热点文献带您关注AI在光神经网络领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(53)
2021-11-29
在上一期AI文献推荐中,我们为您推荐了人工智能在集成电路领域的热点文献,包括使用纳米级CMOS工艺在同一晶片上协同集成单晶体管神经元和突触来制造高度可扩展的类脑神经拟态硬件,用于高性能神经形态计算和神经网络剪枝的基于拓扑相变的模拟记忆突触,一种由包含片上内存的计算芯片网络组成的DNN推理系统,基于二维半导体光电二极管阵列神经网络图像传感器的超快机器视觉等方面的文献。
本期我们为您选取了4篇文献,介绍AI在光神经网络领域的热点文献,包括用于光学神经网络的11-TOPS光子卷积加速器,用于光纤非线性补偿的硅光子神经网络,用于人工智能和神经形态计算的光子学,一种实现复值神经网络的光学神经芯片等文献,推送给相关领域的科研人员。
文献一 用于光学神经网络的11-TOPS光子卷积加速器
11 TOPS photonic convolutional accelerator for optical neural networks
Xu, Xingyuan, etc.
NATURE, 2021, 589(7840): 44-51
Convolutional neural networks, inspired by biological visual cortex systems, are a powerful category of artificial neural networks that can extract the hierarchical features of raw data to provide greatly reduced parametric complexity and to enhance the accuracy of prediction. They are of great interest for machine learning tasks such as computer vision, speech recognition, playing board games and medical diagnosis. Optical neural networks offer the promise of dramatically accelerating computing speed using the broad optical bandwidths available. Here we demonstrate a universal optical vector convolutional accelerator operating at more than ten TOPS (trillions (1012) of operations per second, or tera-ops per second), generating convolutions of images with 250,000 pixels-sufficiently large for facial image recognition. We use the same hardware to sequentially form an optical convolutional neural network with ten output neurons, achieving successful recognition of handwritten digit images at 88 per cent accuracy. Our results are based on simultaneously interleaving temporal, wavelength and spatial dimensions enabled by an integrated microcomb source. This approach is scalable and trainable to much more complex networks for demanding applications such as autonomous vehicles and real-time video recognition.
阅读原文 https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-020-03063-0
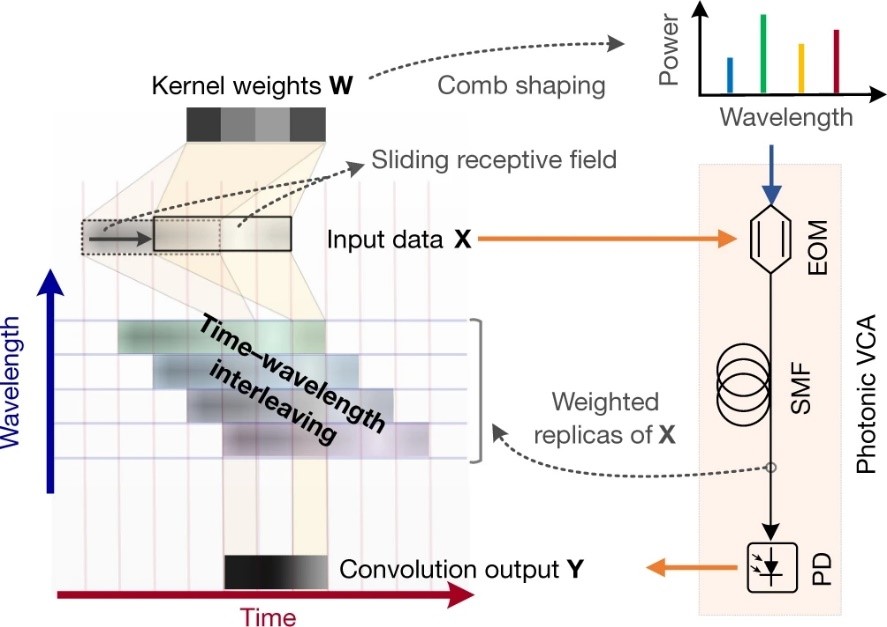
文献二 用于光纤非线性补偿的硅光子神经网络
A silicon photonic–electronic neural network for fibre nonlinearity compensation
Huang, Chaoren, etc.
