热点文献带您关注AI Transformer的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(76)
2023-03-20

在上一期热点文献推荐中,我们为您推荐了低轨卫星通信技术的最新发展前沿,包括智能反射表面辅助低轨卫星通信,利用低轨卫星解决加拿大偏远地区宽带接入与数字鸿沟的方案,基于深度学习的低轨卫星大规模MIMO系统信道预测和混合波束赋形,星地量子大气信道的统计验证和深度学习预测。
继大热的ChatGPT之后,当地时间3月14日,OpenAI推出了最新大型多模态模型GPT-4,被称为“深度学习的最新里程碑”。本期我们为您选取了4篇文献,介绍作为GPT核心技术之一的Transformer的最新发展前沿,包括半密集特征匹配Transformer及其在多视图几何中的应用,基于Transformer的任务感知弱监督目标定位,用于精确场景文本识别的图像-字符-单词Transformer,使用多模态Transformer生成情感视觉字幕,推送给相关领域的科研人员。

Semi-Dense Feature Matching with Transformers and its Applications in Multiple-View Geometry
Shen, Zehong, etc.
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON PATTERN ANALYSIS AND MACHINE INTELLIGENCE, NOV 2022, Early Access
We present a novel method for local image feature matching. Instead of performing image feature detection, description, and matching sequentially, we propose to first establish pixel-wise dense matches at a coarse level and later refine the good matches at a fine level. In contrast to dense methods that use a cost volume to search correspondences, we use self and cross attention layers in Transformer to obtain feature descriptors that are conditioned on both images. The global receptive field provided by Transformer enables our method to produce dense matches in low-texture areas, where feature detectors usually struggle to produce repeatable interest points. The experiments on indoor and outdoor datasets show that LoFTR outperforms state-of-the-art methods by a large margin. We further adapt LoFTR to modern SfM systems and illustrate its application in multiple-view geometry. The proposed method demonstrates superior performance in Image Matching Challenge 2021 and ranks first on two public benchmarks of visual localization among the published methods. The code is available at https://zju3dv.github.io/loftr .
阅读原文:https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9956767
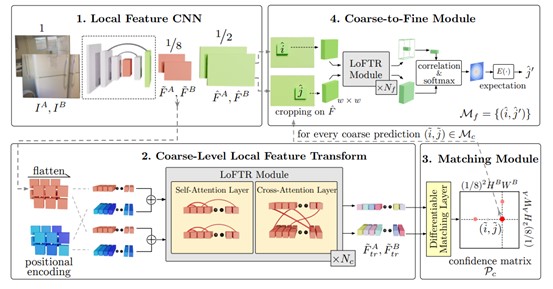
Overview of the proposed method

Task-Aware Weakly Supervised Object Localization With Transformer
Meng, Meng, etc.
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON PATTERN ANALYSIS AND MACHINE INTELLIGENCE, DEC 2022, Early Access
Weakly supervised object localization (WSOL) aims to predict both object locations and categories with only image-level class labels. However, most existing methods rely on class-specific image regions for localization, resulting in incomplete object localization. To alleviate this problem, we propose a novel end-to-end task-aware framework with a transformer encoder-decoder architecture (TAFormer) to learn class-agnostic foreground maps, including a representation encoder, a localization decoder, and a classification decoder. The proposed TAFormer enjoys several merits. First, the designed three modules can effectively perform class-agnostic localization and classification in a task-aware manner, achieving remarkable performance for both tasks. Second, an optimal transport algorithm is proposed to provide pixel-level pseudo labels to online refine foreground maps. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work by exploring a task-aware framework with a transformer architecture and an optimal transport algorithm to achieve accurate object localization for WSOL. Extensive experiments with four backbones on two standard benchmarks demonstrate that our TAFormer achieves favorable performance against state-of-the-art methods. Furthermore, we show that the proposed TAFormer provides higher robustness against adversarial attacks and noisy labels.
阅读原文:https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9996553
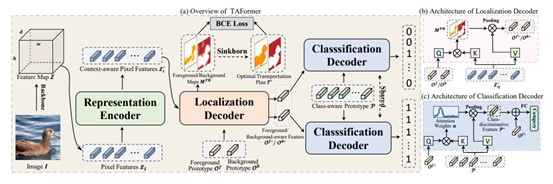
Illustration of the proposed TAFormer

Image-to-Character-to-Word Transformers for Accurate Scene Text Recognition
Xue, Chuhui, etc.
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON PATTERN ANALYSIS AND MACHINE INTELLIGENCE, FEB 2023, Early Access
Leveraging the advances of natural language processing, most recent scene text recognizers adopt an encoder-decoder architecture where text images are first converted to representative features and then a sequence of characters via ‘sequential decoding’. However, scene text images suffer from rich noises of different sources such as complex background and geometric distortions which often confuse the decoder and lead to incorrect alignment of visual features at noisy decoding time steps. This paper presents I2C2W, a novel scene text recognition technique that is tolerant to geometric and photometric degradation by decomposing scene text recognition into two inter-connected tasks. The first task focuses on image-to-character (I2C) mapping which detects a set of character candidates from images based on different alignments of visual features in an non-sequential way. The second task tackles character-to-word (C2W) mapping which recognizes scene text by decoding words from the detected character candidates. The direct learning from character semantics (instead of noisy image features) corrects falsely detected character candidates effectively which improves the final text recognition accuracy greatly. Extensive experiments over nine public datasets show that the proposed I2C2W outperforms the state-of-the-art by large margins for challenging scene text datasets with various curvature and perspective distortions. It also achieves very competitive recognition performance over multiple normal scene text datasets.
阅读原文:https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10041804
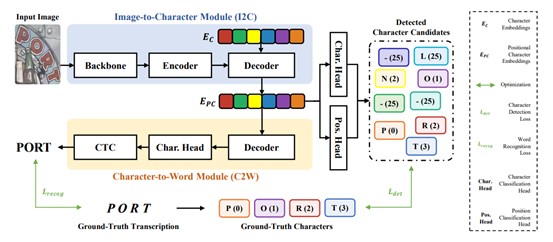
The framework of the proposed I2C2W

