热点文献带您关注惯性测量单元的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(74)
2022-12-08

在上一期热点文献推荐中,我们为您推荐了存算一体技术的最新发展前沿,包括三星电子发表的全球首个基于MRAM交叉阵列的存内计算研究,基于阻变存储器RRAM的存算一体芯片,基于三维阻变存储器的存内计算宏芯片,基于集成铁电突触阵列的CMOS兼容存内计算加速器。
当前,卡塔尔世界杯正在如火如荼地进行,赛场上的新科技也备受瞩目,其中半自动越位判罚技术(SAOT)更是引起了各界的热烈讨论。SAOT系统主要由特制摄像机、球内传感器和人工智能系统三部分组成,本次世界杯官方指定用球中内置的惯性测量单元(IMU)传感器就是SAOT系统的重要组成部分。本期我们为您选取了4篇文献,介绍IMU的最新发展前沿,包括IMU辅助在线视频背景识别,基于深度学习的传感器驱动在线视频稳定方法,基于多IMU的轮式机器人航位推算解决方案,基于单个RGB相机和IMU传感器进行步态分析,推送给相关领域的科研人员。
文献一 IMU辅助在线视频背景识别
IMU-Assisted Online Video Background Identification
Rong, Jian-Xiang, etc.
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON IMAGE PROCESSING, 2022, 31: 4336-4351
Distinguishing between dynamic foreground objects and a mostly static background is a fundamental problem in many computer vision and computer graphics tasks. This paper presents a novel online video background identification method with the assistance of inertial measurement unit (IMU). Based on the fact that the background motion of a video essentially reflects the 3D camera motion, we leverage IMU data to realize a robust camera motion estimation for identifying background feature points by only investigating a few historical frames. We observe that the displacement of the 2D projection of a scene point caused by camera rotation is depth-invariant, and the rotation estimation by using IMU data can be quite accurate. We thus propose to analyze 2D feature points by decomposing the 2D motion into two components: rotation projection and translation projection. In our method, after establishing the 3D camera rotations, we generate the depth-relevant 2D feature point movement induced by the camera 3D translation. Then, by examining the disparity between inter-frame offset and the projection of estimated 3D camera motion, we can identify the background feature points. In the experiments, our online method is able to run at 30FPS with only 1 frame latency and outperforms state-of-the-art background identification and other relevant methods. Our method directly leads to a better camera motion estimation, which is beneficial to many applications like online video stabilization, SLAM, image stitching, etc.
阅读原文:https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9802831
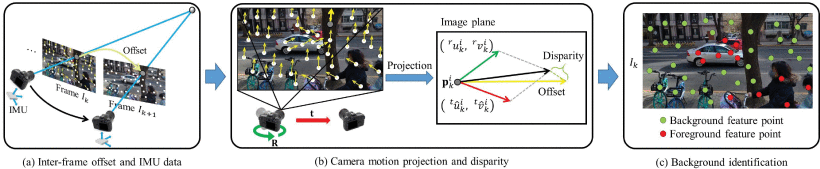
The overview of the method
文献二 基于深度学习的传感器驱动在线视频稳定方法
Deep Online Video Stabilization using IMU Sensors
Li, Chen, etc.
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MULTIMEDIA, 2022
In this paper, we propose a deep learning based sensor-driven method for online video stabilization. This method utilizes euler angle and acceleration estimated from the gyroscope and accelerator to assist stable video reconstruction. We introduce two simple sub-networks for trajectory optimization, the first network exploits real unstable trajectory and acceleration of camera to detect shooting scenarios. This network also generates an attention mask to choose scenario-specific features adaptively. Then the second network predicts smooth camera paths based on real unstable trajectory using LSTM under the supervision of the former mask. The output of trajectory optimization network is filtered with a two-step modification process to guarantee the smoothness. The real and smoothed camera paths are then utilized as guidance to projectively generate stable frames. We also capture videos with sensor data covering seven typical shooting scenarios, and design a groundtruth generation method to construct pseud-labels. Moreover, the trajectory smoothing network allows 3 or 10 frames buffer as the future information to construct a lookahead filter. Experimental results show that our online method could outperform other offline state-of-the-art methods in several shaky video clips with fewer buffer frames over both general and low-quality videos. Furthermore, our method could effectively reduce running times without image content analysis, and the stabilization efficiency reaches 25 fps on 1080p videos.
阅读原文:https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9681170
文献三 基于多IMU的轮式机器人航位推算解决方案
Wheel-INS2: Multiple MEMS IMU-Based Dead Reckoning System With Different Configurations for Wheeled Robots
Wu, Yibin, etc.
