热点文献带您关注AI与集成电路领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(83)
2023-12-08
本期我们为您选取了4篇文献,介绍人工智能与集成电路交叉学科的最新发展前沿,包括一种用于高效语音识别与转录的模拟AI芯片,一种用于深度神经网络推理的64核混合信号存内计算芯片,提高AI边缘设备安全性的CMOS集成自旋电子nvCIM宏,用于AI边缘推理的28nm RRAM nvCIM宏。

An analog-AI chip for energy-efficient speech recognition and transcription
Ambrogio, S., etc.
NATURE, 2023, 620(7975): 768–775
Models of artificial intelligence (AI) that have billions of parameters can achieve high accuracy across a range of tasks, but they exacerbate the poor energy efficiency of conventional general-purpose processors, such as graphics processing units or central processing units. Analog in-memory computing (analog-AI) can provide better energy efficiency by performing matrix-vector multiplications in parallel on 'memory tiles'. However, analog-AI has yet to demonstrate software-equivalent (SWeq) accuracy on models that require many such tiles and efficient communication of neural-network activations between the tiles. Here we present an analog-AI chip that combines 35 million phase-change memory devices across 34 tiles, massively parallel inter-tile communication and analog, low-power peripheral circuitry that can achieve up to 12.4 tera-operations per second per watt (TOPS/W) chip-sustained performance. We demonstrate fully end-to-end SWeq accuracy for a small keyword-spotting network and near-SWeq accuracy on the much larger MLPerf recurrent neural-network transducer (RNNT), with more than 45 million weights mapped onto more than 140 million phase-change memory devices across five chips.
阅读原文:https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-023-06337-5
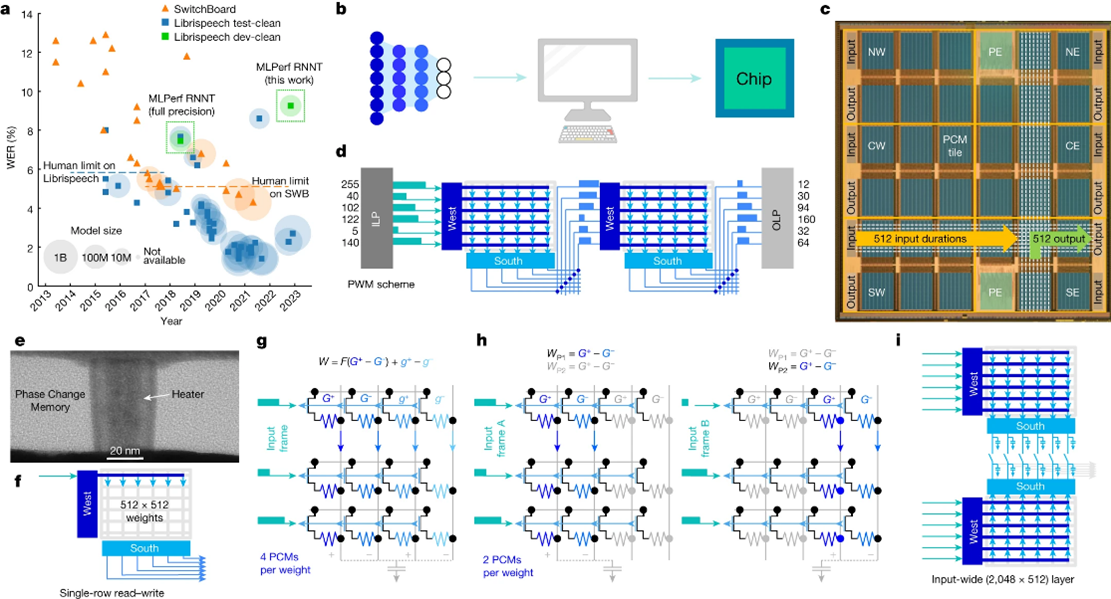
The chip architecture

A 64-core mixed-signal in-memory compute chip based on phase-change memory for deep neural network inference
Le Gallo, Manuel, etc.
