技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(26)
热点文献带您关注AI神经网络与忆阻器——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(27)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G电子器件和太赫兹方面的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(28)
热点文献带您关注AI与机器人——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(29)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G热点技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(30)
热点文献带您关注AI与触觉传感技术——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(31)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G热点技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(32)
热点文献带您关注AI深度学习与计算机视觉——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(33)
热点论文与带您领略未来通信的热点技术及最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(34)
热点文献带您关注AI强化学习——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(35)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G基础研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(36)
热点文献带您关注AI与边缘计算——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(37)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G领域热点研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(38)
热点文献带您关注AI技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(39)
热点论文与带您领略5G相关领域研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(40)
热点文献带您关注AI视觉跟踪——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(41)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在海空领域研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(42)
热点文献带您关注AI与医学研究——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(43)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在材料领域研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(44)
热点文献带您关注AI与医学图像——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(45)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在光电材料及信息编码领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(46)
热点文献带您关注AI与生物学——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(47)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在新材料技术领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(48)
热点文献带您关注AI与人脸识别——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(49)
热点论文带您领略光电半导体领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(50)
热点文献带您关注AI在集成电路领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(51)
热点论文带您领略半导体领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(52)
热点文献带您关注AI在光神经网络领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(53)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在新材料技术领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(54)
热点文献带您关注AI深度神经网络的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(55)
热点论文带您领略新材料半导体领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(56)
热点文献带您关注AI视频动作识别的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(57)
热点论文带您领略未来通信热点技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(58)
热点文献带您关注AI深度学习的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(59)
热点论文带您领略未来通信研究热点的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(60)
热点文献带您关注AI领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(61)
热点论文带您探索智能化以及超表面在未来通信中的应用——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(62)
热点文献带您关注AI领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(63)
热点论文带您领略半导体领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(64)
热点文献带您关注AI领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(65)
热点论文带您探索新型网络架构以及超表面在未来通信中的应用——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(66)
热点文献带您关注AI深度强化学习的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(67)
热点论文带您探索新型网络架构以及超材料在未来通信中的应用——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(68)
热点文献带您关注AI图神经网络的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(69)