热点文献带您关注AI视频动作识别的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(57)
2022-01-06
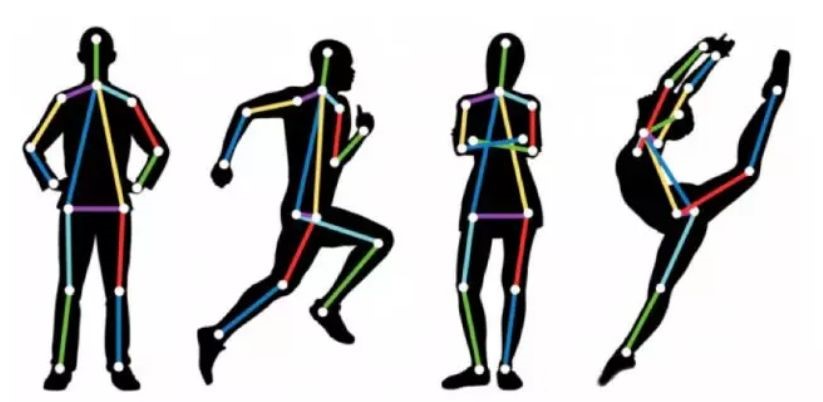
在上一期AI文献推荐中,我们为您推荐了深度神经网络的热点文献,包括进一步提高DNN防止过度拟合能力的贝叶斯Dropout优化自适应方法,使用分子数据预测癌症状态的生物信息深度学习预测模型“P-NET”,将深度神经网络折叠成具有多个时间延迟反馈回路的单个神经元的方法,实现半自动化二维核磁共振光谱分析的基于深度神经网络的光谱反卷积方法等方面的文献。
近年来,越来越多的学者开始关注视频理解和动作识别,本期我们为您选取了4篇文献,介绍视频动作识别的热点文献。包括野生灵长类动物行为的自动化视听动作识别,基于多任务深度学习的实时三维人体姿态估计和动作识别,在缺乏上下文的情况下基于单个时间卷积浅神经网络的动作识别,基于骨骼的人类动作识别,推送给相关领域的科研人员。
文献一 野生灵长类动物行为的自动化视听动作识别
Automated audiovisual behavior recognition in wild primates
Bain, Max, etc.
SCIENCE ADVANCES, 2021, 7(46)
Large video datasets of wild animal behavior are crucial to produce longitudinal research and accelerate conservation efforts; however, large-scale behavior analyses continue to be severely constrained by time and resources. We present a deep convolutional neural network approach and fully automated pipeline to detect and track two audiovisually distinctive actions in wild chimpanzees: buttress drumming and nut cracking. Using camera trap and direct video recordings, we train action recognition models using audio and visual signatures of both behaviors, attaining high average precision (buttress drumming: 0.87 and nut cracking: 0.85), and demonstrate the potential for behavioral analysis using the automatically parsed video. Our approach produces the first automated audiovisual action recognition of wild primate behavior, setting a milestone for exploiting large datasets in ethology and conservation.
