热点文献带您关注AI的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(91)
2024-07-05

本期我们为您选取了4篇文献,介绍AI扩散模型的最新进展,包括双重扩散模型实现基于靶标口袋的3D分子生成,利用生成扩散模型合成Lagrangian湍流,用于分子连接设计的等变3D条件扩散模型,具有扩散模型的量子电路综合。

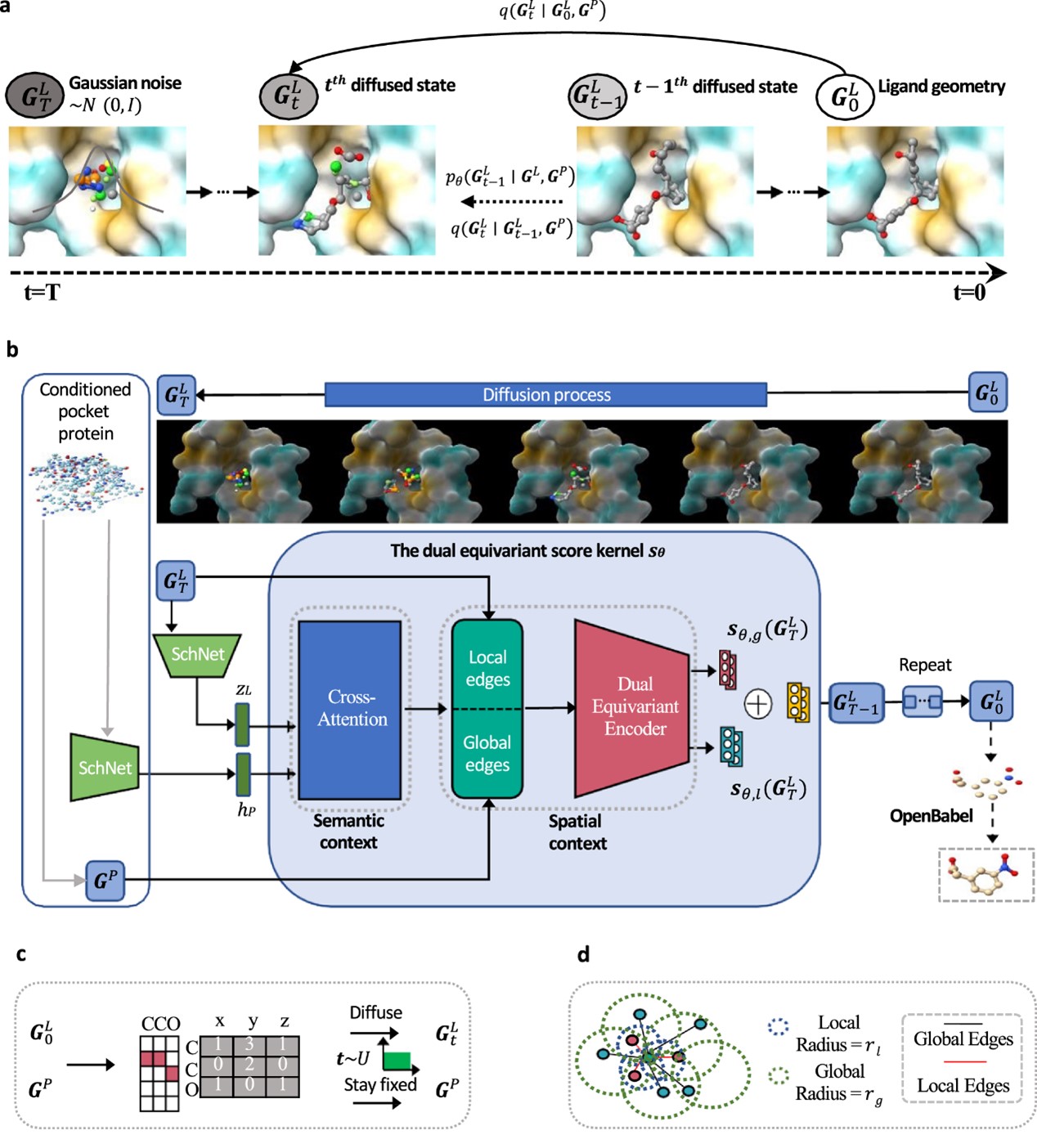
A dual diffusion model enables 3D molecule generation and lead optimization based on target pockets
Huang, Lei, etc.
