热点文献带您关注通信领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(78)
2023-05-16

在上一期热点文献推荐中,我们为您推荐了半导体领域的最新发展前沿,包括用于像差校正3D摄影的集成成像传感器,光子集成的连续行波光参量放大器,用于互补电路的垂直有机电化学晶体管,接近二维半导体接触的量子极限。
本期我们为您选取了4篇文献,介绍通信领域的最新发展前沿,包括基于拓扑约束的光纤信息通路扩展,用于分米级地面定位的光-无线混合网络,用于无线回程的千兆亚太赫兹通信,6G面临的十二大科学挑战,推送给相关领域的科研人员。
Scaling information pathways in optical fibers by topological confinement
Ma, Zelin, etc.
Science, 2023, 380(6642): 278–282
Spatial mode-count scalability in optical fibers is of paramount importance for addressing the upcoming information-capacity crunch, reducing energy consumption per bit, and for enabling advanced quantum computing networks, but this scalability is severely limited by perturbative mode mixing. We show an alternative means of light guidance, in which light’s orbital angular momentum creates a centrifugal barrier for itself, thereby enabling low-loss transmission of light in a conventionally forbidden regime wherein the mode mixing can be naturally curtailed. This enables kilometer-length-scale transmission of a record ~50 low-loss modes with cross-talk as low as −45 decibels/kilometer and mode areas of ~800 square micrometers over a 130-nanometer telecommunications spectral window. This distinctive light-guidance regime promises to substantially increase the information content per photon for quantum or classical networks.
阅读原文:https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.add1874

The principle of light transport with TCMs
A hybrid optical–wireless network for decimetre-level terrestrial positioning
Koelemeij, Jeroen C. J., etc.
NATURE, 2022, 611(7936): 473–478
Global navigation satellite systems (GNSS) are widely used for navigation and time distribution, features that are indispensable for critical infrastructure such as mobile communication networks, as well as emerging technologies such as automated driving and sustainable energy grids. Although GNSS can provide centimetre-level precision, GNSS receivers are prone to many-metre errors owing to multipath propagation and an obstructed view of the sky, which occur particularly in urban areas where accurate positioning is most needed. Moreover, the vulnerabilities of GNSS, combined with the lack of a back-up system, pose a severe risk to GNSS-dependent technologies. Here we demonstrate a terrestrial positioning system that is independent of GNSS and offers superior performance through a constellation of radio transmitters, connected and time-synchronized at the subnanosecond level through a fibre-optic Ethernet network. Using optical and wireless transmission schemes similar to those encountered in mobile communication networks, and exploiting spectrally efficient virtual wideband signals, the detrimental effects of multipath propagation are mitigated, thus enabling robust decimetre-level positioning and subnanosecond timing in a multipath-prone outdoor environment. This work provides a glimpse of a future in which telecommunication networks provide not only connectivity but also GNSS-independent timing and positioning services with unprecedented accuracy and reliability.
阅读原文:https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-022-05315-7
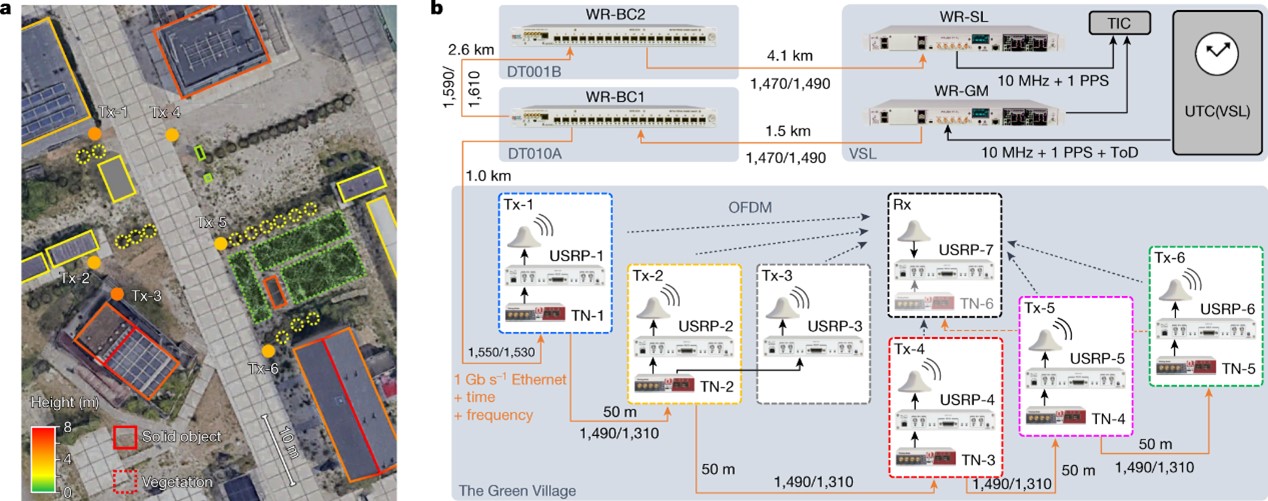
The terrestrial networked positioning system (TNPS) based on a hybrid optical–wireless telecommunication infrastructure
Multi-kilometre and multi-gigabit-per-second sub-terahertz communications for wireless backhaul applications
Sen, Priyangshu, etc.