阅读原文:https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/sciadv.abi4883
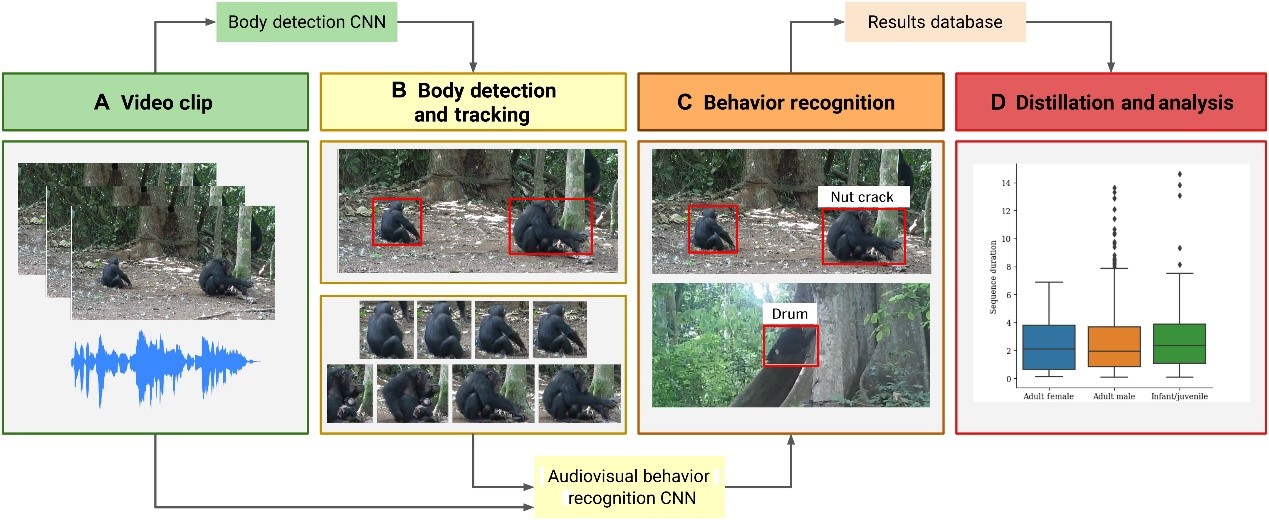
Fully unified pipeline for wild chimpanzee behavior recognition and analysis
文献二 基于多任务深度学习的实时三维人体姿态估计和动作识别
Multi-Task Deep Learning for Real-Time 3D Human Pose Estimation and Action Recognition
Luvizon, Diogo C., etc.
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON PATTERN ANALYSIS AND MACHINE INTELLIGENCE, 2021, 43(8): 2752-2764
Human pose estimation and action recognition are related tasks since both problems are strongly dependent on the human body representation and analysis. Nonetheless, most recent methods in the literature handle the two problems separately. In this article, we propose a multi-task framework for jointly estimating 2D or 3D human poses from monocular color images and classifying human actions from video sequences. We show that a single architecture can be used to solve both problems in an efficient way and still achieves state-of-the-art or comparable results at each task while running with a throughput of more than 100 frames per second. The proposed method benefits from high parameters sharing between the two tasks by unifying still images and video clips processing in a single pipeline, allowing the model to be trained with data from different categories simultaneously and in a seamlessly way. Additionally, we provide important insights for end-to-end training the proposed multi-task model by decoupling key prediction parts, which consistently leads to better accuracy on both tasks. The reported results on four datasets (MPII, Human3.6M, Penn Action and NTU RGB+D) demonstrate the effectiveness of our method on the targeted tasks. Our source code and trained weights are publicly available at https://github.com/dluvizon/deephar.
阅读原文:https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9007695
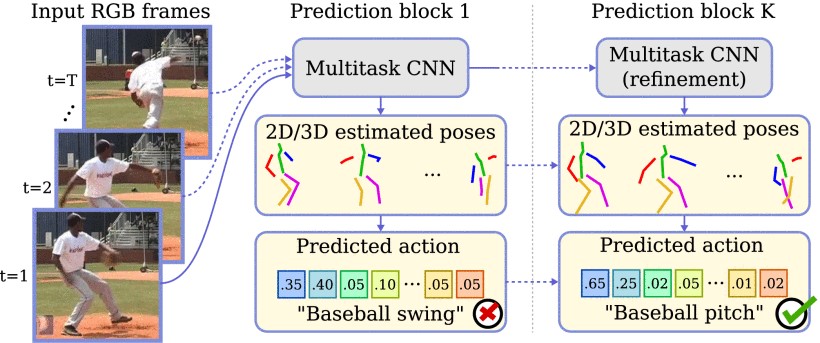
The end-to-end trainable multi-task approach for human pose estimation and action recognition
文献三 基于单个时间卷积浅神经网络的动作识别
Mimetics: Towards Understanding Human Actions Out of Context
Weinzaepfel, Philippe, etc.