NATURE COMMUNICATIONS, 2024, 15(1)
Structure-based generative chemistry is essential in computer-aided drug discovery by exploring a vast chemical space to design ligands with high binding affinity for targets. However, traditional in silico methods are limited by computational inefficiency, while machine learning approaches face bottlenecks due to auto-regressive sampling. To address these concerns, we have developed a conditional deep generative model, PMDM, for 3D molecule generation fitting specified targets. PMDM consists of a conditional equivariant diffusion model with both local and global molecular dynamics, enabling PMDM to consider the conditioned protein information to generate molecules efficiently. The comprehensive experiments indicate that PMDM outperforms baseline models across multiple evaluation metrics. To evaluate the applications of PMDM under real drug design scenarios, we conduct lead compound optimization for SARS-CoV-2 main protease (Mpro) and Cyclin-dependent Kinase 2 (CDK2), respectively. The selected lead optimization molecules are synthesized and evaluated for their in-vitro activities against CDK2, displaying improved CDK2 activity.
阅读原文:https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-024-46569-1

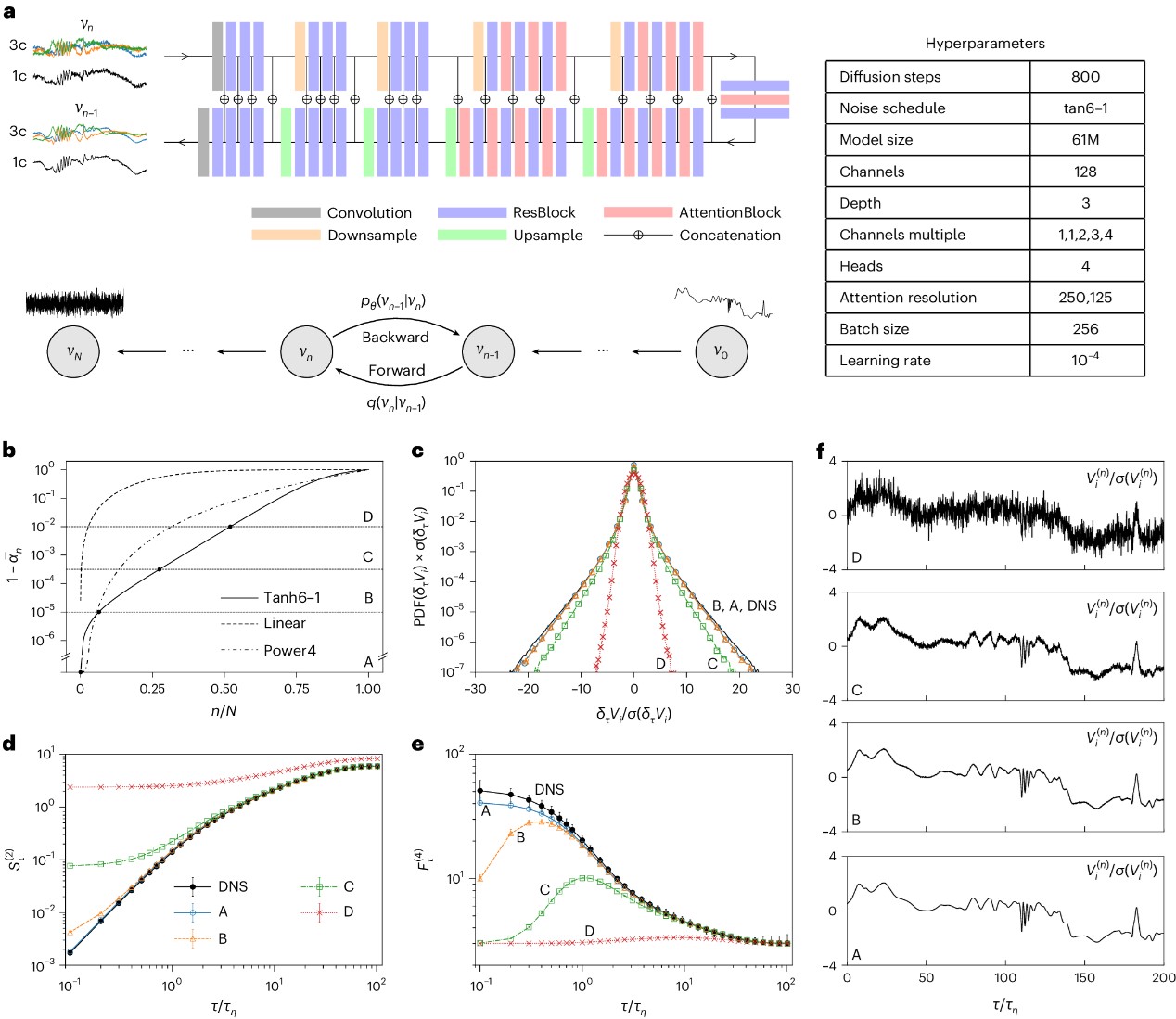
Synthetic Lagrangian turbulence by generative diffusion models
Li, T., etc.
NATURE MACHINE INTELLIGENCE, 2024, 6
Lagrangian turbulence lies at the core of numerous applied and fundamental problems related to the physics of dispersion and mixing in engineering, biofluids, the atmosphere, oceans and astrophysics. Despite exceptional theoretical, numerical and experimental efforts conducted over the past 30 years, no existing models are capable of faithfully reproducing statistical and topological properties exhibited by particle trajectories in turbulence. We propose a machine learning approach, based on a state-of-the-art diffusion model, to generate single-particle trajectories in three-dimensional turbulence at high Reynolds numbers, thereby bypassing