NATURE ELECTRONICS, 2023, 6(9): 680–693
Analogue in-memory computing (AIMC) with resistive memory devices could reduce the latency and energy consumption of deep neural network inference tasks by directly performing computations within memory. However, to achieve end-to-end improvements in latency and energy consumption, AIMC must be combined with on-chip digital operations and on-chip communication. Here we report a multicore AIMC chip designed and fabricated in 14 nm complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor technology with backend-integrated phase-change memory. The fully integrated chip features 64 AIMC cores interconnected via an on-chip communication network. It also implements the digital activation functions and additional processing involved in individual convolutional layers and long short-term memory units. With this approach, we demonstrate near-software-equivalent inference accuracy with ResNet and long short-term memory networks, while implementing all the computations associated with the weight layers and the activation functions on the chip. For 8-bit input/output matrix-vector multiplications, in the four-phase (high-precision) or one-phase (low-precision) operational read mode, the chip can achieve a maximum throughput of 16.1 or 63.1 tera-operations per second at an energy efficiency of 2.48 or 9.76 tera-operations per second per watt, respectively.
阅读原文:https://www.nature.com/articles/s41928-023-01010-1


A CMOS-integrated spintronic compute-in-memory macro for secure AI edge devices
Chiu, Yen-Cheng, etc.
NATURE ELECTRONICS, 2023, 6(7): 534–543
A non-volatile compute-in-memory macro that is based on spin-transfer torque magnetic random-access memory can offer secure access control, data protection, rapid response times and high energy efficiency for dot-product edge computing.
Artificial intelligence edge devices should offer high inference accuracy and rapid response times, as well as being energy efficient. Ensuring the security of these devices against malicious attacks and illegal access requires data protection mechanisms and secure access control. Here we report a spintronic non-volatile compute-in-memory macro for efficient dot-product edge computing with secure access control for activation, key and data protection