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF COMPUTER VISION, 2021, 129(5): 1675-1690
Recent methods for video action recognition have reached outstanding performances on existing benchmarks. However, they tend to leverage context such as scenes or objects instead of focusing on understanding the human action itself. For instance, a tennis field leads to the prediction playing tennis irrespectively of the actions performed in the video. In contrast, humans have a more complete understanding of actions and can recognize them without context. The best example of out-of-context actions are mimes, that people can typically recognize despite missing relevant objects and scenes. In this paper, we propose to benchmark action recognition methods in such absence of context and introduce a novel dataset, Mimetics, consisting of mimed actions for a subset of 50 classes from the Kinetics benchmark. Our experiments show that (a) state-of-the-art 3D convolutional neural networks obtain disappointing results on such videos, highlighting the lack of true understanding of the human actions and (b) models leveraging body language via human pose are less prone to context biases. In particular, we show that applying a shallow neural network with a single temporal convolution over body pose features transferred to the action recognition problem performs surprisingly well compared to 3D action recognition methods.
阅读原文:https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11263-021-01446-y
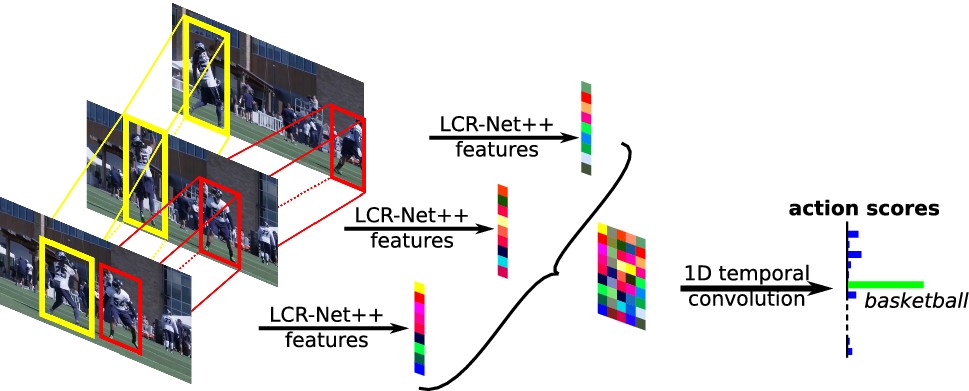
Overview of the implicit pose baseline, SIP-Net
文献四 基于骨骼的人类动作识别
Quo Vadis, Skeleton Action Recognition?
Gupta, Pranay, etc.
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF COMPUTER VISION, 2021, 129(7): 2097-2112
In this paper, we study current and upcoming frontiers across the landscape of skeleton-based human action recognition. To study skeleton-action recognition in the wild, we introduce Skeletics-152, a curated and 3-D pose-annotated subset of RGB videos sourced from Kinetics-700, a large-scale action dataset. We extend our study to include out-of-context actions by introducing Skeleton-Mimetics, a dataset derived from the recently introduced Mimetics dataset. We also introduce Metaphorics, a dataset with caption-style annotated YouTube videos of the popular social game Dumb Charades and interpretative dance performances. We benchmark state-of-the-art models on the NTU-120 dataset and provide multi-layered assessment of the results. The results from benchmarking the top performers of NTU-120 on the newly introduced datasets reveal the challenges and domain gap induced by actions in the wild. Overall, our work characterizes the strengths and limitations of existing approaches and datasets. Via the introduced datasets, our work enables new frontiers for human action recognition.