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INTELLIGENT TRANSPORTATION SYSTEMS, 2022
A reliable self-contained navigation system is essential for autonomous vehicles. Based on our previous study on Wheel-INS niu2019, a wheel-mounted inertial measurement unit (Wheel-IMU)-based dead reckoning (DR) system, in this paper, we propose a multiple IMUs-based DR solution for the wheeled robots. The IMUs are mounted at different places on the wheeled vehicles to acquire various dynamic information. In particular, at least one IMU has to be mounted at the wheel to measure the wheel velocity and take advantage of the rotation modulation. The system is implemented through a distributed extended Kalman filter structure where each subsystem (corresponding to each IMU) retains and updates its own states separately. The relative position constraints between the multiple IMUs are exploited to further limit the error drift and improve the system's robustness. Particularly, we present the DR systems using dual Wheel-IMUs, one Wheel-IMU plus one vehicle body-mounted IMU (Body-IMU), and dual Wheel-IMUs plus one Body-IMU as examples for analysis and comparison. Field tests illustrate that the proposed multi-IMU DR system outperforms the single Wheel-INS in terms of both positioning and heading accuracy. By comparing with the centralized filter, the proposed distributed filter shows unimportant accuracy degradation while holding significant computation efficiency. Moreover, among the three multi-IMU configurations, the one Body-IMU plus one Wheel-IMU design obtains the minimum drift rate. The position drift rates of the three configurations are 0.82% (dual Wheel-IMUs), 0.69% (one Body-IMU plus one Wheel-IMU), and 0.73% (dual Wheel-IMUs plus one Body-IMU), respectively.
阅读原文:https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9950438
文献四 基于单个RGB相机和IMU传感器进行步态分析
Verification of gait analysis method fusing camera-based pose estimation and an IMU sensor in various gait conditions
Yamamoto, Masataka, etc.
SCIENTIFIC REPORTS, 2022, 12(1)
A markerless gait analysis system can measure useful gait metrics to determine effective clinical treatment. Although this gait analysis system does not require a large space, several markers, or time constraints, it inaccurately measure lower limb joint kinematics during gait. In particular, it has a substantial ankle joint angle error. In this study, we investigated the markerless gait analysis method capability using single RGB camera-based pose estimation by OpenPose (OP) and an inertial measurement unit (IMU) sensor on the foot segment to measure ankle joint kinematics under various gait conditions. Sixteen healthy young adult males participated in the study. We compared temporo-spatial parameters and lower limb joint angles during four gait conditions with varying gait speeds and foot progression angles. These were measured by optoelectronic motion capture, markerless gait analysis method using OP, and proposed method using OP and IMU. We found that the proposed method using OP and an IMU significantly decreased the mean absolute errors of peak ankle joint angles compared with OP in the four gait conditions. The proposed method has the potential to measure temporo-spatial gait parameters and lower limb joint angles, including ankle angles, in various gait conditions as a clinical settings gait assessment tool.
阅读原文:https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-022-22246-5
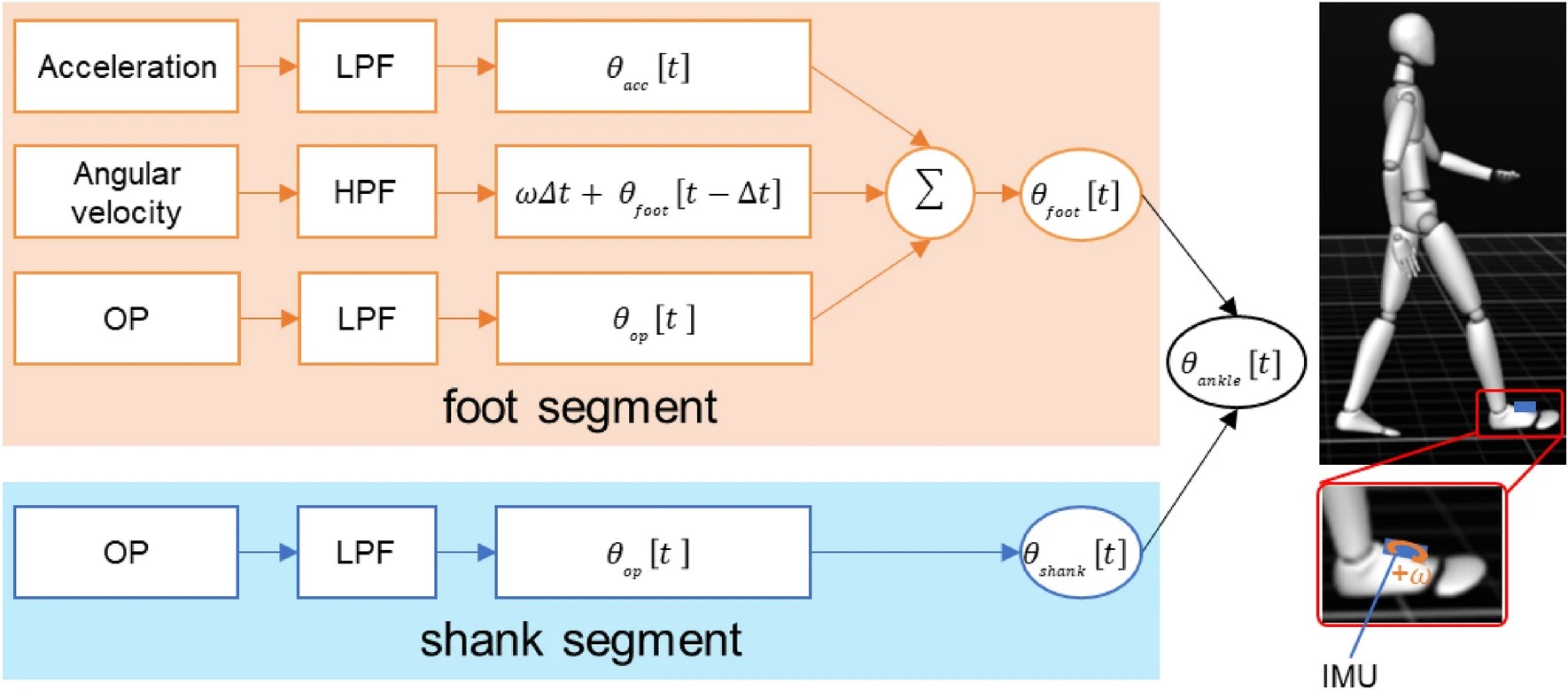
The proposed method fusing RGB camera-based pose estimation by OP and an IMU sensor on the foot segment
往期精彩推荐
热点论文解读AI应用领域 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(3)
热点论文带您探究5G和未来通信——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务 (4)
前沿文献带您解读自然语言处理技术 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(5)
热点论文带您探究5G和未来通信材料技术领域 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(6)
热点文献带您关注AI情感分类技术 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(7)
热点论文带您探究6G的无限可能——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(8)
热点文献带您关注AI文本摘要自动生成 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(9)
热点论文:5G/6G引领社会新进步——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(10)
热点文献带您关注AI机器翻译 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(11)
热点论文与您探讨5G/6G网络技术新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(12)
热点文献带您关注AI计算机视觉 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(13)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G的硬科技与新思路 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(14)
热点文献带您关注AI计算机视觉 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(15)
热点论文带您领略5G/6G的最新技术动向 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(18)