against power-on and power-off probing. The approach relies on spintronic-based physically unclonable functions and two-dimensional half-complement physical encryption, as well as a snoop-proof self-decryption burst-read scheme in conjunction with a sparsity-and-rectified-linear-unit-aware early-termination compute-in-memory engine. The 6.6 megabit complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS)-integrated macro uses 22 nm spin-transfer torque magnetic random-access memory technology. The macro achieves high randomness (inter-Hamming distance, 0.4999) and high reliability for physically unclonable functionality (intra-Hamming distance, 0), as well as a high energy efficiency for dot-product computation (between 30.1 and 68.0 tera-operations per second per watt).
阅读原文:https://www.nature.com/articles/s41928-023-00994-0
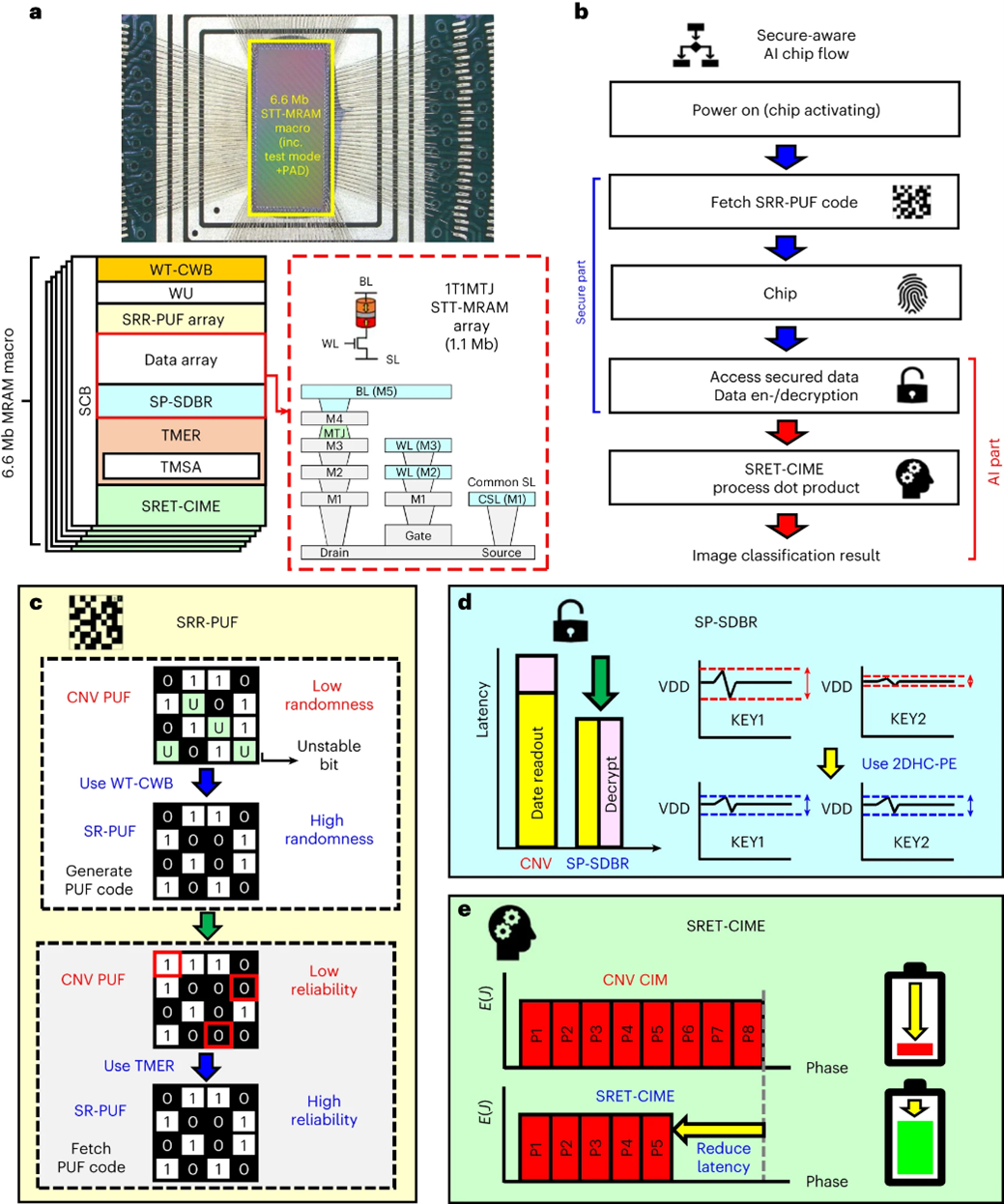

A 28-nm RRAM Computing-in-Memory Macro Using Weighted Hybrid 2T1R Cell Array and Reference Subtracting Sense Amplifier for AI Edge Inference
Ye, Wang, etc.
IEEE JOURNAL OF SOLID-STATE CIRCUITS, 2023, 58(10): 2839–2850
Non-volatile computing-in-memory (nvCIM) can potentially meet the ever-increasing demands on improving the energy efficiency (EF) for intelligent edge devices. However, it still suffers from limited input parallelism due to the parasitic effects, signal margin degradation due to device non-idealities, and large hardware cost for analog readout. In this work, we present a two-transistor-one-resistor (2T1R) resistive memory (RRAM) nvCIM macro featuring: 1) a macro structure with decoupled memory and computing data paths; 2) the weighted hybrid 2T1R (WH-2T1R) cell array; 3) the redundant sub-array mapping scheme of the most-significant-bit (RSM-MSB); and 4) reference-subtracting current sense amplifier (RS-CSA). A test-chip is silicon-verified using the 28-nm high-k/metal-gate (HKMG) logic process with foundry-developed RRAM. The test-chip performs linear analog multiply-and-accumulate (MAC) operations over 32 accumulation channels and achieves 30.34-154.04 TOPS/W with 1-bit input (IN), 3-bit weight (W), and 4-bit output (O). Evaluations with the ResNet-18 model show that the MSB-RSM scheme results in 0.96% and 2.83% improvement on CIFAR-10 and CIFAR-100 inference accuracy, respectively.