阅读原文:https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11263-021-01470-y
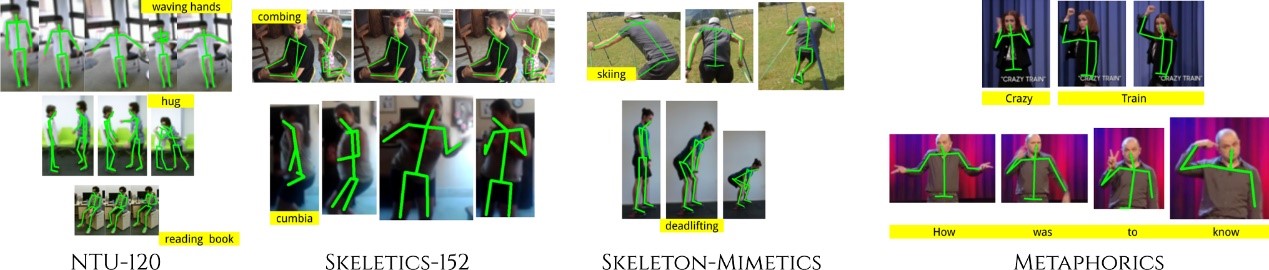
A pictorial illustration of the landscape for skeleton-based action recognition
往期精彩推荐
前沿论文带您解读5G应用领域 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(2)
热点论文解读AI应用领域 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(3)
热点论文带您探究5G和未来通信——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务 (4)
前沿文献带您解读自然语言处理技术 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(5)
热点论文带您探究5G和未来通信材料技术领域 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(6)
热点论文解读AI应用领域 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(3)
热点论文带您探究5G和未来通信——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务 (4)
前沿文献带您解读自然语言处理技术 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(5)
热点论文带您探究5G和未来通信材料技术领域 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(6)
热点文献带您关注AI情感分类技术 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(7)
热点论文带您探究6G的无限可能——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(8)
热点文献带您关注AI文本摘要自动生成 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(9)
热点论文:5G/6G引领社会新进步——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(10)
热点文献带您关注AI机器翻译 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(11)
热点论文与您探讨5G/6G网络技术新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(12)
热点文献带您关注AI计算机视觉 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(13)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G的硬科技与新思路 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(14)
热点文献带您关注AI计算机视觉 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(15)
热点论文带您领略5G/6G的最新技术动向 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(18)
热点文献带您关注图神经网络——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(19)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G材料技术的最新发展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(20)
热点文献带您关注模式识别——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(21)
热点论文与带您领略6G网络技术的最新发展趋势 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(22)
热点文献带您关注机器学习与量子物理 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(23)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G通信器件材料的最新进展 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(24)
热点文献带您关注AI自动驾驶——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(25)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G网络安全和技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(26)
热点文献带您关注AI神经网络与忆阻器——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(27)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G电子器件和太赫兹方面的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(28)
热点文献带您关注AI与机器人——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(29)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G热点技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(30)
热点文献带您关注AI与触觉传感技术——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(31)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G热点技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(32)
热点文献带您关注AI深度学习与计算机视觉——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(33)
热点论文与带您领略未来通信的热点技术及最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(34)
热点文献带您关注AI强化学习——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(35)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G基础研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(36)
热点文献带您关注AI与边缘计算——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(37)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G领域热点研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(38)
热点文献带您关注AI技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(39)
热点论文与带您领略5G相关领域研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(40)
热点文献带您关注AI视觉跟踪——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(41)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在海空领域研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(42)
热点文献带您关注AI与医学研究——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(43)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在材料领域研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(44)
热点文献带您关注AI与医学图像——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(45)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在光电材料及信息编码领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(46)
热点文献带您关注AI与生物学——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(47)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在新材料技术领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(48)
热点文献带您关注AI与人脸识别——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(49)
热点论文带您领略光电半导体领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(50)
热点文献带您关注AI在集成电路领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(51)
热点论文带您领略半导体领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(52)
热点文献带您关注AI在光神经网络领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(53)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在新材料技术领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(54)
热点文献带您关注AI深度神经网络的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(55)
热点论文带您领略新材料半导体领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(56)