Sentimental Visual Captioning using Multimodal Transformer
Wu, Xinxiao, etc.
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF COMPUTER VISION, 2023, 131: 1073–1090
We propose a new task called sentimental visual captioning that generates captions with the inherent sentiment reflected by the input image or video. Compared with the stylized visual captioning task that requires a predefined style independent of the image or video, our new task automatically analyzes the inherent sentiment tendency from the visual content. With this in mind, we propose a multimodal Transformer model namely Senti-Transformer for sentimental visual captioning, which integrates both content and sentiment information from multiple modalities and incorporates prior sentimental knowledge to generate sentimental sentence. Specifically, we extract prior knowledge from sentimental corpus to obtain sentimental textual information and design a multi-head Transformer encoder to encode multimodal features. Then we decompose the attention layer in the middle of Transformer decoder to focus on important features of each modality, and the attended features are integrated through an intra- and inter-modality fusion mechanism for generating sentimental sentences. To effectively train the proposed model using the external sentimental corpus as well as the paired images or videos and factual sentences in existing captioning datasets, we propose a two-stage training strategy that first learns to incorporate sentimental elements into the sentences via a regularization term and then learns to generate fluent and relevant sentences with the inherent sentimental styles via reinforcement learning with a sentimental reward. Extensive experiments on both image and video datasets demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of our Senti-Transformer on sentimental visual captioning. Source code is available at https://github.com/ezeli/InSentiCap_ext.
阅读原文:https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11263-023-01752-7
往期精彩推荐
热点论文解读AI应用领域 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(3)
热点论文带您探究5G和未来通信——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务 (4)
前沿文献带您解读自然语言处理技术 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(5)
热点论文带您探究5G和未来通信材料技术领域 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(6)
热点文献带您关注AI情感分类技术 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(7)
热点论文带您探究6G的无限可能——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(8)
热点文献带您关注AI文本摘要自动生成 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(9)
热点论文:5G/6G引领社会新进步——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(10)
热点文献带您关注AI机器翻译 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(11)
热点论文与您探讨5G/6G网络技术新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(12)
热点文献带您关注AI计算机视觉 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(13)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G的硬科技与新思路 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(14)
热点文献带您关注AI计算机视觉 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(15)
热点论文带您领略5G/6G的最新技术动向 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(18)
热点文献带您关注图神经网络——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(19)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G材料技术的最新发展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(20)
热点文献带您关注模式识别——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(21)
热点论文与带您领略6G网络技术的最新发展趋势 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(22)
热点文献带您关注机器学习与量子物理 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(23)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G通信器件材料的最新进展 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(24)
热点文献带您关注AI自动驾驶——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(25)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G网络安全和技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(26)
热点文献带您关注AI神经网络与忆阻器——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(27)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G电子器件和太赫兹方面的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(28)
热点文献带您关注AI与机器人——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(29)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G热点技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(30)
热点文献带您关注AI与触觉传感技术——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(31)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G热点技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(32)
热点文献带您关注AI深度学习与计算机视觉——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(33)
热点论文与带您领略未来通信的热点技术及最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(34)
热点文献带您关注AI强化学习——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(35)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G基础研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(36)
热点文献带您关注AI与边缘计算——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(37)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G领域热点研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(38)
热点文献带您关注AI技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(39)
热点论文与带您领略5G相关领域研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(40)
热点文献带您关注AI视觉跟踪——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(41)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在海空领域研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(42)
热点文献带您关注AI与医学研究——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(43)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在材料领域研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(44)
热点文献带您关注AI与医学图像——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(45)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在光电材料及信息编码领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(46)
热点文献带您关注AI与生物学——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(47)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在新材料技术领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(48)
热点文献带您关注AI与人脸识别——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(49)
热点论文带您领略光电半导体领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(50)
热点文献带您关注AI在集成电路领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(51)
热点论文带您领略半导体领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(52)
热点文献带您关注AI在光神经网络领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(53)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在新材料技术领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(54)
热点文献带您关注AI深度神经网络的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(55)
热点论文带您领略新材料半导体领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(56)
热点文献带您关注AI视频动作识别的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(57)
热点论文带您领略未来通信热点技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(58)
热点文献带您关注AI深度学习的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(59)
热点论文带您领略未来通信研究热点的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(60)
热点文献带您关注AI领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(61)
热点论文带您探索智能化以及超表面在未来通信中的应用——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(62)
热点文献带您关注AI领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(63)
热点论文带您领略半导体领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(64)
热点文献带您关注AI领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(65)
热点论文带您探索新型网络架构以及超表面在未来通信中的应用——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(66)
热点文献带您关注AI深度强化学习的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(67)
热点论文带您探索新型网络架构以及超材料在未来通信中的应用——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(68)
热点文献带您关注AI图神经网络的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(69)
热点论文带您探索未来网络中使用的新材料以及相关技术 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(70)
热点文献带您关注AI的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(71)
热点文献带您关注电子皮肤的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(72)
热点文献带您关注存算一体技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(73)
热点文献带您关注惯性测量单元的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(74)
热点文献带您关注低轨卫星通信技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(75)