热点文献带您关注图神经网络——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(19)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G材料技术的最新发展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(20)
热点文献带您关注模式识别——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(21)
热点论文与带您领略6G网络技术的最新发展趋势 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(22)
热点文献带您关注机器学习与量子物理 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(23)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G通信器件材料的最新进展 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(24)
热点文献带您关注AI自动驾驶——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(25)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G网络安全和技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(26)
热点文献带您关注AI神经网络与忆阻器——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(27)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G电子器件和太赫兹方面的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(28)
热点文献带您关注AI与机器人——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(29)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G热点技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(30)
热点文献带您关注AI与触觉传感技术——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(31)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G热点技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(32)
热点文献带您关注AI深度学习与计算机视觉——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(33)
热点论文与带您领略未来通信的热点技术及最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(34)
热点文献带您关注AI强化学习——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(35)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G基础研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(36)
热点文献带您关注AI与边缘计算——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(37)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G领域热点研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(38)
热点文献带您关注AI技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(39)
热点论文与带您领略5G相关领域研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(40)
热点文献带您关注AI视觉跟踪——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(41)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在海空领域研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(42)
热点文献带您关注AI与医学研究——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(43)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在材料领域研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(44)
热点文献带您关注AI与医学图像——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(45)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在光电材料及信息编码领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(46)
热点文献带您关注AI与生物学——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(47)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在新材料技术领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(48)
热点文献带您关注AI与人脸识别——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(49)
热点论文带您领略光电半导体领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(50)
热点文献带您关注AI在集成电路领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(51)
热点论文带您领略半导体领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(52)
热点文献带您关注AI在光神经网络领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(53)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在新材料技术领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(54)
热点文献带您关注AI深度神经网络的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(55)
热点论文带您领略新材料半导体领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(56)
热点文献带您关注AI视频动作识别的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(57)
热点论文带您领略未来通信热点技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(58)
热点文献带您关注AI深度学习的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(59)
热点论文带您领略未来通信研究热点的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(60)
热点文献带您关注AI领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(61)
热点论文带您探索智能化以及超表面在未来通信中的应用——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(62)
热点文献带您关注AI领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(63)
热点论文带您领略半导体领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(64)
热点文献带您关注AI领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(65)
热点论文带您探索新型网络架构以及超表面在未来通信中的应用——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(66)
热点文献带您关注AI深度强化学习的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(67)
热点论文带您探索新型网络架构以及超材料在未来通信中的应用——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(68)
热点文献带您关注AI图神经网络的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(69)
热点论文带您探索未来网络中使用的新材料以及相关技术 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(70)
热点文献带您关注AI的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(71)
热点文献带您关注电子皮肤的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(72)
热点文献带您关注存算一体技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(73)