Nature Electronics, 2021
In optical communication systems, fibre nonlinearity is the major obstacle in increasing the transmission capacity. Typically, digital signal processing techniques and hardware are used to deal with optical communication signals, but increasing speed and computational complexity create challenges for such approaches. Highly parallel, ultrafast neural networks using photonic devices have the potential to ease the requirements placed on digital signal processing circuits by processing the optical signals in the analogue domain. Here we report a silicon photonic–electronic neural network for solving fibre nonlinearity compensation in submarine optical-fibre transmission systems. Our approach uses a photonic neural network based on wavelength-division multiplexing built on a silicon photonic platform compatible with complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor technology. We show that the platform can be used to compensate for optical fibre nonlinearities and improve the quality factor of the signal in a 10,080 km submarine fibre communication system. The Q-factor improvement is comparable to that of a software-based neural network implemented on a workstation assisted with a 32-bit graphic processing unit.
阅读原文 https://www.nature.com/articles/s41928-021-00661-2
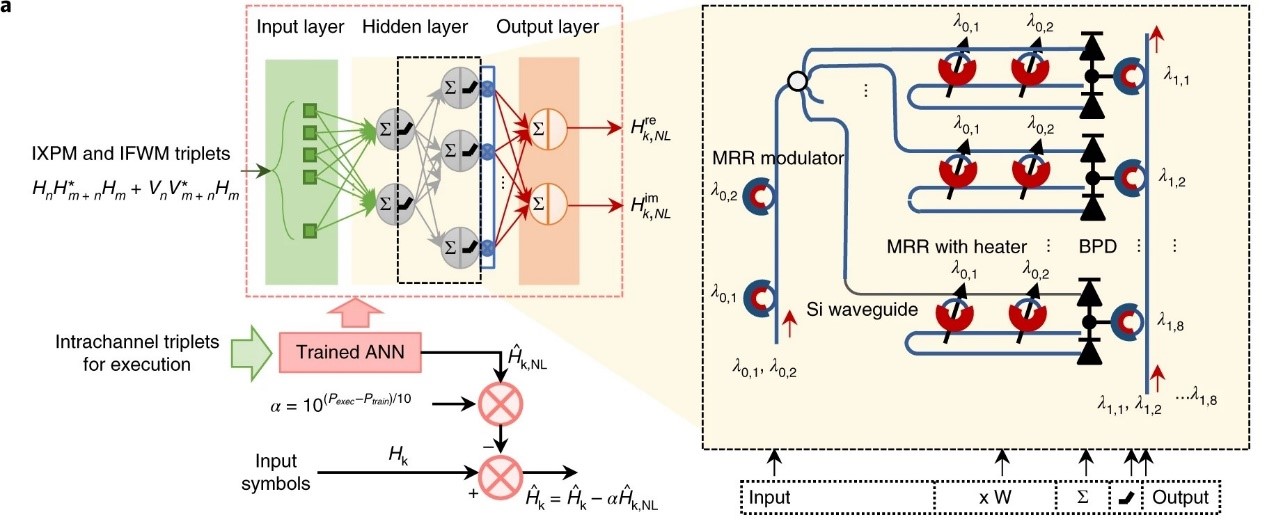
文献三 用于人工智能和神经形态计算的光子学
Photonics for artificial intelligence and neuromorphic computing
Shastri, Bhavin J., etc.
NATURE PHOTONICS, 2021, 15(2): 102-114
Research in photonic computing has flourished due to the proliferation of optoelectronic components on photonic integration platforms. Photonic integrated circuits have enabled ultrafast artificial neural networks, providing a framework for a new class of information processing machines. Algorithms running on such hardware have the potential to address the growing demand for machine learning and artificial intelligence in areas such as medical diagnosis, telecommunications, and high-performance and scientific computing. In parallel, the development of neuromorphic electronics has highlighted challenges in that domain, particularly related to processor latency. Neuromorphic photonics offers sub-nanosecond latencies, providing a complementary opportunity to extend the domain of artificial intelligence. Here, we review recent advances in integrated photonic neuromorphic systems, discuss current and future challenges, and outline the advances in science and technology needed to meet those challenges.