the need for direct numerical simulations or experiments to obtain reliable Lagrangian data. Our model demonstrates the ability to reproduce most statistical benchmarks across time scales, including the fat-tail distribution for velocity increments, the anomalous power law and the increased intermittency around the dissipative scale. Slight deviations are observed below the dissipative scale, particularly in the acceleration and flatness statistics. Surprisingly, the model exhibits strong generalizability for extreme events, producing events of higher intensity and rarity that still match the realistic statistics. This paves the way for producing synthetic high-quality datasets for pretraining various downstream applications of Lagrangian turbulence.
阅读原文:https://www.nature.com/articles/s42256-024-00810-0

Equivariant 3D-conditional diffusion model for molecular linker design
Igashov, Ilia, etc.
NATURE MACHINE INTELLIGENCE, 2024, 6
Fragment-based drug discovery has been an effective paradigm in early-stage drug development. An open challenge in this area is designing linkers between disconnected molecular fragments of interest to obtain chemically relevant candidate drug molecules. In this work, we propose DiffLinker, an E(3)-equivariant three-dimensional conditional diffusion model for molecular linker design. Given a set of disconnected fragments, our model places missing atoms in between and designs a molecule incorporating all the initial fragments. Unlike previous approaches that are only able to connect pairs of molecular fragments, our method can link an arbitrary number of fragments. Additionally, the model automatically determines the number of atoms in the linker and its attachment points to the input fragments. We demonstrate that DiffLinker outperforms other methods on the standard datasets, generating more diverse and synthetically accessible molecules. We experimentally test our method in real-world applications, showing that it can successfully generate valid linkers conditioned on target protein pockets.