NATURE ELECTRONICS, 2023, 6(2): 164–175
Sub-terahertz- and terahertz-band—that is, from 100 GHz to 10 THz—communication technologies will be required for next-generation (6G and beyond) wireless communication networks. Considerable progress has been made in terahertz device technology for personal and local area networks, but there are many applications that could benefit from the large capacity of sub-terahertz and terahertz wireless links if longer communication distances were possible. The generation of high-power information-bearing ultrabroadband signals for long-distance communication is though challenging. Here we report a multi-kilometre and multi-gigabit-per-second link operating at 210–240 GHz. We use on-chip power-combining frequency multiplier designs based on Schottky diode technology to achieve a transmit power of 200 mW. A tailored software-defined ultrabroadband digital signal processing back end is also used to generate the modulated signal and process it in the receiver.
阅读原文:https://www.nature.com/articles/s41928-022-00897-6

Experimental setup and system design at 210–240 GHz
Twelve Scientific Challenges for 6G: Rethinking the Foundations of Communications Theory
Chafii, Marwa, etc.
IEEE COMMUNICATIONS SURVEYS AND TUTORIALS, 2023, Early Access
The research in the sixth generation of wireless networks needs to tackle new challenges in order to meet the requirements of emerging applications in terms of high data rate, low latency, high reliability, and massive connectivity. To this end, the entire communication chain needs to be optimized, including the channel and the surrounding environment, as it is no longer sufficient to control the transmitter and/or the receiver only. Investigating large intelligent surfaces, ultramassive multiple-input-multiple-output, and smart constructive environments will ultimately contribute to this direction. In addition, to allow the exchange of high dimensional sensing data between connected intelligent devices, semantic and goaloriented communications need to be considered for a more efficient and context-aware information encoding. In particular, for multi-agent systems, where agents are collaborating together to achieve a complex task, emergent communication, instead of hard-coded communication, can be learned for more efficient task execution and communication resources use. Moreover, new physical phenomena, such as the thermodynamics of communication and the interaction between information theory and electromagnetism should be exploited to better understand the physical limitations of different technologies, e.g., holographic communications. Another new communication paradigm is to consider the end-to-end communication system optimization instead of block-by-block optimization, which requires exploiting machine learning theory, non-linear signal processing theory, and non-coherent communications theory. Within this context, we identify and investigate twelve scientific challenges for rebuilding the theoretical foundation of communications. Furthermore, we present an overview of each of the challenges, along with their respective research opportunities and associated challenges.