阅读原文 https://www.nature.com/articles/s41566-020-00754-y
文献四 一种实现复值神经网络的光学神经芯片
An optical neural chip for implementing complex-valued neural network
Zhang, H., etc.
NATURE COMMUNICATIONS, 2021, 12(1)
Complex-valued neural networks have many advantages over their real-valued counterparts. Conventional digital electronic computing platforms are incapable of executing truly complex-valued representations and operations. In contrast, optical computing platforms that encode information in both phase and magnitude can execute complex arithmetic by optical interference, offering significantly enhanced computational speed and energy efficiency. However, to date, most demonstrations of optical neural networks still only utilize conventional real-valued frameworks that are designed for digital computers, forfeiting many of the advantages of optical computing such as efficient complex-valued operations. In this article, we highlight an optical neural chip (ONC) that implements truly complex-valued neural networks. We benchmark the performance of our complex-valued ONC in four settings: simple Boolean tasks, species classification of an Iris dataset, classifying nonlinear datasets (Circle and Spiral), and handwriting recognition. Strong learning capabilities (i.e., high accuracy, fast convergence and the capability to construct nonlinear decision boundaries) are achieved by our complex-valued ONC compared to its real-valued counterpart. Most demonstrations of optical neural networks for computing have been so far limited to real-valued frameworks. Here, the authors implement complex-valued operations in an optical neural chip that integrates input preparation, weight multiplication and output generation within a single device.
阅读原文 https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-020-20719-7

往期精彩推荐
前沿论文带您解读5G应用领域 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(2)
热点论文解读AI应用领域 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(3)
热点论文带您探究5G和未来通信——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务 (4)
前沿文献带您解读自然语言处理技术 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(5)
热点论文带您探究5G和未来通信材料技术领域 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(6)
热点论文解读AI应用领域 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(3)
热点论文带您探究5G和未来通信——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务 (4)
前沿文献带您解读自然语言处理技术 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(5)
热点论文带您探究5G和未来通信材料技术领域 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(6)
热点文献带您关注AI情感分类技术 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(7)
热点论文带您探究6G的无限可能——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(8)
热点文献带您关注AI文本摘要自动生成 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(9)
热点论文:5G/6G引领社会新进步——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(10)
热点文献带您关注AI机器翻译 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(11)
热点论文与您探讨5G/6G网络技术新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(12)
热点文献带您关注AI计算机视觉 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(13)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G的硬科技与新思路 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(14)
热点文献带您关注AI计算机视觉 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(15)
热点论文带您领略5G/6G的最新技术动向 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(18)
热点文献带您关注图神经网络——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(19)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G材料技术的最新发展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(20)
热点文献带您关注模式识别——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(21)
热点论文与带您领略6G网络技术的最新发展趋势 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(22)
热点文献带您关注机器学习与量子物理 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(23)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G通信器件材料的最新进展 ——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(24)
热点文献带您关注AI自动驾驶——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(25)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G网络安全和技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(26)
热点文献带您关注AI神经网络与忆阻器——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(27)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G电子器件和太赫兹方面的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(28)
热点文献带您关注AI与机器人——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(29)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G热点技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(30)
热点文献带您关注AI与触觉传感技术——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(31)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G热点技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(32)
热点文献带您关注AI深度学习与计算机视觉——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(33)
热点论文与带您领略未来通信的热点技术及最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(34)
热点文献带您关注AI强化学习——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(35)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G基础研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(36)
热点文献带您关注AI与边缘计算——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(37)
热点论文与带您领略5G/6G领域热点研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(38)
热点文献带您关注AI技术的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(39)
热点论文与带您领略5G相关领域研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(40)
热点文献带您关注AI视觉跟踪——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(41)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在海空领域研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(42)
热点文献带您关注AI与医学研究——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(43)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在材料领域研究的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(44)
热点文献带您关注AI与医学图像——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(45)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在光电材料及信息编码领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(46)
热点文献带您关注AI与生物学——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(47)
热点论文带您领略未来通信在新材料技术领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(48)
热点文献带您关注AI与人脸识别——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(49)
热点论文带您领略光电半导体领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(50)
热点文献带您关注AI在集成电路领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(51)
热点论文带您领略半导体领域的最新进展——图书馆前沿文献专题推荐服务(52)