热点文献带您关注AI大型语言模型的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(82)
2023-09-18

本期我们为您选取了4篇文献,介绍AI大型语言模型在医学与生物学领域的最新发展前沿,包括由Google科研人员提出的用于评估LLM模型在临床知识方面的MultiMed QA评估基准、利用结构化和非结构化记录基于语言模型进行临床预测、大型语言模型生成跨家族可预测功能的蛋白质序列、使用大型语言模型从初级序列直接推断全原子级蛋白质结构。

Wireless communications sensing and security above 100 GHz
Jornet, Josep M., etc.
NATURE COMMUNICATIONS, 2023, 14(1)
Large language models encode clinical knowledge
Singhal, Karan, etc.
NATURE, 2023, 620(7972): 172-180
Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated impressive capabilities, but the bar for clinical applications is high. Attempts to assess the clinical knowledge of models typically rely on automated evaluations based on limited benchmarks. Here, to address these limitations, we present MultiMedQA, a benchmark combining six existing medical question answering datasets spanning professional medicine, research and consumer queries and a new dataset of medical questions searched online, HealthSearchQA. We propose a human evaluation framework for model answers along multiple axes including factuality, comprehension, reasoning, possible harm and bias. In addition, we evaluate Pathways Language Model (PaLM, a 540-billion parameter LLM) and its instruction-tuned variant, Flan-PaLM on MultiMedQA. Using a combination of prompting strategies, Flan-PaLM achieves state-of-the-art accuracy on every MultiMedQA multiple-choice dataset (MedQA, MedMCQA, PubMedQA and Measuring Massive Multitask Language Understanding (MMLU) clinical topics), including 67.6% accuracy on MedQA (US Medical Licensing Exam-style questions), surpassing the prior state of the art by more than 17%. However, human evaluation reveals key gaps. To resolve this, we introduce instruction prompt tuning, a parameter-efficient approach for aligning LLMs to new domains using a few exemplars. The resulting model, Med-PaLM, performs encouragingly, but remains inferior to clinicians. We show that comprehension, knowledge recall and reasoning improve with model scale and instruction prompt tuning, suggesting the potential utility of LLMs in medicine. Our human evaluations reveal limitations of today's models, reinforcing the importance of both evaluation frameworks and method development in creating safe, helpful LLMs for clinical applications.
阅读原文:https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-023-06291-2
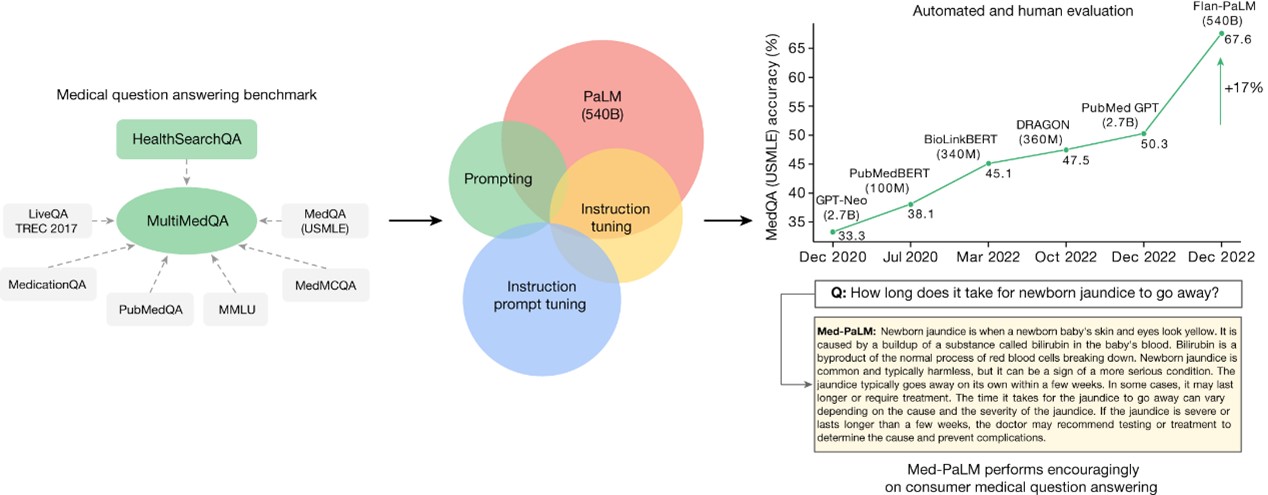
Overview of the contributions