阅读原文:https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10041914
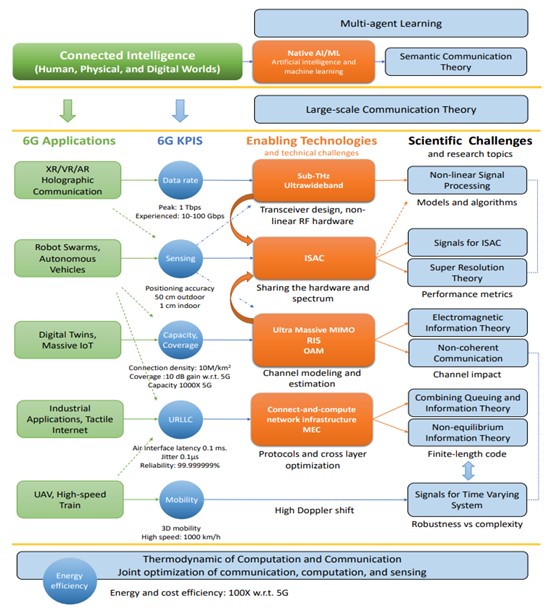
Synergy between 6G Scientific Challenges
往期精彩推荐
热点论文解读AI应用领域 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(3)
热点论文带您探究5G和未来通信——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务 (4)
前沿文献带您解读自然语言处理技术 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(5)
热点论文带您探究5G和未来通信材料技术领域 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(6)
热点文献带您关注AI情感分类技术 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(7)
热点论文带您探究6G的无限可能——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(8)
热点文献带您关注AI文本摘要自动生成 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(9)
热点论文:5G/6G引领社会新进步——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(10)
热点文献带您关注AI机器翻译 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(11)
热点论文与您探讨5G/6G网络技术新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(12)
热点文献带您关注AI计算机视觉 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(13)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G的硬科技与新思路 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(14)
热点文献带您关注AI计算机视觉 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(15)
热点论文带您领略5G/6G的最新技术动向 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(18)
热点文献带您关注图神经网络——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(19)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G材料技术的最新发展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(20)
热点文献带您关注模式识别——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(21)
热点论文与带您领略6G网络技术的最新发展趋势 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(22)
热点文献带您关注机器学习与量子物理 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(23)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G通信器件材料的最新进展 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(24)
热点文献带您关注AI自动驾驶——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(25)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G网络安全和技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(26)
热点文献带您关注AI神经网络与忆阻器——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(27)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G电子器件和太赫兹方面的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(28)
热点文献带您关注AI与机器人——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(29)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G热点技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(30)
热点文献带您关注AI与触觉传感技术——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(31)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G热点技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(32)
热点文献带您关注AI深度学习与计算机视觉——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(33)
热点论文与带您领略未来通信的热点技术及最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(34)
热点文献带您关注AI强化学习——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(35)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G基础研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(36)
热点文献带您关注AI与边缘计算——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(37)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G领域热点研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(38)
热点文献带您关注AI技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(39)
热点论文与带您领略5G相关领域研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(40)
热点文献带您关注AI视觉跟踪——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(41)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在海空领域研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(42)
热点文献带您关注AI与医学研究——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(43)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在材料领域研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(44)
热点文献带您关注AI与医学图像——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(45)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在光电材料及信息编码领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(46)
热点文献带您关注AI与生物学——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(47)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在新材料技术领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(48)
热点文献带您关注AI与人脸识别——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(49)
热点论文带您领略光电半导体领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(50)
热点文献带您关注AI在集成电路领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(51)
热点论文带您领略半导体领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(52)
热点文献带您关注AI在光神经网络领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(53)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在新材料技术领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(54)
热点文献带您关注AI深度神经网络的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(55)
热点论文带您领略新材料半导体领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(56)
热点文献带您关注AI视频动作识别的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(57)
热点论文带您领略未来通信热点技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(58)
热点文献带您关注AI深度学习的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(59)
热点论文带您领略未来通信研究热点的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(60)
热点文献带您关注AI领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(61)
热点论文带您探索智能化以及超表面在未来通信中的应用——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(62)
热点文献带您关注AI领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(63)
热点论文带您领略半导体领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(64)
热点文献带您关注AI领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(65)
热点论文带您探索新型网络架构以及超表面在未来通信中的应用——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(66)
热点文献带您关注AI深度强化学习的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(67)
热点论文带您探索新型网络架构以及超材料在未来通信中的应用——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(68)
热点文献带您关注AI图神经网络的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(69)
热点论文带您探索未来网络中使用的新材料以及相关技术 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(70)
热点文献带您关注AI的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(71)
热点文献带您关注电子皮肤的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(72)
热点文献带您关注存算一体技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(73)
热点文献带您关注惯性测量单元的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(74)
热点文献带您关注低轨卫星通信技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(75)
热点文献带您关注AI Transformer的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(76)
热点文献带您关注半导体领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(77)