阅读原文:https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10145046/
联系人:杨老师 闫老师
邮箱:yandong80@bupt.edu.cn
电话:西土城校区图书馆125室 62281933 62283502
沙河校区图书馆东205室 66605330 66605331
往期精彩推荐
热点文献带您关注AI大型语言模型的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(82)
热点文献带您关注通信领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(81)
热点文献带您关注半导体领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(80)
热点文献带您关注AI领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(79)
热点文献带您关注通信领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(78)
热点文献带您关注半导体领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(77)
热点文献带您关注AI Transformer的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(76)
热点文献带您关注低轨卫星通信技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(75)
热点文献带您关注惯性测量单元的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(74)
热点文献带您关注存算一体技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(73)
热点文献带您关注电子皮肤的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(72)
热点文献带您关注AI的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(71)
热点论文带您探索未来网络中使用的新材料以及相关技术 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(70)
热点文献带您关注AI图神经网络的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(69)
热点论文带您探索新型网络架构以及超材料在未来通信中的应用——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(68)
热点文献带您关注AI深度强化学习的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(67)
热点论文带您探索新型网络架构以及超表面在未来通信中的应用——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(66)
热点文献带您关注AI领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(65)
热点论文带您领略半导体领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(64)
热点文献带您关注AI领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(63)
热点论文带您探索智能化以及超表面在未来通信中的应用——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(62)
热点文献带您关注AI领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(61)
热点论文带您领略未来通信研究热点的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(60)
热点文献带您关注AI深度学习的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(59)
热点论文带您领略未来通信热点技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(58)
热点文献带您关注AI视频动作识别的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(57)
热点论文带您领略新材料半导体领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(56)
热点文献带您关注AI深度神经网络的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(55)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在新材料技术领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(54)
热点文献带您关注AI在光神经网络领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(53)
热点论文带您领略半导体领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(52)
热点文献带您关注AI在集成电路领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(51)
热点论文带您领略光电半导体领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(50)
热点文献带您关注AI与人脸识别——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(49)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在新材料技术领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(48)
热点文献带您关注AI与生物学——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(47)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在光电材料及信息编码领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(46)
热点文献带您关注AI与医学图像——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(45)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在材料领域研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(44)
热点文献带您关注AI与医学研究——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(43)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在海空领域研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(42)
热点文献带您关注AI视觉跟踪——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(41)
热点论文与带您领略5G相关领域研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(40)
热点文献带您关注AI技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(39)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G领域热点研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(38)
热点文献带您关注AI与边缘计算——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(37)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G基础研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(36)
热点文献带您关注AI强化学习——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(35)
热点论文与带您领略未来通信的热点技术及最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(34)
热点文献带您关注AI深度学习与计算机视觉——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(33)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G热点技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(32)
热点文献带您关注AI与触觉传感技术——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(31)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G热点技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(30)
热点文献带您关注AI与机器人——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(29)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G电子器件和太赫兹方面的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(28)
热点文献带您关注AI自动驾驶——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(25)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G通信器件材料的最新进展 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(24)
热点文献带您关注机器学习与量子物理 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(23)
热点论文与带您领略6G网络技术的最新发展趋势 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(22)
热点文献带您关注模式识别——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(21)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G材料技术的最新发展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(20)
热点文献带您关注图神经网络——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(19)
热点论文带您领略5G/6G的最新技术动向 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(18)
热点文献带您关注AI主动视觉——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(17)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G的最新技术演进 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(16)
热点文献带您关注AI计算机视觉 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(15)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G的硬科技与新思路 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(14)
热点文献带您关注AI机器翻译 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(11)
热点论文:5G/6G引领社会新进步——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(10)
热点文献带您关注AI文本摘要自动生成 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(9)
热点论文带您探究6G的无限可能——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(8)
热点文献带您关注AI情感分类技术 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(7)
热点论文带您探究5G和未来通信材料技术领域 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(6)
前沿文献带您解读自然语言处理技术 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(5)
热点论文带您探究5G和未来通信——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务 (4)
热点论文解读AI应用领域 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(3)