Health system-scale language models are all-purpose prediction engines
Jiang, Lavender Yao, etc.
NATURE, 2023, 619(7969): 357-362
Physicians make critical time-constrained decisions every day. Clinical predictive models can help physicians and administrators make decisions by forecasting clinical and operational events. Existing structured data-based clinical predictive models have limited use in everyday practice owing to complexity in data processing, as well as model development and deployment. Here we show that unstructured clinical notes from the electronic health record can enable the training of clinical language models, which can be used as all-purpose clinical predictive engines with low-resistance development and deployment. Our approach leverages recent advances in natural language processing to train a large language model for medical language (NYUTron) and subsequently fine-tune it across a wide range of clinical and operational predictive tasks. We evaluated our approach within our health system for five such tasks: 30-day all-cause readmission prediction, in-hospital mortality prediction, comorbidity index prediction, length of stay prediction, and insurance denial prediction. We show that NYUTron has an area under the curve (AUC) of 78.7-94.9%, with an improvement of 5.36-14.7% in the AUC compared with traditional models. We additionally demonstrate the benefits of pretraining with clinical text, the potential for increasing generalizability to different sites through fine-tuning and the full deployment of our system in a prospective, single-arm trial. These results show the potential for using clinical language models in medicine to read alongside physicians and provide guidance at the point of care.
阅读原文:https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-023-06160-y
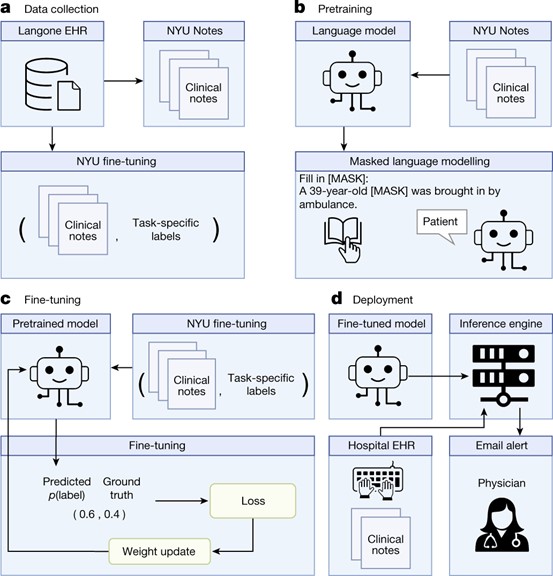

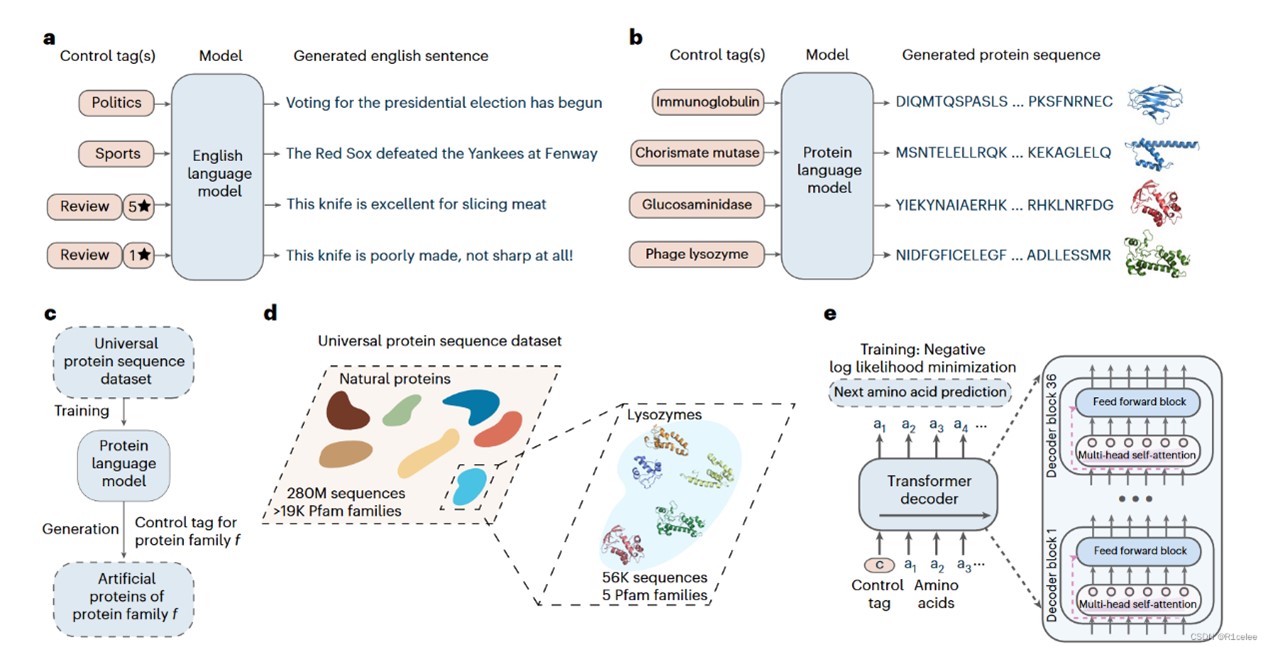
Large language models generate functional protein sequences across diverse families
Madani, Ali, etc.
NATURE BIOTECHNOLOGY, 2023, 41(8): 1099–1106
Deep-learning language models have shown promise in various biotechnological applications, including protein design and engineering. Here we describe ProGen, a language model that can generate protein sequences with a predictable function across large protein families, akin to generating grammatically and semantically correct natural language sentences on diverse topics. The model was trained on 280 million protein sequences from >19,000 families and is augmented with control tags specifying protein properties. ProGen can be further fine-tuned to curated sequences and tags to improve controllable generation performance of proteins from families with sufficient homologous samples. Artificial proteins fine-tuned to five distinct lysozyme families showed similar catalytic efficiencies as natural lysozymes, with sequence identity to natural proteins as low as 31.4%. ProGen is readily adapted to diverse protein families, as we demonstrate with chorismate mutase and malate dehydrogenase.
阅读原文:https://www.nature.com/articles/s41587-022-01618-2