阅读原文:https://www.nature.com/articles/s42256-024-00815-9


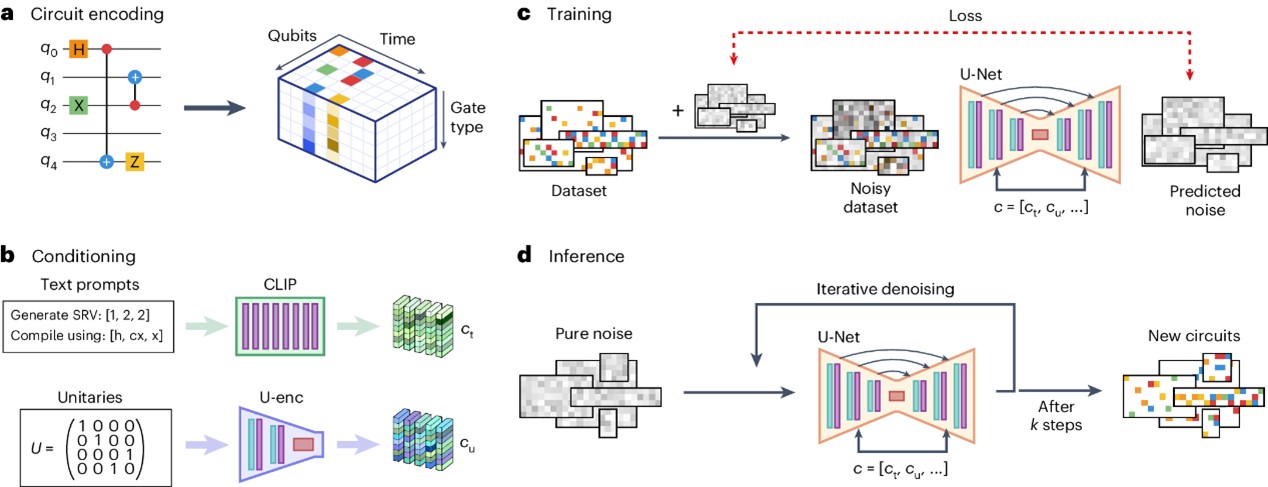
Quantum circuit synthesis with diffusion models
Fuerrutter, Florian, etc.
NATURE MACHINE INTELLIGENCE, 2024, 6(5)
Quantum computing has recently emerged as a transformative technology. Yet, its promised advantages rely on efficiently translating quantum operations into viable physical realizations. Here we use generative machine learning models, specifically denoising diffusion models (DMs), to facilitate this transformation. Leveraging text conditioning, we steer the model to produce desired quantum operations within gate-based quantum circuits. Notably, DMs allow to sidestep during training the exponential overhead inherent in the classical simulation of quantum dynamics—a consistent bottleneck in preceding machine learning techniques. We demonstrate the model’s capabilities across two tasks: entanglement generation and unitary compilation. The model excels at generating new circuits and supports typical DM extensions such as masking and editing to, for instance, align the circuit generation to the constraints of the targeted quantum device. Given their flexibility and generalization abilities, we envision DMs as pivotal in quantum circuit synthesis, both enhancing practical applications and providing insights into theoretical quantum computation.