Evolutionary-scale prediction of atomic-level protein structure with a language model
Lin, Zeming, etc.
SCIENCE, 2023, 379(6637): 1123–1130
Recent advances in machine learning have leveraged evolutionary information in multiple sequence alignments to predict protein structure. We demonstrate direct inference of full atomic-level protein structure from primary sequence using a large language model. As language models of protein sequences are scaled up to 15 billion parameters, an atomic-resolution picture of protein structure emerges in the learned representations. This results in an order-of-magnitude acceleration of high-resolution structure prediction, which enables large-scale structural characterization of metagenomic proteins. We apply this capability to construct the ESM Metagenomic Atlas by predicting structures for >617 million metagenomic protein sequences, including >225 million that are predicted with high confidence, which gives a view into the vast breadth and diversity of natural proteins.
阅读原文:https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.ade2574
联系电话:62281933 62283502
地址:西土城校区图书馆125室情报服务部
联系人:杨老师 闫老师
邮箱:yandong80@bupt.edu.cn
往期精彩推荐
热点文献带您关注通信领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(81)
热点文献带您关注半导体领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(80)
热点文献带您关注AI领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(79)
热点文献带您关注通信领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(78)
热点文献带您关注半导体领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(77)
热点文献带您关注AI Transformer的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(76)
热点文献带您关注低轨卫星通信技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(75)
热点文献带您关注惯性测量单元的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(74)
热点文献带您关注存算一体技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(73)
热点文献带您关注电子皮肤的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(72)
热点文献带您关注AI的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(71)
热点论文带您探索未来网络中使用的新材料以及相关技术 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(70)
热点文献带您关注AI图神经网络的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(69)
热点论文带您探索新型网络架构以及超材料在未来通信中的应用——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(68)
热点文献带您关注AI深度强化学习的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(67)
热点论文带您探索新型网络架构以及超表面在未来通信中的应用——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(66)
热点文献带您关注AI领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(65)
热点论文带您领略半导体领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(64)
热点文献带您关注AI领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(63)
热点论文带您探索智能化以及超表面在未来通信中的应用——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(62)
热点文献带您关注AI领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(61)
热点论文带您领略未来通信研究热点的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(60)
热点文献带您关注AI深度学习的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(59)
热点论文带您领略未来通信热点技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(58)
热点文献带您关注AI视频动作识别的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(57)
热点论文带您领略新材料半导体领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(56)
热点文献带您关注AI深度神经网络的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(55)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在新材料技术领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(54)
热点文献带您关注AI在光神经网络领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(53)
热点论文带您领略半导体领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(52)
热点文献带您关注AI在集成电路领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(51)
热点论文带您领略光电半导体领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(50)
热点文献带您关注AI与人脸识别——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(49)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在新材料技术领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(48)
热点文献带您关注AI与生物学——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(47)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在光电材料及信息编码领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(46)
热点文献带您关注AI与医学图像——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(45)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在材料领域研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(44)
热点文献带您关注AI与医学研究——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(43)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在海空领域研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(42)
热点文献带您关注AI视觉跟踪——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(41)
热点论文与带您领略5G相关领域研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(40)
热点文献带您关注AI技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(39)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G领域热点研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(38)
热点文献带您关注AI与边缘计算——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(37)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G基础研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(36)
热点文献带您关注AI强化学习——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(35)
热点论文与带您领略未来通信的热点技术及最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(34)
热点文献带您关注AI深度学习与计算机视觉——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(33)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G热点技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(32)
热点文献带您关注AI与触觉传感技术——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(31)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G热点技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(30)
热点文献带您关注AI与机器人——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(29)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G电子器件和太赫兹方面的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(28)
热点文献带您关注AI自动驾驶——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(25)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G通信器件材料的最新进展 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(24)
热点文献带您关注机器学习与量子物理 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(23)
热点论文与带您领略6G网络技术的最新发展趋势 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(22)
热点文献带您关注模式识别——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(21)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G材料技术的最新发展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(20)
热点文献带您关注图神经网络——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(19)
热点论文带您领略5G/6G的最新技术动向 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(18)
热点文献带您关注AI主动视觉——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(17)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G的最新技术演进 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(16)
热点文献带您关注AI计算机视觉 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(15)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G的硬科技与新思路 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(14)
热点文献带您关注AI机器翻译 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(11)
热点论文:5G/6G引领社会新进步——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(10)
热点文献带您关注AI文本摘要自动生成 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(9)
热点论文带您探究6G的无限可能——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(8)
热点文献带您关注AI情感分类技术 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(7)
热点论文带您探究5G和未来通信材料技术领域 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(6)
前沿文献带您解读自然语言处理技术 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(5)
热点论文带您探究5G和未来通信——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务 (4)
热点论文解读AI应用领域 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(3)