“前沿文献专题推荐服务”是图书馆情报服务部学科服务的重要内容。欢迎有相关需求的科研人员与我们联系,我们将为您提供更有针对性的定题服务。
联系人:杨老师 闫老师
邮箱:yandong80@bupt.edu.cn
电话:沙河校区图书馆东205室 66605330 66605331
西土城校区图书馆125室 62283502 62281933
往期精彩推荐
热点文献带您关注通信领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(90)
热点文献带您关注集成电路的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(89)
热点文献带您关注AI大模型的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(88)
热点文献带您关注通信领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(87)
热点文献带您关注半导体集成电路的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(86)
热点文献带您关注AI在气候领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(85)
热点文献带您关注通信领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(84)
热点文献带您关注AI与集成电路领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(83)
热点文献带您关注AI大型语言模型的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(82)
热点文献带您关注通信领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(81)
热点文献带您关注半导体领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(80)
热点文献带您关注AI领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(79)
热点文献带您关注通信领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(78)
热点文献带您关注半导体领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(77)
热点文献带您关注AI Transformer的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(76)
热点文献带您关注低轨卫星通信技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(75)
热点文献带您关注惯性测量单元的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(74)
热点文献带您关注存算一体技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(73)
热点文献带您关注电子皮肤的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(72)
热点文献带您关注AI的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(71)
热点论文带您探索未来网络中使用的新材料以及相关技术 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(70)
热点文献带您关注AI图神经网络的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(69)
热点论文带您探索新型网络架构以及超材料在未来通信中的应用——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(68)
热点文献带您关注AI深度强化学习的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(67)
热点论文带您探索新型网络架构以及超表面在未来通信中的应用——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(66)
热点文献带您关注AI领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(65)
热点论文带您领略半导体领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(64)
热点文献带您关注AI领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(63)
热点论文带您探索智能化以及超表面在未来通信中的应用——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(62)
热点文献带您关注AI领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(61)
热点论文带您领略未来通信研究热点的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(60)
热点文献带您关注AI深度学习的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(59)
热点论文带您领略未来通信热点技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(58)
热点文献带您关注AI视频动作识别的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(57)
热点论文带您领略新材料半导体领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(56)
热点文献带您关注AI深度神经网络的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(55)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在新材料技术领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(54)
热点文献带您关注AI在光神经网络领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(53)
热点论文带您领略半导体领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(52)
热点文献带您关注AI在集成电路领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(51)
热点论文带您领略光电半导体领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(50)
热点文献带您关注AI与人脸识别——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(49)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在新材料技术领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(48)
热点文献带您关注AI与生物学——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(47)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在光电材料及信息编码领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(46)
热点文献带您关注AI与医学图像——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(45)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在材料领域研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(44)
热点文献带您关注AI与医学研究——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(43)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在海空领域研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(42)
热点文献带您关注AI视觉跟踪——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(41)
热点论文与带您领略5G相关领域研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(40)
热点文献带您关注AI技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(39)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G领域热点研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(38)
热点文献带您关注AI与边缘计算——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(37)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G基础研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(36)
热点文献带您关注AI强化学习——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(35)
热点论文与带您领略未来通信的热点技术及最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(34)
热点文献带您关注AI深度学习与计算机视觉——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(33)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G热点技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(32)
热点文献带您关注AI与触觉传感技术——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(31)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G热点技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(30)
热点文献带您关注AI与机器人——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(29)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G电子器件和太赫兹方面的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(28)
热点文献带您关注AI自动驾驶——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(25)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G通信器件材料的最新进展 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(24)
热点文献带您关注机器学习与量子物理 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(23)
热点论文与带您领略6G网络技术的最新发展趋势 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(22)
热点文献带您关注模式识别——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(21)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G材料技术的最新发展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(20)
热点文献带您关注图神经网络——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(19)
热点论文带您领略5G/6G的最新技术动向 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(18)
热点文献带您关注AI主动视觉——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(17)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G的最新技术演进 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(16)
热点文献带您关注AI计算机视觉 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(15)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G的硬科技与新思路 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(14)
热点文献带您关注AI机器翻译 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(11)
热点论文:5G/6G引领社会新进步——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(10)
热点文献带您关注AI文本摘要自动生成 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(9)
热点论文带您探究6G的无限可能——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(8)
热点文献带您关注AI情感分类技术 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(7)
热点论文带您探究5G和未来通信材料技术领域 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(6)
前沿文献带您解读自然语言处理技术 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(5)
热点论文带您探究5G和未来通信——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务 (4)
热点论文解读AI应用领域 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(3)